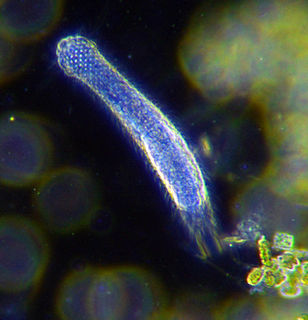
The gastrotrichs, commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06-3.0 mm), worm-like, pseudocoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environments. They are mostly benthic and live within the periphyton, the layer of tiny organisms and detritus that is found on the seabed and the beds of other water bodies. The majority live on and between particles of sediment or on other submerged surfaces, but a few species are terrestrial and live on land in the film of water surrounding grains of soil. Gastrotrichs are divided into two orders, the Macrodasyida which are marine, and the Chaetonotida, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Nearly 800 species of gastrotrich have been described.

Disko Island is a large island in Baffin Bay, off the west coast of Greenland. It has an area of 8,578 km2 (3,312.0 sq mi), making it the second largest of Greenland after the main island and one of the 100 largest islands in the world. The name Qeqertarsuaq means The Large Island.

Macrodasyida is an order of gastrotrichs. Members of this order are somewhat worm-like in form, and not more than 1 to 1.5 mm in length.
Paucitubulatina is a suborder of gastrotrichs in the order Chaetonotida.

Chaetonotidae is a family of gastrotrichs in the order Chaetonotida. It is the largest family of gastrotrichs with almost 400 species, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Current classification is largely based on shape and external structures but these are highly variable. Molecular studies show a high level of support for a clade containing Dasydytidae nested within Chaetonotidae.

Diuronotus aspetos is a species of large sized meiofaunal chaetonotid gastrotrich found in the North Atlantic. With Diuronotus rupperti, it is one of the only two species representing the genus Diuronotus.

Macrodasys caudatus is a species of microscopic worm-like metazoan in the family Macrodasyidae in the phylum Gastrotricha. It lives in the interstices between particles of sediment on the seabed in shallow water. It is found in the Indian Ocean, the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea and the North Sea.

Paradasys subterraneus is a Gastrotricha with a bodylength up to 0.6 mm. The species is marine.

Lepidodermella squamata is a freshwater species of minute worm in the phylum Gastrotricha.

Kelisia is a genus of delphacid planthoppers in the family Delphacidae. There are more than 50 described species in Kelisia.
Heterolepidoderma is a genus of gastrotrichs belonging to the family Chaetonotidae.
Dactylopodolidae is a family of worms belonging to the order Macrodasyida.
Macrodasyidae is a family of worms belonging to the order Macrodasyida.
Turbanellidae is a family of worms belonging to the order Macrodasyida.
Cephalodasyidae is a family of worms belonging to the order Macrodasyida.

Thaumastodermatidae is a family of worms belonging to the order Macrodasyida.
Paradasys is a genus of gastrotrichs belonging to the family Cephalodasyidae.
Tetranchyroderma is a genus of gastrotrichs belonging to the family Thaumastodermatidae.
Turbanella is a genus of gastrotrichs belonging to the family Turbanellidae.
Macrodasys is a genus of gastrotrichs belonging to the family Macrodasyidae.







