
U2 is a line of the Berlin U-Bahn. The U2 line starts at Pankow S-Bahn station, runs through the eastern city centre (Alexanderplatz) to Potsdamer Platz, the western city centre and finally to the Ruhleben terminal station.

U5 is a line on the Berlin U-Bahn. It runs from Hauptbahnhof in Mitte eastwards through Alexanderplatz, Friedrichshain, Lichtenberg and Friedrichsfelde, surfaces in Biesdorf-Süd to pass Kaulsdorf and Hellersdorf above ground and finally reaches city limits at Hönow.

The Vienna U-Bahn, where U-Bahn is an abbreviation of the German word Untergrundbahn, is a rapid transit system serving Vienna, Austria. The five-line network consists of 83.1 kilometers (51.6 mi) of route, serving 109 stations. 459.8 million passengers rode the U-Bahn in 2019.
The Munich U-Bahn is an electric rail rapid transit network in Munich, Germany. The system began operation in 1971, and is operated by the municipally owned Münchner Verkehrsgesellschaft. The network is integrated into the Münchner Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund and interconnected with the Munich S-Bahn. The U-Bahn currently comprises eight lines, serving 96 stations, and encompassing 103.1 kilometres (64.1 mi) of routes.

The Hamburg U-Bahn is a rapid transit system serving the cities of Hamburg, Norderstedt, and Ahrensburg in Germany. Although referred to by the term U-Bahn, most of the system's track length is above ground. The network is interconnected with the city's S-Bahn system, which also has underground sections. It is operated by Hamburger Hochbahn within the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV). It was opened in February 1912, and comprises four lines serving 93 stations, with a route length of 106.4 kilometres (66.1 mi) in 2019.

The Nuremberg U-Bahn is a rapid transit system run by Verkehrs-Aktiengesellschaft Nürnberg, which itself is a member of the Verkehrsverbund Großraum Nürnberg. The Nuremberg U-Bahn is Germany's newest metro system, having begun operation in 1972, although the Nuremberg-Fürth route (U1) uses part of the right of way of the Bavarian Ludwig Railway, Germany's first passenger railway opened in 1835. The current network of the U-Bahn is composed of three lines, serving 49 stations, and comprising 38.2 kilometres (23.7 mi) of operational route, making it the shortest of the four metro systems in Germany, behind Berlin, Hamburg and Munich.

Niendorf Nord is the western terminus station for the rapid transit trains of Hamburg U-Bahn line U2. The station is located in the Niendorf quarter of Hamburg, Germany.

The U1 is an underground line in Nuremberg. The first part of the line was opened on 1 March 1972. It is about 18.5 kilometres (11.5 mi) long and has 27 stations. The termini are Langwasser Süd in the southeast and Fürth Hardhöhe in the northwest. Until 11 December 2016 it shared tracks with the former booster line U11 between Eberhardshof and Messe. Those services are still run but no longer designated U11, instead being signed U1 like trains doing the full Langwasser-Hardhöhe run. Unlike U2 and U3 all trains are operated by a driver and there are no plans to automate U1.

The U2 is an underground line in Nuremberg, opened on 28 January 1984 and the last station along the line to open was Flughafen (Airport) in 1999. The line is about 13.1 kilometres (8.1 mi) long and has 16 stations; the termini are Röthenbach and Flughafen. Since 2010 all trains in regular operations are run driverless. At 2,388 metres (7,835 ft) the stretch between Ziegelstein station and Flughafen station is the longest interval between two stations in the network and the only single track section on any subway line in Germany.
The Hamburg-Altona link line is a railway line in Hamburg, Germany. Nowadays, it connects the lines from the north and northwest of Hamburg and Altona station with Hamburg Hauptbahnhof and the lines to the southwest, south and east. Initially designed as a freight line only, it is now one of the busiest lines in Germany. It includes the suburban tracks of the Hamburg Stadtbahn, originally the core of the Hamburg S-Bahn.
The City S-Bahn is a 5,380 metre-long tunnel section of the Hamburg S-Bahn. It runs between Altona station and Hamburg Hauptbahnhof through the city centre of Hamburg and the districts of Altona and St. Pauli. The S-Bahn lines S1 and S3 of the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund run through the tunnel. Seven S-Bahn stations are located in the tunnel, including the tourist-oriented stations of Landungsbrücken and Reeperbahn.

The A line is the north-to-south main line of the Frankfurt U-Bahn. It is the oldest and longest line of the U-Bahn system. Served by four routes starting at Südbahnhof Railway Station in Sachsenhausen, the A line runs through downtown Frankfurt up to Heddernheim Station in the north of the city, where it branches out to Ginnheim, Oberursel (U3), Riedberg and Bad Homburg (U2). The U9 service between Ginnheim, Riedberg and Nieder-Eschbach does not use the central section and tunnels of the line, making it the only light rail service of the network that does not serve downtown Frankfurt. The Riedberg and Ginnheim branches were planned as parts of the future D line subway but are operationally part of the A line until the D line development and construction is finished.

The Berlin U-Bahn originated in 1880 with Werner Siemens' idea to build an urban railway in Berlin. During the nine years after the German Empire was founded, the city's population grew by over one-third and traffic problems increased. In 1896, Siemens & Halske began to construct the first stretch of overhead railway. On 1 April 1897, the company began construction of an electric underground railway. The Berliner Verkehrs Aktiengesellschaft (BVG) was formed in 1928, and took over further construction and operation of the network. In 1938, the company was renamed Berlin Transport Company; the original acronym, however, remained. Since 1994, the BVG has been a public company.

The U4 is a line of the Hamburg U-Bahn, which opened in 2012, serving 12 stations. It is the shortest line of the network, with a length of 11.9 kilometres (7.39 mi) and from Jungfernstieg to Billstedt it shares tracks with the U2. Its identifying colour, as seen on route maps, trains, and station signs is turquoise.

Langenhorn Markt is a station on the Hamburg U-Bahn line U1. It was opened in July 1921 and is located in Hamburg, Germany, in the quarter of Langenhorn. Langenhorn is part of the borough of Hamburg-Nord.
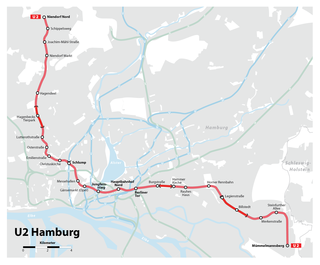
The U2 is a line of the Hamburg U-Bahn which has a length of 24.543 kilometres (15.25 mi). It serves 25 stations. The line opened in 1913. It starts in Niendorf Nord and leads via the city center at Hauptbahnhof Nord to Mümmelmannsberg.

Hagenbecks Tierpark is a metro station on the Hamburg U-Bahn line U2. It is located in the Stellingen district of Hamburg within the borough of Eimsbüttel. It serves the Tierpark Hagenbeck.

Hagendeel is a metro station on the Hamburg U-Bahn line U2.

Joachim-Mähl-Straße is a metro station in Niendorf, Hamburg on the Hamburg U-Bahn line U2.

Schippelsweg is a metro station in Niendorf, Hamburg, on the Hamburg U-Bahn line U2.


















