In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. The main two categories are derivational and inflectional affixes. The first ones, such as -un, -ation, anti-, pre- etc, introduce a semantic change to the word they are attached to. The latter ones introduce a syntactic change, such as singular into plural, or present simple tense into present continuous or past tense by adding -ing, -ed to an English word. All of them are bound morphemes by definition; prefixes and suffixes may be separable affixes.
Metathesis is the transposition of sounds or syllables in a word or of words in a sentence. Most commonly, it refers to the interchange of two or more contiguous segments or syllables, known as adjacent metathesis or local metathesis:

The Salishan languages are a family of languages of the Pacific Northwest in North America. They are characterised by agglutinativity and syllabic consonants. For instance the Nuxalk word clhp’xwlhtlhplhhskwts’, meaning "he had had [in his possession] a bunchberry plant", has twelve obstruent consonants in a row with no phonetic or phonemic vowels.
Lushootseed, formerly known as Puget Salish, Puget Sound Salish, or Skagit-Nisqually, is a Central Coast Salish language of the Salishan language family. Lushootseed is the general name for the dialect continuum composed of two main dialects, Northern Lushootseed and Southern Lushootseed, which are further separated into smaller sub-dialects.
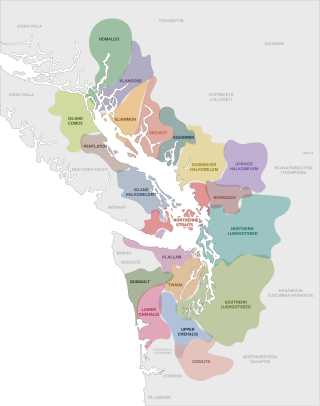
The Coast Salish languages, also known as the Central Salish languages, are a branch of the Salishan language family. These languages are spoken by First Nations or Native American peoples inhabiting the Pacific Northwest, in the territory that is now known as the southwest coast of British Columbia around the Strait of Georgia and Washington State around Puget Sound. The term "Coast Salish" also refers to the cultures in British Columbia and Washington who speak one of these languages or dialects.

The Saanich or W̱sáneć are indigenous nations from the north coast of the Gulf and San Juan Islands, southern Vancouver Island and the southern edge of the Lower Mainland in British Columbia.

Klallam,Clallam, Ns'Klallam or S'klallam, is a Straits Salishan language that was traditionally spoken by the Klallam peoples at Becher Bay on Vancouver Island in British Columbia and across the Strait of Juan de Fuca on the north coast of the Olympic Peninsula in Washington. The last speaker of Klallam as a first language died in 2014, but there is a growing group of speakers of Klallam as a second language.
Brent Douglas Galloway was an American linguist noted for his work with endangered Amerindian languages, specializing in several of the Pacific Northwest and British Columbia. He completed his degrees through a doctorate in linguistics in 1977 at the University of California, Berkeley, undertaking extensive fieldwork in that period.
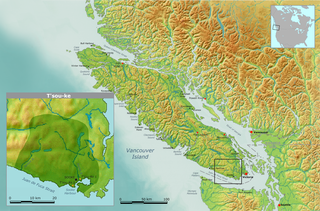
The T'sou-ke Nation of the Coast Salish peoples, is a band government whose reserve community is located on Vancouver Island, in the province of British Columbia, Canada. In February 2013, the T'sou-ke Nation had 251 registered members, with two reserves around the Sooke Basin on the Strait of Juan de Fuca at the southern end of Vancouver Island, with a total area of 67 hectares. The T'Souk-e people are the namesake of the town of Sooke, British Columbia and its surrounding harbour and basin.

Saanich is the language of the First Nations Saanich people in the Pacific Northwest region of northwestern North America. Saanich is a Coast Salishan language in the Northern Straits dialect continuum, the varieties of which are closely related to the Klallam language.
The Samish are a Native American people who live in the U.S. state of Washington. They are a Central Coast Salish people. Through the years, they were assigned to reservations dominated by other Tribes, for instance, the Swinomish Indians of the Swinomish Reservation of Washington and the Tulalip Tribes of the Tulalip Reservation. They are also enrolled in the Samish Indian Nation, formerly known as the Samish Indian Tribe, which regained federal recognition in 1996.
Lummi is a dialect of the North Straits Salish language traditionally spoken by the Lummi people of northwest Washington, in the United States. Although traditionally referred to as a language, it is mutually intelligible with the other dialects of North Straits.
Malahat First Nation is a Coast Salish First Nations community of W̱SÁNEĆ representing approximately 350 members with two reserve lands located on the western shore of Saanich Inlet, Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. The Malahat First Nation is one of many nations within the Coastal Salish group that live on their traditional lands. The Coastal Salish are Indigenous to the Northwest mainland, coast, and islands. The Malahat First Nation is a member nation of the Naut'sa mawt Tribal Council and was the ninth First Nation in Canada to be certified by the First Nations Financial Management Board. The ancestral languages of Malahat Nation are Hul̓q̓umín̓um̓ and SENĆOŦEN. The Hul̓q̓umín̓um̓ or Halkomelem language is spoken in Washington State and British Columbia and is within the Coastal Salish language family. Currently it is being revitalized, as it is mainly spoken by elders in the community. The Chief of Malahat Nation is George Harry. George served on the council for four years before being elected as Chief on June 10, 2019.

The Lekwungen or Lekungen nation are an Indigenous North American Coast Salish people who reside on southeastern Vancouver Island, British Columbia in the Greater Victoria area. Their government is the Songhees First Nation, a member of the Te'mexw Treaty Association and the Naut'sa Mawt Tribal Council. Their traditional language is Lekwungen, a dialect of the North Straits Salish language.
The Pauaquachin are a Coast Salish indigenous people whose territory is in the Greater Victoria area of southern Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. Their houses stand between Gordon Head and Cowichan Head. They are one of the five groups of houses or 'families' of Saanich, along with the Tsawout, the Tseycum, the Malahat, the T'sou-ke, and the Tsartlip First Nations. According to a 2016 census, 330 people were recognized as Pauquachin.

The Salish peoples are indigenous peoples of the American and Canadian Pacific Northwest, identified by their use of the Salish languages which diversified out of Proto-Salish between 3,000 and 6,000 years ago.

The Samish Indian Nation is a Coast Salish nation and a signatory to the Treaty of Point Elliott of 1855. Samish has a government-to-government relationship with the United States of America. The Samish are a Northern Straits branch of Central Coast Salish peoples. The Samish Nation is headquartered in Anacortes, Fidalgo Island, in Washington, north of Puget Sound.

The Mitchell Bay Band of the San Juan Islands is an indigenous Coast Salish community based in the San Juan Islands of Washington, United States. The community was first referred to as the Mitchell Bay Tribe by Office of Indian Affairs agent Charles Roblin in his 1919 Census of Unenrolled Indians, in reference to one of several bays with historically significant indigenous populations.
Gumuz is a dialect cluster spoken along the border of Ethiopia and Sudan. It has been tentatively classified within the Nilo-Saharan family. Most Ethiopian speakers live in Kamashi Zone and Metekel Zone of the Benishangul-Gumuz Region, although a group of 1,000 reportedly live outside the town of Welkite. The Sudanese speakers live in the area east of Er Roseires, around Famaka and Fazoglo on the Blue Nile, extending north along the border. Dimmendaal et al. (2019) suspect that the poorly attested varieties spoken along the river constitute a distinct language, Kadallu.
Samish is a dialect of the North Straits Salish dialect continuum spoken by the Indigenous Samish people of the Pacific Northwest. Samish is traditionally referred to as a language, but it is mutually intelligible with the other dialects of North Straits Salish. Samish is a Coast Salish language and is closely related to other languages in that family.











