The multiple nuclei model is an economical model created by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman in the 1945 article "The Nature of Cities". [1]

The multiple nuclei model is an economical model created by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman in the 1945 article "The Nature of Cities". [1]
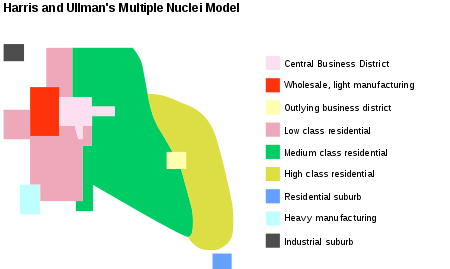
The model describes the layout of a city, based on Chicago. It says that even though a city may have begun with a central business district, or CBD, other smaller CBDs develop on the outskirts of the city near the more valuable housing areas to allow shorter commutes from the outskirts of the city. This creates nodes or nuclei in other parts of the city besides the CBD thus the name multiple nuclei model. Their aim was to produce a more realistic, if more complicated, model. Their main goals in this were to:
The model assumes that:
Harris and Ullman argued that cities do not grow around a single nucleus, but rather several separate nuclei. Each nucleus acts like a growth point.
The theory was formed based on the idea that people have greater movement due to increased car ownership. This increase of movement allows for the specialization of regional centers (e.g. heavy industry, business parks, retail areas). The model is suitable for large, expanding cities. The number of nuclei around which the city expands depends upon situational as well as historical factors. Multiple nuclei develop because:
As the multiple nuclei develop, transportation hubs such as airports are constructed which allow industries to be established with reduced transportation costs. These transportation hubs have negative externality such as noise pollution and lower land values, making land around the hub cheaper. Hotels are also constructed near airports because people who travel tend to want to stay near the source of travel. Housing develops in wedges and gets more expensive the farther it is from the CBD. [2]

Urban geography is the subdiscipline of geography that derives from a study of cities and urban processes. Urban geographers and urbanists examine various aspects of urban life and the built environment. Scholars, activists, and the public have participated in, studied, and critiqued flows of economic and natural resources, human and non-human bodies, patterns of development and infrastructure, political and institutional activities, governance, decay and renewal, and notions of socio-spatial inclusions, exclusions, and everyday life. Urban geography includes different other fields in geography such as the physical, social, and economic aspects of urban geography. The physical geography of urban environments is essential to understand why a town is placed in a specific area, and how the conditions in the environment play an important role with regards to whether or not the city successfully develops. Social geography examines societal and cultural values, diversity, and other conditions that relate to people in the cities. Economic geography is important to examine the economic and job flow within the urban population. These various aspects involved in studying urban geography are necessary to better understand the layout and planning involved in the development of urban environments worldwide.

Urban structure is the arrangement of land use in urban areas, in other words, how the land use of a city is set out. Urban planners, economists, and geographers have developed several models that explain where different types of people and businesses tend to exist within the urban setting. Urban structure can also refer to urban spatial structure, which concerns the arrangement of public and private space in cities and the degree of connectivity and accessibility.
Urban economics is broadly the economic study of urban areas; as such, it involves using the tools of economics to analyze urban issues such as crime, education, public transit, housing, and local government finance. More specifically, it is a branch of microeconomics that studies the urban spatial structure and the location of households and firms.

A residential area is a land used in which housing predominates, as opposed to industrial and commercial areas.

Edge city is a term that originated in the United States for a concentration of business, shopping, and entertainment outside a traditional downtown or central business district, in what had previously been a suburban residential or rural area. The term was popularized by the 1991 book Edge City: Life on the New Frontier by Joel Garreau, who established its current meaning while working as a reporter for The Washington Post. Garreau argues that the edge city has become the standard form of urban growth worldwide, representing a 20th-century urban form unlike that of the 19th-century central downtown. Other terms for these areas include suburban activity centers, megacenters, and suburban business districts. These districts have now developed in many countries.

Urban sprawl is defined as "the spreading of urban developments on undeveloped land near a more or less densely populated city". Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growth in many urban areas of housing, commercial development, and roads over large expanses of land, with little concern for very dense urban planning. Sometimes the urban areas described as the most "sprawling" are the most densely populated. In addition to describing a special form of urbanization, the term also relates to the social and environmental consequences associated with this development. In modern times some suburban areas described as "sprawl" have less detached housing and higher density than the nearby core city. Medieval suburbs suffered from the loss of protection of city walls, before the advent of industrial warfare. Modern disadvantages and costs include increased travel time, transport costs, pollution, and destruction of the countryside. The revenue for building and maintaining urban infrastructure in these areas are gained mostly through property and sales taxes. Most jobs in the US are now located in suburbs generating much of the revenue, although a lack of growth will require higher tax rates.

The concentric zone model, also known as the Burgess model or the CCD model, is one of the earliest theoretical models to explain urban social structures. It was created by sociologist Ernest Burgess in 1925.

The sector model, also known as the Hoyt model, is a model of urban land use proposed in 1939 by land economist Homer Hoyt. It is a modification of the concentric zone model of city development. The benefits of the application of this model include the fact it allows for an outward progression of growth. As with all simple models of such complex phenomena, its validity is limited.
Land-use forecasting undertakes to project the distribution and intensity of trip generating activities in the urban area. In practice, land-use models are demand-driven, using as inputs the aggregate information on growth produced by an aggregate economic forecasting activity. Land-use estimates are inputs to the transportation planning process.

Intermodal passenger transport, also called mixed-mode commuting, involves using two or more modes of transportation in a journey. Mixed-mode commuting is often used to combine the strengths of various transportation options. A major goal of modern intermodal passenger transport is to reduce dependence on the automobile as the major mode of ground transportation and increase use of public transport. To assist the traveller, various intermodal journey planners such as Rome2rio and Google Transit have been devised to help travellers plan and schedule their journey.

The Bandra Kurla Complex is a business and residential district in the city of Mumbai, India. It is a prominent upscale commercial hub which commands some of the highest property rates in the country. According to MMRDA, the complex is the first of a series of "growth centres" created to "arrest further concentration" of offices and commercial activities in eastern parts of Mumbai. It has aided to decongest the CBD in South Mumbai while seeding new areas of planned commercial real estate in the metropolitan region.

In neuroanatomy, thalamocortical radiations, also known as thalamocortical fibres, are the efferent fibres that project from the thalamus to distinct areas of the cerebral cortex. They form fibre bundles that emerge from the lateral surface of the thalamus.

Transportation forecasting is the attempt of estimating the number of vehicles or people that will use a specific transportation facility in the future. For instance, a forecast may estimate the number of vehicles on a planned road or bridge, the ridership on a railway line, the number of passengers visiting an airport, or the number of ships calling on a seaport. Traffic forecasting begins with the collection of data on current traffic. This traffic data is combined with other known data, such as population, employment, trip rates, travel costs, etc., to develop a traffic demand model for the current situation. Feeding it with predicted data for population, employment, etc. results in estimates of future traffic, typically estimated for each segment of the transportation infrastructure in question, e.g., for each roadway segment or railway station. The current technologies facilitate the access to dynamic data, big data, etc., providing the opportunity to develop new algorithms to improve greatly the predictability and accuracy of the current estimations.

The bid rent theory is a geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand for real estate change as the distance from the central business district (CBD) increases. It states that different land users will compete with one another for land close to the city centre. This is based upon the idea that retail establishments wish to maximize their profitability, so they are much more willing to pay more for land close to the CBD and less for land further away from this area. This theory is based upon the reasoning that the more accessible an area, the more profitable.

Car dependency is the concept that some city layouts cause cars to be favoured over alternate forms of transportation, such as bicycles, public transit, and walking.

The Core frame model is a model showing the urban structure of the Central Business District of a town or city. The model was first suggested by Ronald R. Boyce and Edgar M. Horwood in 1959.

Chauncy Dennison Harris was a pioneer of modern geography. His seminal works in the field of American urban geography along with his work on the Soviet Union during and after the Cold War era established him as one of the world's foremost urban geographers. He also made significant contributions to the geographical study of ethnicity, specifically with respect to non-Russian minorities living within the Soviet Union. Harris traveled regularly to the Soviet Union and played a key role in establishing a healthy dialog between Soviet and American scholars.

The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.
Urban freight distribution is the system and process by which goods are collected, transported, and distributed within urban environments. The urban freight system can include seaports, airports, manufacturing facilities, and warehouse/distribution centers that are connected by a network of railroads, rail yards, pipelines, highways, and roadways that enable goods to get to their destinations.

Morphology in architecture is the study of the evolution of form within the built environment. Often used in reference to a particular vernacular language of building, this concept describes changes in the formal syntax of buildings and cities as their relationship to people evolves and changes. Often morphology describes processes, such as in the evolution of a design concept from first conception to production, but can also be understood as the categorical study in the change of buildings and their use from a historical perspective. Similar to genres of music, morphology concertizes 'movements' and arrives at definitions of architectural 'styles' or typologies. Paradoxically morphology can also be understood to be the qualities of a built space which are style-less or irreducible in quality.