| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 176 seats in the National Assembly 89 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
The next Mauritanian parliamentary election will be held by 2028 to elect the 176 seats of the 11th National Assembly of Mauritania.
| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 176 seats in the National Assembly 89 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
The next Mauritanian parliamentary election will be held by 2028 to elect the 176 seats of the 11th National Assembly of Mauritania.
The 176 members of the National Assembly are elected by two methods (with Mauritanians being able to cast four different votes in a parallel voting system); 125 are elected from single- or multi-member electoral districts based on the departments (or moughataas) that the country is subdivided in (which the exception of Nouakchott, which is divided in three 7-seat constituencies based on the three regions (or wilayas) the city is subdivided in [1] using either the two-round system or proportional representation; in single-member constituencies candidates require a majority of the vote to be elected in the first round and a plurality in the second round. In two-seat constituencies, voters vote for a party list (which must contain one man and one woman); if no list receives more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a second round is held, with the winning party taking both seats. In constituencies with three or more seats, closed list proportional representation is used, with seats allocated using the largest remainder method. [2] For three-seat constituencies, party lists must include a female candidate in first or second on the list; for larger constituencies a zipper system is used, with alternate male and female candidates. [2] The Mauritanian diaspora gets allocated four two-round majoritarian seats. [1]
The remaining 51 seats are elected from three nationwide constituencies, also using closed list proportional representation: a 20-seat national list (which uses a zipper system), a 20-seat women's national list and a new 11-seat youth list (with two reserved for people with special needs), which also uses a zipper system to guarantee the representation of women. [1] [2]
| Polling firm | Fieldwork date | Sample size | El Insaf | RNRD | UDP | Sawab+ | El Islah | HATEM | El Karama | AJD/MR | HIWAR | UFP | El Vadila | RFD | PSJN | APP | Ribat | Others | N/A | Excluded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afrobarometer | 6 November – 6 December 2023 | 1,200 | 28.5 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 3.6 | 55.2 |
| 2023 election | 13 May 2023 (national list vote) | – | 35.25 | 10.24 | 6.06 | 4.10 | 3.28 | 2.90 | 2.62 | 2.18 | 2.08 | 1.79 | 1.78 | 1.51 | 1.48 | 1.25 | 1.07 | 22.41 | – | – |

Proportional representation (PR) refers to any type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast – or almost all votes cast – contribute to the result and are effectively used to help elect someone – not just a bare plurality or (exclusively) the majority – and that the system produces mixed, balanced representation reflecting how votes are cast.

Party-list proportional representation (list-PR) is a subset of proportional representation electoral systems in which multiple candidates are elected through their position on an electoral list. They can also be used as part of mixed-member electoral systems.
Single non-transferable vote or SNTV is an electoral system used to elect multiple winners. It is a generalization of first-past-the-post, applied to multi-member districts with each voter casting just one vote. Unlike FPTP, which is a single-winner system, in SNTV multiple winners are elected, typically in electoral districts; additionally, unlike FPTP, SNTV produces mixed representation and makes it unlikely for a single party to take all the seats in a city or a set area, which can happen under FPTP.

The additional-member system (AMS) is a mixed electoral system under which most representatives are elected in single-member districts (SMDs), and the other "additional members" are elected to make the seat distribution in the chamber more proportional to the way votes are cast for party lists. It is distinct from parallel voting in that the "additional member" seats are awarded to parties taking into account seats won in SMDs, which is not done under parallel voting.

Mixed-member proportional representation is a mixed electoral system which combines local majoritarian elections with a compensatory tier of party list votes, which are used to allocate additional members in a way that aims to produce proportional representation overall. In most MMP systems, voters get two votes: one to decide the representative for their single-seat constituency, and one for a political party. Some countries use single vote variants of MMP, although this article focuses primarily on dual vote versions of MMP.
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is an apportionment method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in proportional representation among political parties. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. The D'Hondt method reduces compared to ideal proportional representation somewhat the political fragmentation for smaller electoral district sizes, where it favors larger political parties over small parties.
Parallel voting is a type of mixed electoral system in which representatives are voted into a single chamber using two or more different systems, most often first-past-the-post voting (FPTP) with party-list proportional representation (PR). It is the most common form of mixed member majoritarian representation (MMM), which is why these terms are often used synonymously with each other. In some countries, parallel voting is known as the supplementary member (SM) system, while in academic literature it is sometimes called the superposition method within mixed systems.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 members, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 9 April 2006, with a second round of voting in 110 of the 176 single-member constituencies on 23 April. The Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP) emerged as the largest party in the National Assembly with 186 of the 386 seats, and continued the coalition government with the Alliance of Free Democrats (SZDSZ). It marked the first time a government had been re-elected since the end of Communist rule. To date, this is the most recent national election in Hungary not won by Fidesz-KDNP, and the last in which the victorious party did not win a two-thirds supermajority in parliament.
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 23 November. The opposition has vowed to boycott the election unless the president steps down beforehand. A total of 1,096 candidates have registered to compete for the leadership of 218 local councils across Mauritania, whilst 438 candidates are contesting for the 146 parliamentary seats. Some 1.2 million Mauritanians were eligible to vote in the election. The first round results yielded a landslide victory for the ruling UPR winning 56 seats and their 14 coalition partners winning 34 seats. The Islamist Tewassoul party won 12 seats. The remaining seats were contested in a runoff on 21 December 2013. The UPR won the majority with 75 seats in the Assembly.

General elections were held in Uruguay on 26 October 2014, alongside a constitutional referendum. As no presidential candidate received an absolute majority in the first round of voting, a runoff took place on 30 November. Primary elections to determine each party's presidential candidate had been held on 1 June.
Scorporo is a partially compensatory, mixed-member majoritarian electoral system, sometimes referred to as a negative vote transfer system (NVT) whereby a portion of members are elected in single-member districts (SMDs) and a portion are elected from a list. It may be fully defined as a parallel voting system which excludes a portion of the SMD winners' votes in electing the proportional tier, to result in a more proportional outcome. The exclusion of a portion of the SMD winners' votes is what makes scorporo fundamentally different from parallel voting and somewhat closer to mixed member proportional representation, and thereby between the two in terms of proportionality. The system is only known to have been used in Italy and for a portion of the compensatory tier of the National Assembly of Hungary.

The Italian electoral law of 2017, colloquially known by the nickname Rosatellum bis or simply Rosatellum after Ettore Rosato, the Democratic Party (PD) leader in the Chamber of Deputies who first proposed the new law, is a parallel voting system, which acts as a mixed electoral system, with 37% of seats allocated using a first-past-the-post electoral system and 63% using a proportional method, with one round of voting. The Chamber and Senate of the Republic did not differ in the way they allocated the proportional seats, both using the largest remainder method of allocating seats.
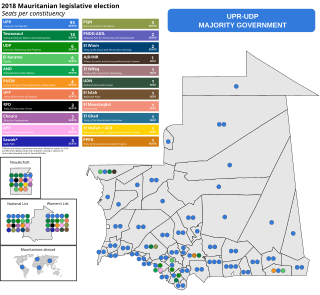
Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.
Apportionment in the Hellenic Parliament refers to those provisions of the Greek electoral law relating to the distribution of Greece's 300 parliamentary seats to the parliamentary constituencies, as well as to the method of seat allocation in Greek legislative elections for the various political parties. The electoral law was codified for the first time through a 2012 Presidential Decree. Articles 1, 2, and 3 deal with how the parliamentary seats are allocated to the various constituencies, while articles 99 and 100 legislate the method of parliamentary apportionment for political parties in an election. In both cases, Greece uses the largest remainder method.
Mixed member majoritarian representation (MMM) is type of a mixed electoral system combining majoritarian and proportional methods, where the disproportional results of the majoritarian side of the system prevail over the proportional component. Mixed member majoritarian systems are therefore also as a type of semi-proportional representation, and are usually contrasted with mixed-member proportional representation (MMP) which aims to provide proportional representation via additional compensation ("top-up") seats.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 13 and 27 May 2023, alongside regional and local elections.

Mauritania is divided into several electoral districts for the election of deputies to the National Assembly, based on the departments of the country, with the exception of the capital city of Nouakchott, where the electoral districts are based on the three regions the city is divided in.
This is the results breakdown of the parliamentary elections held in Mauritania on 13 and 27 May 2023. The following tables will show detailed results in all of the electoral districts of the country.