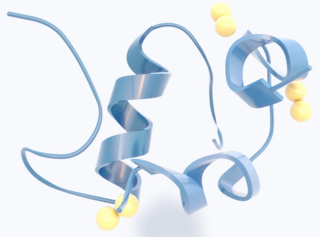
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets; it is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially of reserve body fat.

The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach.
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia.

The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of the pancreas volume and receive 10–15% of its blood flow. The pancreatic islets are arranged in density routes throughout the human pancreas, and are important in the metabolism of glucose.

An insulinoma is a tumour of the pancreas that is derived from beta cells and secretes insulin. It is a rare form of a neuroendocrine tumour. Most insulinomas are benign in that they grow exclusively at their origin within the pancreas, but a minority metastasize. Insulinomas are one of the functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour (PNET) group. In the Medical Subject Headings classification, insulinoma is the only subtype of "islet cell adenoma".
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia describes the condition and effects of low blood glucose caused by excessive insulin. Hypoglycemia due to excess insulin is the most common type of serious hypoglycemia. It can be due to endogenous or injected insulin.

Hyperinsulinism refers to an above normal level of insulin in the blood of a person or animal. Normal insulin secretion and blood levels are closely related to the level of glucose in the blood, so that a given level of insulin can be normal for one blood glucose level but low or high for another. Hyperinsulinism can be associated with several types of medical problems, which can be roughly divided into two broad and largely non-overlapping categories: those tending toward reduced sensitivity to insulin and high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia), and those tending toward excessive insulin secretion and low glucose levels (hypoglycemia).

Congenital hyperinsulinism is a medical term referring to a variety of congenital disorders in which hypoglycemia is caused by excessive insulin secretion. Congenital forms of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia can be transient or persistent, mild or severe. These conditions are present at birth and most become apparent in early infancy. Mild cases can be treated by frequent feedings, more severe cases can be controlled by medications that reduce insulin secretion or effects.

Hyperinsulinemia is a condition in which there are excess levels of insulin circulating in the blood relative to the level of glucose. While it is often mistaken for diabetes or hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinemia can result from a variety of metabolic diseases and conditions, as well as non-nutritive sugars in the diet. While hyperinsulinemia is often seen in people with early stage type 2 diabetes mellitus, it is not the cause of the condition and is only one symptom of the disease. Type 1 diabetes only occurs when pancreatic beta-cell function is impaired. Hyperinsulinemia can be seen in a variety of conditions including diabetes mellitus type 2, in neonates and in drug-induced hyperinsulinemia. It can also occur in congenital hyperinsulinism, including nesidioblastosis.

Diazoxide, sold under the brand name Proglycem and Balila(India), is a medication used to treat low blood sugar due to a number of specific causes. This includes islet cell tumors that cannot be removed and leucine sensitivity. It can also be used in refractory cases of sulfonylurea toxicity. It is generally taken by mouth.

Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is co-secreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels.

Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when very little or no insulin is produced by the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for energy and it helps regulate normal glucose levels in the bloodstream. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. The common symptoms of this elevated blood sugar are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other serious complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. Symptoms typically develop over a short period of time, often a matter of weeks.
In molecular biology, the sulfonylurea receptors (SUR) are membrane proteins which are the molecular targets of the sulfonylurea class of antidiabetic drugs whose mechanism of action is to promote insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. More specifically, SUR proteins are subunits of the inward-rectifier potassium ion channels Kir6.x. The association of four Kir6.x and four SUR subunits form an ion conducting channel commonly referred to as the KATP channel.

Kir6.2 is a major subunit of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel, a lipid-gated inward-rectifier potassium ion channel. The gene encoding the channel is called KCNJ11 and mutations in this gene are associated with congenital hyperinsulinism.

PDX1, also known as insulin promoter factor 1, is a transcription factor in the ParaHox gene cluster. In vertebrates, Pdx1 is necessary for pancreatic development, including β-cell maturation, and duodenal differentiation. In humans this protein is encoded by the PDX1 gene, which was formerly known as IPF1. The gene was originally identified in the clawed frog Xenopus laevis and is present widely across the evolutionary diversity of bilaterian animals, although it has been lost in evolution in arthropods and nematodes. Despite the gene name being Pdx1, there is no Pdx2 gene in most animals; single-copy Pdx1 orthologs have been identified in all mammals. Coelacanth and cartilaginous fish are, so far, the only vertebrates shown to have two Pdx genes, Pdx1 and Pdx2.
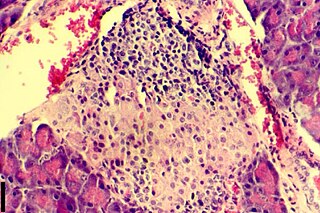
Insulitis is an inflammation of the islets of Langerhans, a collection of endocrine tissue located in the pancreas that helps regulate glucose levels, and is classified by specific targeting of immune cell infiltration in the islets of Langerhans. This immune cell infiltration can result in the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells of the islets, which plays a major role in the pathogenesis, the disease development, of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Insulitis is present in 19% of individuals with type 1 diabetes and 28% of individuals with type 2 diabetes. It is know that genetic and environmental factors contribute to insulitis initiation, however, the exact process that causes it is unknown. Insulitis is often studied using the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of type 1 diabetes. The chemokine family of proteins may play a key role in promoting leukocytic infiltration into the pancreas prior to pancreatic beta-cell destruction.

Neurogenin-3 (NGN3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the Neurog3 gene.
In medicine, a nesidioblastoma is an uncommon, insulin-secreting, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (PanNET). The term dates to at least 1938. In that report, these lesions were adjudicated as histologically benign adenoma growths, that were associated with severe, long-standing hypoglycemia due to hyperinsulinism. Surgical removal corrected the low glucose problems. There is no rigorous definitional separation from insulinoma, other than the original emphasis that was placed on the observed precise histological recapitulation of normal islet cell structure within the adenomas, which lacked microscopic features of aggressivity.

Pancreatic progenitor cells are multipotent stem cells originating from the developing fore-gut endoderm which have the ability to differentiate into the lineage specific progenitors responsible for the developing pancreas.













