
The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.

Clean technology, also called cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy, information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lighting, grey water, and more. Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation is also known as a carbon project.
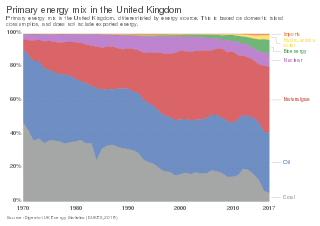
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.

Many countries and territories have installed significant solar power capacity into their electrical grids to supplement or provide an alternative to conventional energy sources. Solar power plants use one of two technologies:

The Edison Electric Institute (EEI) is an association that represents all U.S. investor-owned electric companies.
The energy policy of India is to increase the locally produced energy in India and reduce energy poverty, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy. Net energy import dependency was 40.9% in 2021-22. The primary energy consumption in India grew by 13.3% in FY2022-23 and is the third biggest with 6% global share after China and USA. The total primary energy consumption from coal, crude oil, natural gas, nuclear energy, hydroelectricity and renewable power is 809.2 Mtoe in the calendar year 2018. In 2018, India's net imports are nearly 205.3 million tons of crude oil and its products, 26.3 Mtoe of LNG and 141.7 Mtoe coal totaling to 373.3 Mtoe of primary energy which is equal to 46.13% of total primary energy consumption. India is largely dependent on fossil fuel imports to meet its energy demands – by 2030, India's dependence on energy imports is expected to exceed 53% of the country's total energy consumption.

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. In 2019, nearly 75% of new installed electricity generation capacity used renewable energy and the International Energy Agency (IEA) has predicted that by 2025, renewable capacity will meet 35% of global power generation.
Founded in 2001, the American Council on Renewable Energy (ACORE) is a member-based, 501(c)(3) national non-profit organization that unites finance, policy and technology to accelerate the transition to a renewable energy economy.

According to data from the US Energy Information Administration, renewable energy accounted for 8.4% of total primary energy production and 21% of total utility-scale electricity generation in the United States in 2022.

100% renewable energy is the goal of the use renewable resources for all energy. 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issues, as well as economic and energy security concerns. Shifting the total global primary energy supply to renewable sources requires a transition of the energy system, since most of today's energy is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels.
New Energy for America was a plan led by President Barack Obama and Vice President Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.

India is the world's 3rd largest consumer of electricity and the world's 3rd largest renewable energy producer with 40% of energy capacity installed in the year 2022 coming from renewable sources. Ernst & Young's (EY) 2021 Renewable Energy Country Attractiveness Index (RECAI) ranked India 3rd behind USA and China. In FY2023-24, India is planning to issue 50 GW tenders for wind, solar and hybrid projects. India has committed for a goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030.
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases, more than any country in the world.

The energy policy of the Obama administration was defined by an "all-of-the-above" approach which offered federal support for renewable energy deployment, increased domestic oil and gas extraction, and export of crude oil and natural gas. His presidency's first term was shaped by the failure of his signature climate legislation, the American Clean Energy and Security Act, to pass, and then climate and energy disasters including the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 and then Hurricane Sandy, which took place during the 2012 election. In his second term, Obama lifted the ban on crude oil exports and approved liquified natural gas exports; his planned regulatory approach to reducing greenhouse pollution in the electricity sector, the Clean Power Plan, was blocked by the U.S. Supreme Court.

The 2009 energy efficiency and renewable energy research investment was a part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 and it increased federal funds in renewable energy. The package included $50 billion in spending and $20 billion in tax provisions. The research within the investment also increased; as a result $8.8 billion went into renewable energy research. The investment also included a boost for "green buildings". Federal buildings received $4.5 billion in renovations; public housing was also granted $4 billion in renovations. An additional $250 million was made out to energy-efficient affordable housing, in part by installing insulation. Environment America, an organization of state-based, environmental advocacy organizations, reviewed the final bill and stated there was $32.80 billion in funding for clean energy projects, $26.86 billion for energy efficiency initiatives and $18.95 billion for green transportation, totaling $78.61 billion just for "green" projects.

The 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP 21 or CMP 11 was held in Paris, France, from 30 November to 12 December 2015. It was the 21st yearly session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 11th session of the Meeting of the Parties (CMP) to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol.
The Global Apollo Programme was a historic call for a major global science and economics research programme to make carbon-free baseload electricity less costly than electricity from coal by the year 2025.

The Clean Power Plan was an Obama administration policy aimed at combating climate change that was first proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in June 2014. The final version of the plan was unveiled by President Barack Obama on August 3, 2015. Each state was assigned an individual goal for reducing carbon emissions, which could be accomplished how they saw fit, but with the possibility of the EPA stepping in if the state refused to submit a plan. If every state met its target, the plan was projected to reduce carbon emissions from electricity generation 32% by 2030, relative to 2005 levels, as well as achieving various health benefits due to reduced air pollution.

The Global Covenant of Mayors for Climate & Energy (GCoM) was established in 2016 by bringing formally together the Compact of Mayors and the European Union's Covenant of Mayors. It is a global coalition of city leaders addressing climate change by pledging to cut greenhouse gas emissions and prepare for the future impacts of climate change. The Compact highlights cities' climate impact while measuring their relative risk levels and carbon pollution. The Compact of Mayors seeks to show the importance of city climate action, both at the local level and around the world. The Compact was launched in 2014 by UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon and former New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg, the UN Special Envoy for Cities and Climate Change. The Compact represents a common effort from global city networks C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group (C40), ICLEI, and United Cities and Local Governments (UCLG), as well as UN-Habitat, to unite against climate change. 12,500 cities and local governments have committed to the Compact of Mayors. These cities hail from 6 continents and 144 countries. In total, they represent more than 1 billion people.
Breakthrough Energy is the umbrella name of several organizations, founded by Bill Gates in 2015, that aim to accelerate innovation in sustainable energy and in other technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It invests in a variety of startup companies that are attempting to commercialize new concepts such as nuclear fusion, large-capacity batteries to store renewable energy, and microbe-generated biofuels.














