
Aleurites moluccanus, the candlenut, is a flowering tree in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, also known as candleberry, Indian walnut, kemiri, varnish tree, nuez de la India, buah keras, godou, kukui nut tree, and rata kekuna.

Pandanus is a genus of monocots with some 750 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. The greatest number of species are found in Madagascar and Malaysia. Common names include pandan, screw palm, and screw pine. They are classified in the order Pandanales, family Pandanaceae.

Taro is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in African, Oceanic, and South Asian cultures Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants.

Coccinia grandis, the ivy gourd, also known as scarlet gourd, tindora and kowai fruit, is a tropical vine. It grows primarily in tropical climates and is commonly found in the Indian states, where it forms a part of the local cuisine. Coccinia grandis is cooked as a vegetable.

Dysoxylum is a flowering plant genus of trees and shrubs from the mahogany family, Meliaceae.

Sphagneticola trilobata, commonly known as the Bay Biscayne creeping-oxeye, Singapore daisy, creeping-oxeye, trailing daisy, and wedelia, is a plant in the tribe Heliantheae tribe of the family Asteraceae. It is native to Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean, but now grows throughout the Neotropics. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental groundcover.

Ipomoea pes-caprae, also known as bayhops, bay-hops, beach morning glory or goat's foot, is a common pantropical creeping vine belonging to the family Convolvulaceae. It grows on the upper parts of beaches and endures salted air. It is one of the most common and most widely distributed salt tolerant plants and provides one of the best known examples of oceanic dispersal. Its seeds float and are unaffected by salt water.

Erythrina variegata, commonly known as tiger's claw or Indian coral tree, is a species of Erythrina native to the tropical and subtropical regions of eastern Africa, the Indian subcontinent, northern Australia, and the islands of the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean east to Fiji.

Abutilon indicum is a small shrub in the family Malvaceae, native to tropical and subtropical regions. This plant is a valuable medicinal and ornamental plant, its roots and leaves being used for curing fevers. It has been widely introduced outside of its native range, and is considered invasive on certain tropical islands.

Alternanthera sessilis is a flowering plant known by several common names, including sissoo spinach, Brazilian spinach, sessile joyweed and dwarf copperleaf. It is cultivated as a vegetable worldwide.

Bidens pilosa is an annual species of herbaceous flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. Its many common names include hitch hikers, black-jack, beggarticks, farmer’s friends and Spanish needle, but most commonly referred to as cobblers pegs. It is native to the Americas but is widely distributed as an introduced species in other regions worldwide including Eurasia, Africa, Australia, South America and the Pacific Islands.

Prunella vulgaris, the common self-heal, heal-all, woundwort, heart-of-the-earth, carpenter's herb, brownwort or blue curls, is a herbaceous plant in the mint family Lamiaceae.

Wedelia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. They are one of the genera commonly called "creeping-oxeyes".

Melanthera, is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, native to North and South America, as well as Africa, Asia and Oceania, including Hawaiʻi.
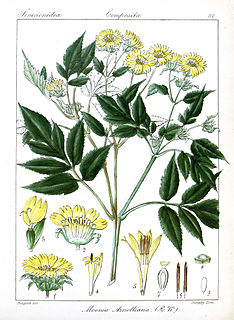
Moonia is a genus of Asian and Australian flowering plants in the daisy family.

Hedyotis (starviolet) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. Many species of this genus such as Hedyotis biflora, H. corymbosa and H. diffusa are well known medicinal plants. Hedyotis is native to tropical and subtropical Asia and to islands of the northwest Pacific. It comprises about 115 species. The type species for the genus is Hedyotis fruticosa.

Terminalia microcarpa is a tree species in the family Combretaceae. It occurs throughout the Philippines, in parts of Malaysia and Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, possibly the Bismarck Archipelago, and northern Australia. It is cultivated on a small scale in the Philippines, where the edible sweet and tart plum-like fruits are eaten as is or are traditionally made into jams, jellies, and wines.

Digitaria ciliaris is a species of grass known by the common names southern crabgrass, tropical finger-grass, tropical crabgrass or summer grass.

Dipteris conjugata is a species of fern. It has a rhizome, and 2-3 tall stems with mid green or dark green fronds, which have several divisions to toothed lobes. It is grows in clearings, mountain ridges and in forest margins, from tropical and temperate Asia, northern Queensland in Australia and some islands in the Pacific Ocean. It has limited native medicinal uses.

Garcinia sessilis, commonly known as heilala in Tongan, is an evergreen tree native to the Pacific regions of Solomon Islands, Fiji, Samoa and Tonga. The heilala flower is the national flower of Tonga.
























