
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of the leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone located on the lateral side of the tibia, with which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and in proportion to its length, the slenderest of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the level of the knee joint, and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia, and forms the lateral part of the ankle-joint.

The ulnar collateral ligament is a thick triangular band at the medial aspect of the elbow uniting the distal aspect of the humerus to the proximal aspect of the ulna.

The olecranon from the Greekolene meaning elbow and kranon meaning head is the large, thick, curved bony eminence of the ulna, a long bone in the forearm that projects behind the elbow. It forms the most pointed portion of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit. The olecranon serves as a lever for the extensor muscles that straighten the elbow joint.
The semimembranosus is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles. It is so named because it has a flat tendon of origin. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus.

In human anatomy, the inguinal triangle is a region of the abdominal wall. It is also known by the eponym Hesselbach's triangle, after Franz Kaspar Hesselbach.

The medial meniscus is a fibrocartilage semicircular band that spans the knee joint medially, located between the medial condyle of the femur and the medial condyle of the tibia. It is also referred to as the internal semilunar fibrocartilage. The medial meniscus has more of a crescent shape while the lateral meniscus is more circular. The anterior aspects of both menisci are connected by the transverse ligament. It is a common site of injury, especially if the knee is twisted.
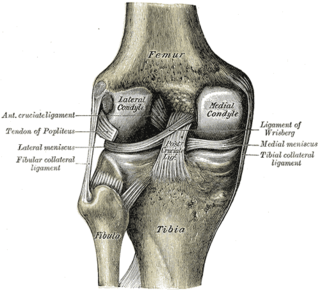
The fibular collateral ligament is a ligament located on the lateral (outer) side of the knee, and thus belongs to the extrinsic knee ligaments and posterolateral corner of the knee.

The lower extremity of the humerus is flattened from before backward, and curved slightly forward; it ends below in a broad, articular surface, which is divided into two parts by a slight ridge.
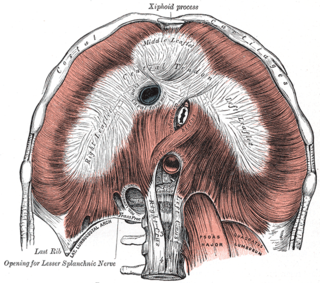
The medial arcuate ligament is a tendinous fascia that arches over the psoas major muscle as it passes through the diaphragm.

The medial epicondyle of the humerus is an epicondyle of the humerus bone of the upper arm in humans. It is larger and more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and is directed slightly more posteriorly in the anatomical position. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is called the ventral epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the more neutral term entepicondyle is used.

The conoid ligament is the posterior and medial fasciculus of the coracoclavicular ligament. It is formed by a dense band of fibers, conical in form, with its base directed upward.

In human anatomy, the glenohumeral ligaments (GHL) are three ligaments on the anterior side of the glenohumeral joint. Reinforcing the anterior glenohumeral joint capsule, the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments play different roles in the stability of the head of the humerus depending on arm position and degree of rotation.

The oblique popliteal ligament is a broad, flat, fibrous band, formed of fasciculi separated from one another by apertures for the passage of vessels and nerves.

The medial umbilical ligament is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds. It should not be confused with the median umbilical ligament, a different structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus.

The deltoid ligament is a strong, flat, triangular band, attached, above, to the apex and anterior and posterior borders of the medial malleolus. The deltoid ligament is composed of: 1. Anterior tibiotalar ligament 2. Tibiocalcaneal ligament 3. Posterior tibiotalar ligament 4. Tibionavicular ligament. It consists of two sets of fibers, superficial and deep.

The superior pubic ramus is a part of the pubic bone which forms a portion of the obturator foramen. The obturator foramen, along with the ilium and other fused bones, forms part of either side of the pelvis.

The pelvis is either the lower part of the trunk of the human body between the abdomen and the thighs or the skeleton embedded in it.
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.


















