Related Research Articles

The Cree are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations.

The Slavey are a First Nations indigenous peoples of the Dene group, indigenous to the Great Slave Lake region, in Canada's Northwest Territories, and extending into northeastern British Columbia and northwestern Alberta.

The Chipewyan are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified with the Taltheilei Shale archaeological tradition. They are part of the Northern Athabascan group of peoples, and come from what is now Western Canada.
The Muskotew Sakahikan Enowuk or Lubicon Lake Nation is a Cree First Nation in northern Alberta, Canada. They are commonly referred to as the Lubicon Lake Nation, Lubicon Cree, or the Lubicon Lake Cree. This should not be confused with the Lubicon Lake Band #453, which is a separate entity created by the Government of Canada by Order in Council in 1973.

The Dane-zaa are an Athabaskan-speaking group of First Nations people. Their traditional territory is around the Peace River in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. Today, about 1,600 Dane-zaa reside in British Columbia and an estimated half of them speak the Dane-zaa language. Approximately 2,000 Dane-zaa live in Alberta.
A tribal council is an association of First Nations bands in Canada, generally along regional, ethnic or linguistic lines.
First Nations in Alberta are a group of people who live in the Canadian province of Alberta. The First Nations are peoples recognized as Indigenous peoples or Plains Indians in Canada excluding the Inuit and the Métis. According to the 2011 Census, a population of 116,670 Albertans self-identified as First Nations. Specifically there were 96,730 First Nations people with registered Indian Status and 19,945 First Nations people without registered Indian Status. Alberta has the third largest First Nations population among the provinces and territories. From this total population, 47.3% of the population lives on an Indian reserve and the other 52.7% live in urban centres. According to the 2011 Census, the First Nations population in Edmonton totalled at 31,780, which is the second highest for any city in Canada. The First Nations population in Calgary, in reference to the 2011 Census, totalled at 17,040. There are 48 First Nations or "bands" in Alberta, belonging to nine different ethnic groups or "tribes" based on their ancestral languages.
First Nations in Manitoba constitute of over 160,000 registered persons as of 2021, about 57% of whom live on reserve. Manitoba is second to Ontario in total on-reserve population and in total First Nation population.
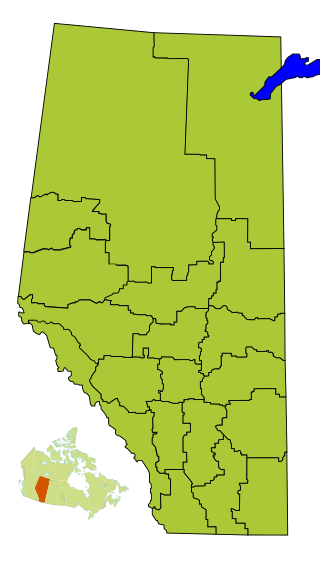
Division No. 17 is a census division in Alberta, Canada. It spans the central and northwest portions of northern Alberta and its largest urban community is the Town of Slave Lake. Division No. 17 is the largest census division in Alberta according to area and also has the lowest population density.

The Dene TháFirst Nation is a First Nations government of the South Slavey in Northern Alberta, Canada. The people call themselves Dene Dháa or 'Ordinary People' in the Dene Dháh language. Its population is centered primarily in three communities: Bushe River, Meander River, and Chateh, but approximately 600 members who live off-reserve. Dene Thá First Nation is Treaty 8 nation and a member of the North Peace Tribal Council.
The Sakāwithiniwak or Woodland Cree, are a Cree people, calling themselves Nîhithaw in their own dialect of the language. They are the largest indigenous group in northern Alberta and are an Algonquian people. Prior to the 18th century, their territory extended west of Hudson Bay, as far north as Churchill. Although in western Northern Saskatchewan and Manitoba, by the 18th century, they acted as middlemen in trade with western tribes. After acquiring guns through trade, they greatly expanded their territory and drove other tribes further west and north.

The Fort McKay First Nation (FMFN) is a First Nations government in northeast Alberta comprising five Indian reserves – Fort McKay 174, Fort McKay 174C, Fort McKay 174D, Namur Lake 174B and Namur River 174A. The FMFN, signed to Treaty 8, is affiliated with the Athabasca Tribal Council and its members are of Cree, Metis and Dene heritage. The FMFN's traditional lands include portions of the Athabasca oil sands.
The Meadow Lake Tribal Council (MLTC) is a tribal council representing nine First Nation band governments in the province of Saskatchewan. The council is based in Meadow Lake, Saskatchewan.

Barren Lands First Nation is a First Nation located on the north shore of Reindeer Lake in northern Manitoba close to the Saskatchewan border. It has one reserve land called Brochet 197, which is 4,339.40 ha in size and adjoins the village of Brochet, Manitoba.

The English River Dene Nation is a Dene First Nation band government in Patuanak, Saskatchewan, Canada. Their reserve is in the northern section of the province. Its territories are in the boreal forest of the Canadian Shield. This First Nation is a member of the Meadow Lake Tribal Council (MLTC).
The Prince Albert Grand Council (PAGC) is a Tribal Council representing the band governments of twelve First Nations in the province of Saskatchewan. Its head offices are located in the city of Prince Albert. The Tribal Council was created in 1977 and is one of the largest in Canada.
Big Island Lake Cree Nation is a Cree First Nation in Saskatchewan, Canada. They have reserved for themselves one reserve, also called Big Island Lake Cree Nation, within Rural Municipality of Beaver River No. 622.
The Lubicon Lake Band is a Cree First Nations band government in northern Alberta, Canada. Missed by government agents during the signing of Treaty 8 in 1899, the Lubicon community was long without federal support. Seeking to have their traditional title acknowledged through the creation of an Indian reserve, Lubicon representatives have maintained an active land claim since 1933. As oil and gas development changed the face of Alberta, development on Lubicon land became an increasingly pressing issue. Between 1979 and 1982, over 400 oil and gas wells were drilled around the community of Little Buffalo, the band's headquarters. Most prominently, the nation mounted a protest campaign during the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, blockading roads crossing its traditional territory in October of the same year.
Kee Tas Kee Now Tribal Council is a Tribal Council representing First Nation communities in north-central Alberta, Canada. The council is based in Atikameg, Alberta.
References
- ↑ "Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada,". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada . Government of Canada. Retrieved 2018-10-25.