
Dorado is a constellation in the Southern Sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the mahi-mahi, which is known as dorado ("golden") in Spanish, although it has also been depicted as a swordfish. Dorado contains most of the Large Magellanic Cloud, the remainder being in the constellation Mensa. The South Ecliptic pole also lies within this constellation.

NGC 346 is a young open cluster of stars with associated nebula located in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) that appears in the southern constellation of Tucana. It was discovered August 1, 1826 by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop. J. L. E. Dreyer described it as, "bright, large, very irregular figure, much brighter middle similar to double star, mottled but not resolved". On the outskirts of the cluster is the multiple star system HD 5980, one of the brightest stars in the SMC.
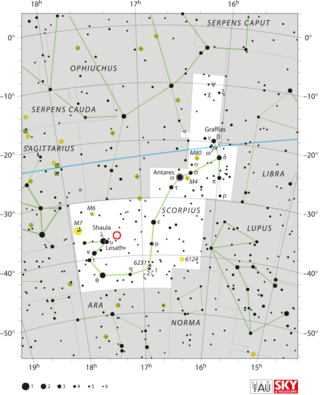
NGC 6334, colloquially known as the Cat's Paw Nebula, or Gum 64, is an emission nebula and star-forming region located in the constellation Scorpius. NGC 6334 was discovered by astronomer John Herschel in 1837, who observed it from the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa. The nebula is located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way, at a distance of approximately 5.5 kilolight-years from the Sun.

NGC 5371 is a face-on spiral galaxy in the northern constellation Canes Venatici. It was discovered on January 14, 1788 by German-British astronomer William Herschel. The nearby NGC 5390 appears to be a duplicate entry for NGC 5371, since there is nothing at the former's position. NGC 5371 has an apparent magnitude of 11.3 and an angular size of 4.4′ × 3.5′. It is located at a distance of 129.5 ± 32.4 million light-years (39.70 ± 9.92 Mpc) from the Milky Way, and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 2,552 km/s. The galaxy appears to be weakly interacting with the nearby, equidistant Hickson 68 group of galaxies, and thus may be a member. Collectively, they are sometimes dubbed the Big Lick galaxy group, after the city of Roanoke, Virginia.

NGC 3195 is a planetary nebula located in the southern constellation of Chamaeleon. Discovered by Sir John Herschel in 1835, this 11.6 apparent magnitude planetary nebula is slightly oval in shape, with dimensions of 40×35 arc seconds, and can be seen visually in telescopic apertures of 10.5 centimetres (4.1 in) at low magnifications.

NGC 5665 is a spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Boötes. It was discovered on January 30, 1784 by German-British astronomer William Herschel. This galaxy is located at a distance of 53.6 ± 7.7 million light-years (16.44 ± 2.37 Mpc), and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 2,237 km/s. It is cataloged in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as object number 49.

NGC 36 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located about 221 million light-years away. It was discovered in October 25, 1785, by the astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 7499 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy within the constellation Pisces. NGC 7499 is its New General Catalogue designation. It was discovered on September 2, 1864 by the astronomer Albert Marth.

Little Ghost Nebula, also known as NGC 6369, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by William Herschel.

NGC 7302 is a lenticular galaxy located around 124 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Aquarius. NGC 7302 was discovered by British astronomer William Herschel on October 3, 1785 and was rediscovered by American astronomer Lewis Swift on August 8, 1896 and was listed in the IC catalogue as IC 5228. It is also part of a group of interacting galaxies.

NGC 4753 is a lenticular galaxy located about 60 million light-years away in the constellation of Virgo. NGC 4753 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on February 22, 1784. It is notable for having distinct dust lanes that surround its nucleus. It is a member of the NGC 4753 Group of galaxies, which is a member of the Virgo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster.

NGC 4523 is a Magellanic spiral galaxy located about 35 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on April 19, 1865. NGC 4523 is a member of the Virgo Cluster. A distance of for NGC 4523 was derived from using yellow supergiants in the galaxy as standard candles.

NGC 4659 is a lenticular galaxy located about 54 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. NGC 4659 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 12, 1784 and is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 5030 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. The object was discovered on 17 March 1881 by the American astronomer Edward Singleton Holden.

NGC 612 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation of Sculptor located approximately 388 million light-years from Earth. It is a type II Seyfert galaxy and thus has an active galactic nucleus. NGC 612 has been identified as an extremely rare example of a non-elliptical radio galaxy, hosting one of the nearest powerful FR-II radio sources.

NGC 4299 is a featureless spiral galaxy located about 55 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 15, 1784 and is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 657 is an open cluster containing very few stars or a group of stars located in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by British astronomer John Herschel in 1831.

NGC 721 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Andromeda about 250 million light years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by the Prussian astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest in 1862.

NGC 5533 is an unbarred spiral galaxy in the constellation Boötes. It was discovered by the astronomer William Herschel on May 1, 1785. It has a regular structure, with one tightly wound spiral; its disk is inclined about 53 degrees towards the line of sight.

NGC 4393 is a spiral galaxy about 46 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 11, 1785. It is a member of the NGC 4274 Group, which is part of the Coma I Group or Cloud.




















