Iran had a comprehensive and effective program of family planning since the beginning of the 1990s. While Iran's population grew at a rate of more than 3% per year between 1956 and 1986, the growth rate began to decline in the late 1980s and early 1990s after the government initiated a major population control program. By 2007 the growth rate had declined to 0.7 percent per year, with a birth rate of 17 per 1,000 persons and a death rate of 6 per 1,000. Reports by the UN show birth control policies in Iran to be effective with the country topping the list of greatest fertility decreases. UN's Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs says that between 1975 and 1980, the total fertility number was 6.5. The projected level for Iran's 2005 to 2010 birth rate is fewer than two.

The first AIDS case identified in Brazil was in 1982. Infection rates climbed exponentially throughout the 1980s, and in 1990 the World Bank famously predicted 1,200,000 cases by 2000, approximately double the actual number that was later reported by the Brazilian Ministry of Health and most international organizations. South and Southeast have 75% or more of this infection. The Northeast has 33% of the population but only 10% of AIDS.
The economy of Thiruvananthapuram, capital of the Indian state of Kerala, mostly consists of tourism and leisure, information technology, rubber plantations, coffee production, tea production, and education. There are many manufacturers, such as Travancore Titanium Products Ltd and English Indian Clays.

A female condom is a barrier device that is used during sexual intercourse as a barrier contraceptive to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Meant as an alternative to the condom for males, it was invented by Danish MD Lasse Hessel and designed to be worn internally by the female partner during vaginal sex to prevent exposure to ejaculated semen or other body fluids. His invention was launched in Europe in 1990 and approved by the FDA for sale in the USA in 1993. Its protection against STIs is inferior to that of male condoms. Internal condoms can be used by the receptive partner during anal sex.

HLL Lifecare Limited (HLL) is an Indian healthcare product manufacturing company based in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. A Government of India-owned corporation.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is an Indian government ministry charged with health policy in India. It is also responsible for all government programs relating to family planning in India.
Life Guard DC is a Washington, DC, condom distribution program and part of The Condom Project, a Tides Center project that is driven by the involvement of peer-to-peer social networks, local businesses, and community-based organization outreach services to destigmatize condoms and to increase their use. The program distributes free condoms at local establishments in historically overlooked communities, 24 hours a day.

Adam & Eve is an American conglomerate company that sells adult products through e-commerce. The company is the largest e-commerce distributor of condoms, sex toys, and erotica in the United States.Its parent company, PHE Inc., is the largest private employer in Hillsborough, North Carolina, where its headquarters are situated.The company funds non-profit social marketing organizations that address issues such as population growth, disease control and sex education in developing countries.
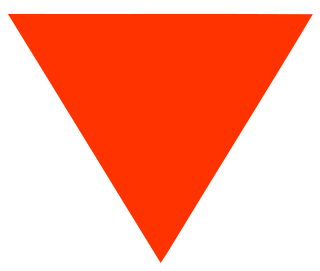
An inverted Red Triangle is the symbol for family planning health and contraception services, much as the red cross is a symbol for medical services. It is especially prevalent in many developing nations such as India, Ghana, Gambia, Zimbabwe, Egypt and Thailand, where it can be seen outside shops and clinics that offer family planning products, and as in commercial and government messages that promote reproductive health services and population control. It is frequently placed on contraceptive products, such as condoms, diaphragms, spermicidal gel, and IUDs.
The history of condoms goes back at least several centuries, and perhaps beyond. For most of their history, condoms have been used both as a method of birth control, and as a protective measure against venereal diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, hepatitis B and more recently HIV/AIDS. Condoms have been made from a variety of materials; prior to the 19th century, chemically treated linen and animal tissue are the best documented varieties. Rubber condoms gained popularity in the mid-19th century, and in the early 20th century major advances were made in manufacturing techniques. Prior to the introduction of the combined oral contraceptive pill, condoms were the most popular birth control method in the Western world. In the second half of the 20th century, the low cost of condoms contributed to their importance in family planning programs throughout the developing world. Condoms have also become increasingly important in efforts to fight the AIDS pandemic. The oldest condoms ever excavated were found in a cesspit located in the grounds of Dudley Castle and were made from animal membrane. The condoms dated back to as early as 1642.

The Gold (Control) Act, 1968 is a repealed Act of the Parliament of India which was enacted to control sale and holding of gold in personal possession. High demand for gold in India with negligible indigenous production results in gold imports, leading to drastic devaluation of the Indian rupee and depletion of foreign exchange reserves to alarming levels. Devaluation of the Indian rupee also leads to steep rises in food commodity prices due to costlier petroleum products imports. In these circumstances, the gold import policy of India aimed at curbing the gold imports to a manageable level time to time by imposing taxes and legal restrictions.

The Indian food security system was established by the Government of India under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution to distribute food and non-food items to India's poor at subsidised rates. Major commodities distributed include staple food grains, such as wheat, rice, sugar and essential fuels like kerosene, through a network of fair price shops established in several states across the country. Food Corporation of India, a government-owned corporation, procures and maintains the public distribution system (PDS).

Avahan is an initiative sponsored by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to reduce the spread of HIV in India. It began in 2003. As of 2009 the Gates Foundation had pledged US$338 million to the programme. The programme aims to reduce HIV transmission and the prevalence of STIs in vulnerable high-risk populations, notably female sex workers, MSM, and transgender people, through prevention education and services such as condom promotion, STI management, behaviour change communication, community mobilisation, and advocacy. Avahan works in six states, whilst India HIV/AIDS Alliance is the state lead partner in Andhra Pradesh. By 2013, control of the program transitioned to the Government of India.
LifeSpring Hospitals is an Indian hospital chain, which provides maternity care to women from the low-income group in Hyderabad, India. Established in 2005, it is a 50-50 joint venture between $30-million Acumen Fund, a U.S.-based nonprofit global venture philanthropy fund and HLL Lifecare Limited, a Government of India -owned corporation and the largest manufacturer of condoms in the world.

Social Marketing Company is a Bangladeshi non-profit organisation which offers education and products for family planning, maternal and child health, and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) and AIDS.

Moods Condoms is a manufacturer of condoms made from natural rubber latex. It is manufactured HLL Lifecare Limited, a Government of India undertaking. HLL was started off in 1966 with the objective of producing condoms for the National Family Planning Program. Moods Condoms came into existence in mid-1968, when HLL Lifecare Limited decided to develop a product to target the premium and upper middle class segment of the urban population in India. HLL today is one of the world's largest manufacturers of condoms. As of December 2012, its annual production totals around 800 million pieces across the globe.
The Society for Family Health (SFH) Nigeria is a non governmental organisation (NGO), founded in 1983 and incorporated in 1985.
Dipper is an Indian condom brand marketed by Tata Motors and Rediffusion Y&R to promote safe sex among truck drivers in India. Manufactured by HLL Lifecare, it is part of an award-winning AIDS awareness campaign that was initiated by Tata. The name, "Dipper", was inspired by the iconic message, "Use Dipper at Night" - that are painted at the back of inter- as well as intrastate trucks in India.
S. Krishna Kumar is a bureaucrat turned Indian politician from Kerala. He was also a technologist, technocrat, trade unionist, political and social worker, sportsman, Engineer and Civil Servant. He was a former leader of Indian National Congress in Kerala and joined Bharatiya Janata Party on 20 April 2019. He has been elected to the Lok Sabha three times during 80s and 90s, and was also a minister in the Rajiv Gandhi ministry and Rao ministry. He served as a member of the Lok Sabha representing Quilon. He was elected to 8th, 9th and 10th Lok Sabha.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana is a food security welfare scheme announced by the Government of India in March 26 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic in India. PM Modi Cabinet Anurag Thakur Extends PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana Till March 2022. The program is operated by the Department of Food and Public Distribution under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.









