The Centaurus Cluster (A3526) is a cluster of hundreds of galaxies, located approximately 170 million light-years away in the Centaurus constellation. The brightest member galaxy is the elliptical galaxy NGC 4696 (~11m). The Centaurus cluster shares its supercluster, the Hydra–Centaurus Supercluster, with IC4329 Cluster and Hydra Cluster.

NGC 4309 is a lenticular galaxy located about 55 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Christian Peters in 1881 and is a member of the Virgo Cluster.
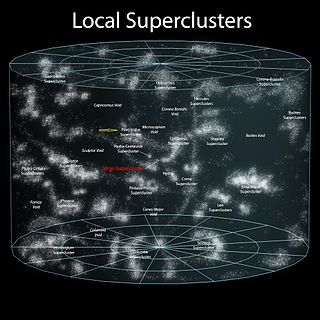
The Pavo–Indus Supercluster is a neighboring supercluster located about 60–70 Mpc (196–228 Mly) away in the constellations of Pavo, Indus, and Telescopium. The supercluster contains three main clusters, Abell 3656, Abell 3698, and Abell 3742.

NGC 4523 is a Magellanic spiral galaxy located about 35 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on April 19, 1865. NGC 4523 is a member of the Virgo Cluster. A distance of for NGC 4523 was derived from using yellow supergiants in the galaxy as standard candles.

NGC 4596 is a barred lenticular galaxy located about 55 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. NGC 4596 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 15, 1784. NGC 4596 is a member of the Virgo Cluster and has an inclination of about 38°.

NGC 4876 is an elliptical galaxy located about 325 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. NGC 4876 was discovered by astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan on May 16, 1885. NGC 4876 is a member of the Coma Cluster.

NGC 1281 is a compact elliptical galaxy located about 200 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus. NGC 1281 was discovered by astronomer John Dreyer on December 12, 1876. It is a member of the Perseus Cluster.

NGC 3860 is a spiral galaxy located about 340 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. NGC 3860 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785. The galaxy is a member of the Leo Cluster and is a low-luminosity AGN (LLAGN). Gavazzi et al. however classified NGC 3860 as a strong AGN which may have been triggered by a supermassive black hole in the center of the galaxy.

NGC 709 is a lenticular galaxy located 150 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered by the Irish engineer and astronomer Bindon Blood Stoney on October 28, 1850 and is a member of the galaxy cluster Abell 262.

NGC 4065 is an elliptical galaxy located 300 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785. It was then rediscovered by John Herschel on April 29, 1832 and was listed as NGC 4057. NGC 4065 is the brightest member of the NGC 4065 Group.

NGC 4074 is a peculiar lenticular galaxy located 310 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785 and is a member of the NGC 4065 Group.

NGC 4299 is a featureless spiral galaxy located about 55 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 15, 1784 and is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 4513 is a lenticular galaxy and a ring galaxy located about 110 million light-years away in the constellation Draco. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on October 16, 1866.

NGC 4306 is a dwarf barred lenticular galaxy located about 100 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on April 16, 1865. Although considered to be a member of the Virgo Cluster, its high radial velocity and similar distance as NGC 4305 suggest that NGC 4306 is a background galaxy. NGC 4306 is a companion of NGC 4305 and appears to be interacting with it.

NGC 4313 is an edge-on spiral galaxy located about 50 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 15, 1784. NGC 4313 is a member of the Virgo Cluster and is classified as LINER and as a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 4316 is an edge-on spiral galaxy located about 70 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer Wilhelm Tempel on March 17, 1882. NGC 4316 is a member of the Virgo Cluster and is classified as LINER and as a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 4324 is a lenticular galaxy located about 85 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on March 4, 1862. NGC 4324 has a stellar mass of 5.62 × 1010M☉, and a baryonic mass of 5.88 × 1010M☉. The galaxy's total mass is around 5.25 × 1011M☉. NGC 4324 is notable for having a ring of star formation surrounding its nucleus. It was considered a member of the Virgo II Groups until 1999, when its distance was recalculated and it was placed in the Virgo W Group.

NGC 4393 is a spiral galaxy about 46 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 11, 1785. It is a member of the NGC 4274 Group, which is part of the Coma I Group or Cloud.

NGC 1396 is a dwarf elliptical galaxy located 61 millon light years away in the constellation of Fornax. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Julius Schmidt on January 19, 1865, and is a member of the Fornax Cluster. Despite the fact that the galaxy PGC 13398 is most commonly identified as NGC 1396, there is uncertainty in its identification.


















