The Nasdaq Stock Market is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second on the list of stock exchanges by market capitalization of shares traded, behind the New York Stock Exchange. The exchange platform is owned by Nasdaq, Inc., which also owns the Nasdaq Nordic stock market network and several U.S.-based stock and options exchanges. According to a Gallup poll conducted in 2022, approximately 58% of American adults reported having money invested in the stock market, either through individual stocks, mutual funds, or retirement accounts.
The National Stock Exchange (NSX) is an electronic stock exchange based in Jersey City, New Jersey. It was founded March 1885 in Cincinnati, Ohio, as the Cincinnati Stock Exchange.

A market maker or liquidity provider is a company or an individual that quotes both a buy and a sell price in a tradable asset held in inventory, hoping to make a profit on the bid–ask spread, or turn. The benefit to the firm is that it makes money from doing so; the benefit to the market is that this helps limit price variation (volatility) by setting a limited trading price range for the assets being traded.
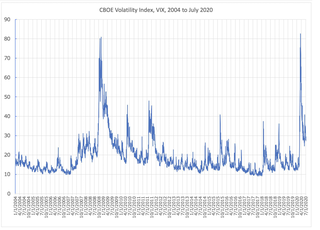
VIX is the ticker symbol and the popular name for the Chicago Board Options Exchange's CBOE Volatility Index, a popular measure of the stock market's expectation of volatility based on S&P 500 index options. It is calculated and disseminated on a real-time basis by the CBOE, and is often referred to as the fear index or fear gauge.
NYSE Euronext, Inc. was a transatlantic multinational financial services corporation that operated multiple securities exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange, Euronext and NYSE Arca. NYSE merged with Archipelago Holdings on March 7, 2006, forming NYSE Group, Inc. On April 4, 2007, NYSE Group, Inc. merged with Euronext N.V. to form the first global equities exchange, with its headquarters in Lower Manhattan. The corporation was then acquired by Intercontinental Exchange, which subsequently spun off Euronext.

Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) is a United States clearing house based in Chicago. It specializes in equity derivatives clearing, providing central counterparty (CCP) clearing and settlement services to 16 exchanges. Started by Wayne Luthringshausen and carried on by Michael Cahill. Its instruments include options, financial and commodity futures, security futures, and securities lending transactions.
The Securities Industry Automation Corporation (SIAC) is a subsidiary of the NYSE Euronext. Its purpose is to provide technical services for the exchanges themselves, members and other financial institutions. In this role, SIAC provides the computers and other systems required to run the exchanges. It also owns communication lines and hardware to provide real-time quotes and transaction information to all market participants from the Consolidated Tape/Ticker System (CTS), Consolidated Quotation System (CQS), and Options Price Reporting Authority (OPRA).
A national market system plan is a structured method of transmitting securities transactions in real-time. In the United States, national market systems are governed by section 11A of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
The Consolidated Tape Association (CTA) oversees the Securities Information Processor that disseminates real-time trade and quote information in New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and American Stock Exchange (AMEX) listed securities. It is currently chaired by Emily Kasparov of the Chicago Stock Exchange, the first woman and the youngest chair elected to the position.

BATS Global Markets is a global stock exchange operator founded in Lenexa, Kansas, with additional offices in London, New York, Chicago, and Singapore. BATS was founded in June 2005, became operator of a licensed U.S. stock exchange in 2008 and opened its pan-European stock market in October 2008. As of February 2016, it operated four U.S. stock exchanges, two U.S. equity options exchanges, the pan-European stock market, and a global market for the trading of foreign exchange products. BATS was acquired by Cboe Global Markets in 2017.
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic financial trading characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools. While there is no single definition of HFT, among its key attributes are highly sophisticated algorithms, co-location, and very short-term investment horizons. HFT can be viewed as a primary form of algorithmic trading in finance. Specifically, it is the use of sophisticated technological tools and computer algorithms to rapidly trade securities. HFT uses proprietary trading strategies carried out by computers to move in and out of positions in seconds or fractions of a second.
Flash trading, otherwise known as a flash order, is a marketable order sent to a market center that is not quoting the industry's best price or that cannot fill that order in its entirety. The order is then flashed to recipients of the venue's proprietary data feed to see if any of those firms wants to take the other side of the order.

Virtu Financial is an American company that provides financial services, trading products and market making services. Virtu provides product suite including offerings in execution, liquidity sourcing, analytics and broker-neutral, multi-dealer platforms in workflow technology and two-sided quotations and trades in equities, commodities, currencies, options, fixed income, and other securities on over 230 exchanges, markets, and dark pools. Virtu uses proprietary technology to trade large volumes of securities. The company went public on the Nasdaq in 2015.

Interactive Brokers LLC (IB) is an American multinational brokerage firm. It operates the largest electronic trading platform in the United States by number of daily average revenue trades. The company brokers stocks, options, futures, EFPs, futures options, forex, bonds, funds, and some cryptocurrencies.

Securities market participants in the United States include corporations and governments issuing securities, persons and corporations buying and selling a security, the broker-dealers and exchanges which facilitate such trading, banks which safe keep assets, and regulators who monitor the markets' activities. Investors buy and sell through broker-dealers and have their assets retained by either their executing broker-dealer, a custodian bank or a prime broker. These transactions take place in the environment of equity and equity options exchanges, regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), or derivative exchanges, regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). For transactions involving stocks and bonds, transfer agents assure that the ownership in each transaction is properly assigned to and held on behalf of each investor.

Cboe Global Markets is an American company that owns the Chicago Board Options Exchange and the stock exchange operator BATS Global Markets.
For three hours on August 22, 2013, trading was halted on the Nasdaq Stock Market. Trading on the exchange stopped at 12:14 pm and resumed at 3:25 pm, with 35 minutes left of trading for the day. One week after the trading halt NASDAQ OMX credited the freeze to an overloading of the Securities Information Processor (SIP) caused by reconnection issues with the New York Stock Exchange Arca. The freeze received substantial media coverage and generated discussions on the security of increasingly technologically advanced stock exchanges. The event coined the term "flash freeze" following the earlier "flash crash" on May 6, 2010.
Unlisted Trading Privileges (UTP) oversees the Securities Information Processor for securities listed on Nasdaq and other securities that do not meet the requirements for listing on an exchange.
A Securities Information Processor (SIP) is a part of the infrastructure of public market data providers in the United States that process, consolidate, and disseminate quotes and trade data from different US securities exchanges and market centers. An important purpose of the SIPs for US securities is to publish the prevailing National Best Bid Offer (NBBO).







