Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.

Flemish Brabant is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Hainaut and East Flanders. Flemish Brabant also surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region. Its capital is Leuven. It has an area of 2,118 km2 (818 sq mi) which is divided into two administrative districts containing 65 municipalities. As of January 2019, Flemish Brabant has a population of 1,146,175.

Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
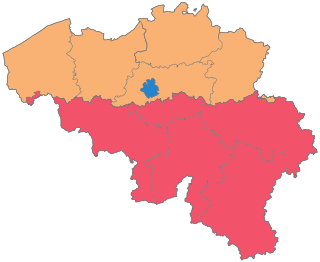
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

Voeren is a Flemish Dutch-speaking municipality with facilities for the French-speaking minority, located in the Belgian province of Limburg. Bordering the Netherlands to the north and the Wallonia region's Liège Province to the south, it is geographically detached from the rest of Flanders, making Voeren an exclave of Flanders. Voeren's name is derived from that of a small right-bank tributary of the Meuse, the Voer, which flows through the municipality.

The Flemish Movement is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promote Flemish culture and Dutch language as well as those seeking greater political autonomy for Flanders within Belgium. It also encompassed nationalists who seek the secession of Flanders from Belgium, either through outright independence or unification with the Netherlands.

The Flemish Region, usually simply referred to as Flanders is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Covering the northern portion of the country, the Flemish Region is primarily Dutch-speaking. With an area of 13,522 km2 (5,221 sq mi), it accounts for only 45% of Belgium's territory, but 57% of its population. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 490/km2 (1,300/sq mi).

There are 27 municipalities with language facilities in Belgium which must offer linguistic services to residents in Dutch, French, or German in addition to their single official languages. All other municipalities – with the exception of those in the bilingual Brussels region – are monolingual and only offer services in their official languages, either Dutch or French.

The area within Belgium known as Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde encompasses the bilingual—French and Dutch—Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking area of Halle-Vilvoorde, which in turn coincides with the arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde. Halle-Vilvoorde contains several municipalities with language facilities, i.e. municipalities where French-speaking people form a considerable part of the population and therefore have special language rights. This area forms the judicial arrondissement of Brussels, which is the location of a tribunal of first instance, enterprise tribunal and a labour tribunal. It was reformed in July 2012, as part of the sixth Belgian state reform.

Elections in Belgium are organised for legislative bodies only, and not for executive functions. Direct elections take place for the European Parliament, the Chamber of Representatives, the Parliaments of the Regions, the Parliaments of the Communities, the provincial councils, the municipal councils and the councils of Districts of Antwerp. Voting is mandatory and all elections use proportional representation which in general requires coalition governments.
A schepen or échevin (French) or Schöffe (German) is a municipal officer in Belgium and formerly the Netherlands. It has been replaced by the wethouder in the Netherlands.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2006 took place on Sunday 8 October 2006. The electors have elected the municipal councillors of 589 cities and towns as well as the ten provincial councils. The voters in the town of Antwerp have also been able to vote for the city's district councils. In seven Flemish municipalities with a special language statute and in the Walloon municipality of Comines-Warneton the aldermen and the members of the OCMW/CPAS council have also been directly elected.

The Kingdom of Belgium has three official languages: Dutch (Flemish), French, and German.

This article outlines the legislative chronology concerning the use of official languages in Belgium.
The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation, which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media, envisioning a split of Belgium along linguistic divisions, with the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) becoming independent states. Alternatively, it is hypothesized that Flanders could join the Netherlands and Wallonia could join France or Luxembourg.

State reform, in the context of Belgium, is the ongoing process of seeking and finding constitutional and legal solutions to the problems and tensions in the different segments of the Belgian population, mostly between the Dutch-speakers of Flanders and the French-speakers of Wallonia. In general, Belgium has evolved from a unitary state to a federal state with communities, regions, and language areas.

The Francization of Brussels refers to the evolution, over the past two centuries, of this historically Dutch-speaking city into one where French has become the majority language and lingua franca. The main cause of this transition was the rapid, yet compulsory assimilation of the Flemish population, amplified by immigration from France and Wallonia.
Water supply and sanitation in Belgium is provided by a large variety of organizations: Most of the 581 municipalities of Belgium have delegated the responsibility for water supply and sanitation to regional or inter-municipal utilities. There are more than 62 water supply utilities, including 2 regional, 30 inter-municipal and 30 municipal utilities. Another 100 mostly small municipalities provide services directly without having a legally of financially separate entity for water supply. Water is not scarce in Belgium and water supply is generally continuous and of good quality. However, wastewater treatment has long lagged behind and Brussels only achieved full treatment of its wastewater in 2007. In 2004 the European Court of Justice ruled condemning Belgium's failure to comply with the EU wastewater directive, and the ruling has not been fully complied with so far. Wallonia satisfies 55% of the national needs in drinking water while it counts only 37% of the population. Flanders and Brussels are dependent on drinking water from Wallonia, at a level of 40% and 98% respectively.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2012 took place on 14 October. As with the previous 2006 elections, these are no longer organised by the Belgian federal state but instead by the respective regions:
The fusion of the Belgian municipalities was a Belgian political process that rationalized and reduced the number of municipalities in Belgium between 1975 and 1983. In 1961, there were 2,663 such municipalities; by 1983, these had been re-arranged and combined into 589 municipalities.