An audit trail is a security-relevant chronological record, set of records, and/or destination and source of records that provide documentary evidence of the sequence of activities that have affected at any time a specific operation, procedure, event, or device. Audit records typically result from activities such as financial transactions, scientific research and health care data transactions, or communications by individual people, systems, accounts, or other entities.
The Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) is an American post-trade financial services company providing clearing and settlement services to the financial markets. It performs the exchange of securities on behalf of buyers and sellers and functions as a central securities depository by providing central custody of securities.
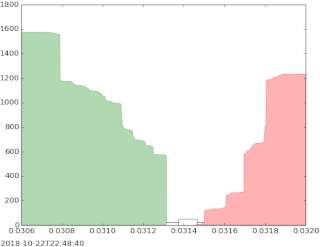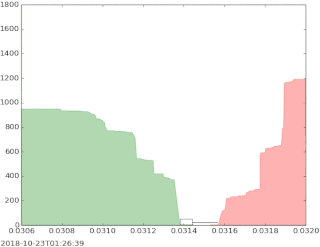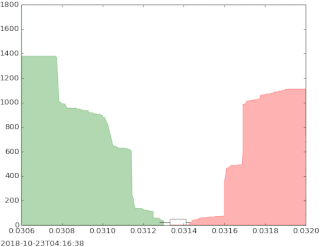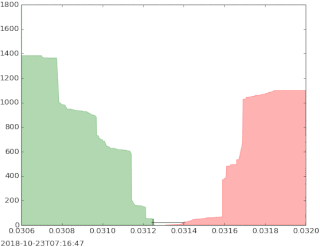
The bid–ask spread is the difference between the prices quoted for an immediate sale (ask) and an immediate purchase (bid) for stocks, futures contracts, options, or currency pairs in some auction scenario. The size of the bid–ask spread in a security is one measure of the liquidity of the market and of the size of the transaction cost. If the spread is 0 then it is a frictionless asset.
In banking and finance, clearing denotes all activities from the time a commitment is made for a transaction until it is settled. This process turns the promise of payment into the actual movement of money from one account to another. Clearing houses were formed to facilitate such transactions among banks.

Osaka Exchange, Inc., renamed from Osaka Securities Exchange Co., Ltd., is the largest derivatives exchange in Japan, in terms of amount of business handled.
Algorithmic trading is a method of executing orders using automated pre-programmed trading instructions accounting for variables such as time, price, and volume. This type of trading attempts to leverage the speed and computational resources of computers relative to human traders. In the twenty-first century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders. A study in 2019 showed that around 92% of trading in the Forex market was performed by trading algorithms rather than humans.

In finance, market data is price and other related data for a financial instrument reported by a trading venue such as a stock exchange. Market data allows traders and investors to know the latest price and see historical trends for instruments such as equities, fixed-income products, derivatives, and currencies.
Regulation National Market System is a 2005 US financial regulation promulgated and described by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as "a series of initiatives designed to modernize and strengthen the National Market System for equity securities". The Reg NMS is intended to assure that investors receive the best (NBBO) price executions for their orders by encouraging competition in the marketplace. Some contend that the rule has contributed to the rise of high-frequency trading, which is sometimes regarded as controversial.
The Kazakhstan Stock Exchange is a stock exchange located in Almaty, Kazakhstan. The exchange was founded in 1993.
The Consolidated Tape Association (CTA) oversees the Securities Information Processor that disseminates real-time trade and quote information in New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and American Stock Exchange (AMEX) listed securities. It is currently chaired by Emily Kasparov of the Chicago Stock Exchange, the first woman and the youngest chair elected to the position.
In finance, a dark pool is a private forum for trading securities, derivatives, and other financial instruments. Liquidity on these markets is called dark pool liquidity. The bulk of dark pool trades represent large trades by financial institutions that are offered away from public exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange and the NASDAQ, so that such trades remain confidential and outside the purview of the general investing public. The fragmentation of electronic trading platforms has allowed dark pools to be created, and they are normally accessed through crossing networks or directly among market participants via private contractual arrangements. Generally, dark pools are not available to the public, but in some cases, they may be accessed indirectly by retail investors and traders via retail brokers.
The Options Price Reporting Authority (OPRA) oversees the Securities Information Processor (SIP) that provides last sale information and current options quotations from a committee of participant exchanges. In turn, this committee is designated as the Options Price Reporting Authority.
The National Market System (NMS) is a regulatory mechanism that governs the operations of securities trading in the United States. Its primary focus is ensuring transparency and full disclosure regarding stock price quotations and trade executions. It was initiated in 1975, when, in the Securities Acts Amendments of 1975, Congress directed the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to use its authority to facilitate the establishment of a national market system. The system has been updated periodically, for example with the Regulation NMS in 2005 which took into account technological innovations and other market changes.

In finance, an electronic trading platform also known as an online trading platform, is a computer software program that can be used to place orders for financial products over a network with a financial intermediary. Various financial products can be traded by the trading platform, over a communication network with a financial intermediary or directly between the participants or members of the trading platform. This includes products such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, derivatives and others, with a financial intermediary such as brokers, market makers, Investment banks or stock exchanges. Such platforms allow electronic trading to be carried out by users from any location and are in contrast to traditional floor trading using open outcry and telephone-based trading. Sometimes the term trading platform is also used in reference to the trading software alone.
A financial data vendor provides market data to financial firms, traders, and investors. The data distributed is collected from sources such as stock exchange feeds, brokers and dealer desks or regulatory filings.
Smart order routing (SOR) is an automated process of handling orders, aimed at taking the best available opportunity throughout a range of different trading venues.

Securities market participants in the United States include corporations and governments issuing securities, persons and corporations buying and selling a security, the broker-dealers and exchanges which facilitate such trading, banks which safe keep assets, and regulators who monitor the markets' activities. Investors buy and sell through broker-dealers and have their assets retained by either their executing broker-dealer, a custodian bank or a prime broker. These transactions take place in the environment of equity and equity options exchanges, regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), or derivative exchanges, regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). For transactions involving stocks and bonds, transfer agents assure that the ownership in each transaction is properly assigned to and held on behalf of each investor.
For three hours on August 22, 2013, trading was halted on the Nasdaq Stock Market. Trading on the exchange stopped at 12:14 pm and resumed at 3:25 pm, with 35 minutes left of trading for the day. One week after the trading halt NASDAQ OMX credited the freeze to an overloading of the Securities Information Processor (SIP) caused by reconnection issues with the New York Stock Exchange Arca. The freeze received substantial media coverage and generated discussions on the security of increasingly technologically advanced stock exchanges. The event coined the term "flash freeze" following the earlier "flash crash" on May 6, 2010.
Unlisted Trading Privileges (UTP) oversees the Securities Information Processor for securities listed on Nasdaq and other securities that do not meet the requirements for listing on an exchange.
A securities information processor (SIP) is a part of the infrastructure of public market data providers in the United States that process, consolidate, and disseminate quotes and trade data from different US securities exchanges and market centers. An important purpose of the SIPs for US securities is to publish the prevailing National Best Bid Offer (NBBO).




