Related Research Articles

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are typically red, or purple on some people with darker skin, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.

Kasabach–Merritt syndrome, also known as hemangioma with thrombocytopenia is a rare disease, usually of infants, in which a vascular tumor leads to decreased platelet counts and sometimes other bleeding problems, which can be life-threatening. It is also known as hemangioma thrombocytopenia syndrome. It is named after Haig Haigouni Kasabach and Katharine Krom Merritt, the two pediatricians who first described the condition in 1940.

Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), is a disorder resulting from mutations in the genes encoding keratin 5 or keratin 14.
Lichen spinulosus is a rare skin disorder characterized by follicular keratotic papules that are grouped into large patches. It is a variant of keratosis pilaris named for its resemblance to a patch of lichen.
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is a rare form of lobular panniculitis occurring in newborns that is usually self-remitting and non-recurring. Proposed causes include perinatal stress, local trauma, hypoxia and hypothermia, though the exact cause is unknown. It has been suggested that the brown fat seen in newborns is more sensitive to hypoxic injury than fat seen in adults, and that such hypoxia, usually in the context of a complicated birth, leads to the fat necrosis. Complications can include hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia and thrombocytopenia, and can present months after the onset of SCFN symptoms.

In veterinary medicine, miliary dermatitis is a multifocal distribution of skin lesions, with no identifiable pattern. The term miliary means millet-like, as the papules on the coat of an affected cat feel similar to millet seeds.
Tropical acne is unusually severe acne occurring in the tropics during seasons when the weather is hot and humid.

Periorbital dermatitis is a skin condition, a variant of perioral dermatitis, occurring on the lower eyelids and skin adjacent to the upper and lower eyelids.
Prurigo gestationis is an eruption consisting of pruritic, excoriated papules of the proximal limbs and upper trunk, most often occurring between the 20th and 34th week of gestation.
Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp presents with pustules, erosions, and crusts on the scalp of primarily older Caucasian females, and on biopsy, has a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with or without foreign body giant cells and pilosebaceous atrophy.
Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei begins in infancy as follicular papules with perifollicular erythema. Initially, the lesions are restricted to the lateral eyebrows, but with time spread to involve the cheeks and forehead, and may also be associated with keratosis pilaris on the extremities and buttocks.

Griscelli syndrome type 2 is a rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by variable cutenous albinism, silver colored metallic looking hair, frequent bacterial or viral infections, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Aquarium granuloma is a skin condition caused by Mycobacterium marinum, characterized by a skin lesion that presents roughly three weeks after exposure.
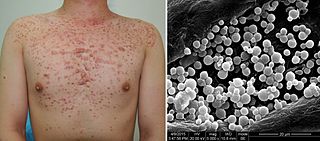
Pityrosporum folliculitis is a skin condition caused by infection by Pityrosporum yeast.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:

Trichilemmoma is a benign cutaneous neoplasm that shows differentiation toward cells of the outer root sheath. The lesion is often seen in the face and neck region. Multifocal occurrence is associated with Cowden syndrome, in which hamartomatous intestinal polyposis is seen in conjunction with multiple tricholemmoma lesions.
Majeed syndrome is an inherited skin disorder characterized by chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, congenital dyserythropoietic anemia and a neutrophilic dermatosis. It is classified as an autoinflammatory bone disorder. The condition is found in people with two defective copies of the LPIN2 gene. LPIN2 encodes lipin-2 which is involved in lipid metabolism. The pathogenesis of this mutation with the clinical manifestations has not been elucidated.
References
- 1 2 Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
| This Dermal and subcutaneous growths article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |