DM Geminorum also known as Nova Geminorum 1903 was a nova which erupted in the constellation Gemini in 1903. It was discovered by Herbert Hall Turner at the Greenwich Observatory on a Carte du Ciel photographic plate taken on 16 March 1903. Post-discovery examination of earlier photographs of the region taken at the Harvard College Observatory showed that the star was fainter than apparent magnitude 9 on 2 March 1903, and magnitude 5.1 on 6 March 1903, making it visible to the naked eye at that time. It had a conspicuous red color due to strong Hα line emission. By 1 April 1903 it had faded to magnitude 8.5. By 1989 it had reached visual magnitude 17.38.
DI Lacertae or Nova Lacertae 1910 was a nova in constellation Lacerta which appeared in 1910. It was discovered by Thomas Henry Espinell Compton Espin at Wolsingham Observatory on 30 Dec 1910, at which time it was an 8th magnitude object. Subsequent examination of pre-discovery photographic plates showed that the outburst occurred sometime between 17 November 1910 and 23 November 1910. It reached a peak brightness of magnitude 4.6 on 26 November 1910, making it visible to the naked eye. Before the nova event DI Lacertae was a 14th magnitude star, and by 1950 it had returned to 14th magnitude.

V604 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1905 is a nova which was first observed in the constellation Aquila in 1905 with a maximum brightness of magnitude 7.6. It was never bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. It was discovered by Williamina Fleming on a Harvard College Observatory photographic plate taken on August 31, 1905. Examination of plates taken earlier indicates that peak brightness occurred in mid-August 1905. The star's quiescent visual band brightness is 19.6.

V373 Scuti was a nova which appeared in 1975 in the southern constellation of Scutum. It was announced on June 15, 1975 by Paul Wild at the Zimmerwald Observatory, Switzerland. At the time the magnitude was about 7.9. The peak magnitude of 7.1 occurred a month earlier on May 11.

NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a nova that appeared in the constellation Vulpecula in 1976. It was discovered visually at 18:20 UT on October 21, 1976 by English amateur astronomer George Alcock. Its apparent magnitude at the time of discovery was 6.5 It reached its maximum brightness of magnitude 6.0 thirteen days after its discovery, at which point it may have been faintly visible to the naked eye. A few days after maximum brightness, it had faded to magnitude 8.3.

DK Lacertae was a nova, which lit up in the constellation Lacerta in 1950. The nova was discovered by Charles Bertaud of the Paris Observatory on a photographic plate taken on 23 January 1950. At the time of its discovery, it had an apparent magnitude of 6.1. DK Lacertae reached peak magnitude 5.0, making it easily visible to the naked eye.

V1059 Sagittarii was a nova, which lit up in 1898 in the constellation Sagittarius. The star reached apparent magnitude 4.5, making it easily visible to the naked eye. It was discovered on 8 March 1898, by Williamina Fleming on a photographic plate taken at the Harvard College Observatory. The discovery plate was an objective prism plate, part of the Henry Draper Memorial Photographs, and Ms Fleming identified it as a nova based on its spectral characteristics.

V606 Aquilae was a nova, which lit up in the constellation Aquila in 1899. The brightest reported magnitude for this nova was apparent magnitude 5.5, making it a naked eye object. It was discovered by Williamina Fleming on a photographic plate taken on 21 April 1899 at the Harvard College Observatory. On the discovery plate, its photographic magnitude was later determined to be 6.75. It was not seen on the plate taken on 1 November 1898, and there were no reported observations of the region around the star during the 171 day interval before Fleming's discovery, so it is possible that the actual maximum of the event was missed. By 27 October 1899 it had faded to 10th magnitude, and on 9 July 1900 Oliver Wendell reported its brightness to be between magnitude 11.5 and 12.0.
CT Serpentis was a nova that appeared in the constellation Serpens in 1948. It was discovered by Ramze Alexander Bartaya at Abastumani Observatory on 9 April 1946. It is thought to have reached magnitude 6.0, but this is an extrapolation of its light curve as it was not observed until 9 April 1948 when it was at magnitude 9.0 and fading—clearly past its maximum.

XX Tauri was a nova, which appeared in the constellation Taurus in 1927. It was discovered by Arnold Schwassmann and Arno Arthur Wachmann at Hamburg Observatory on an objective prism photographic plate taken on 18 November 1927. Subsequent examination of pre-discovery photographic plates taken at the Harvard College Observatory showed that the peak brightness, magnitude 5.9, occurred on 1 October 1927, at which point it may have been faintly visible to the naked eye. By 1988 it had faded below magnitude 19.8.

CK Vulpeculae is an object whose exact nature is unknown. It was once considered to be the oldest reliably-documented nova. It consists of a compact central object surrounded by a bipolar nebula.
Q Cygni, is a star located in the constellation Cygnus. It is also known as Nova Cygni 1876, and has the designation NGC 7114, and HR 8296. Nova Cygni is located in the northwestern portion of Cygnus along the border with Lacerta.

V630 Sagittarii was a nova visible to the naked eye in 1936. It was discovered on 3 October 1936 by Shigeki Okabayashi of Kobe, Japan when it had an apparent magnitude of 4.5.

QZ Aurigae, also known as Nova Aurigae 1964, was a nova which occurred in the constellation Auriga during 1964. It was discovered by Nicholas Sanduleak on an objective prism photographic plate taken at the Warner and Swasey Observatory on 4 November 1964. Examination of pre-discovery plates from Sonneberg Observatory showed that the eruption occurred in early February 1964, and it had a photographic magnitude of 6.0 on 14 February 1964. Its brightness declined in images taken after the 14th, suggesting that its peak brightness was above 6.0. It was probably visible to the naked eye for a short time.
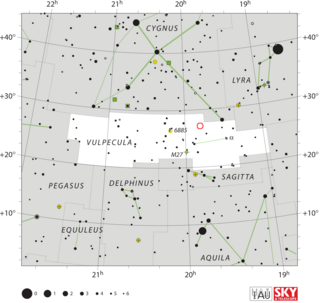
LV Vulpeculae, also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1968 no. 1, was the first of two novae in the constellation of Vulpecula which erupted in 1968. It was discovered by George Alcock who observed it from the back garden of his home in Farcet, England, on the morning of 15 April 1968. The next night it was independently discovered by Midtskoven in Norway. It reached a peak apparent magnitude of 4.79 on 17 April 1968. It was visible to the naked eye at the same time HR Delphini was a naked eye object, and the two novae were less than 15 degrees apart on the sky.

GI Monocerotis, also known as Nova Monocerotis 1918, was a nova that erupted in the constellation Monoceros during 1918. It was discovered by Max Wolf on a photographic plate taken at the Heidelberg Observatory on 4 February 1918. At the time of its discovery, it had a photographic magnitude of 8.5, and had already passed its peak brightness. A search of plates taken at the Harvard College Observatory showed that it had a photographic magnitude of 5.4 on 1 January 1918, so it would have been visible to the naked eye around that time. By March 1918 it had dropped to ninth or tenth magnitude. By November 1920 it was a little fainter than 15th magnitude.

WY Sagittae, also known as Nova Sagittae 1783, is a star in the constellation Sagitta which had a nova eruption visible in 1783. It was discovered on 26 July 1783 by the French astronomer Joseph Lepaute D'Agelet. It is usually difficult to precisely identify novae that were discovered hundreds of years ago, because the positions were often vaguely reported and historically there was not a clear distinction drawn between different sorts of transient astronomical events such as novae and comet apparitions. However D'Agelet observed this nova with a mural quadrant, which produced coordinates accurate enough to allow modern astronomers to identify the star. D'Agelet reported the apparent magnitude of the star as 6, but Benjamin Apthorp Gould, who analysed D'Agelet's records, determined that what D'Agelet called magnitude 6 corresponds to magnitude 5.4 ± 0.4 on the modern magnitude scale, so the nova was visible to the naked eye.

V1370 Aquilae, also known as Nova Aquilae 1982, is a nova that appeared in the constellation Aquila during 1982. It was discovered by Minoru Honda of Kurashiki, Japan at 20:30 UT on 27 January 1982. At that time the Sun had moved just far enough from Aquila to allow the nova to be seen in the morning sky. Although it was discovered photographically, its apparent magnitude was 6–7, making it potentially visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. A possible magnitude 20 progenitor was located on the Palomar Sky Survey prints. Spectra of the object were taken in February 1982 at Asiago Astrophysical Observatory, which confirmed that it is a nova.
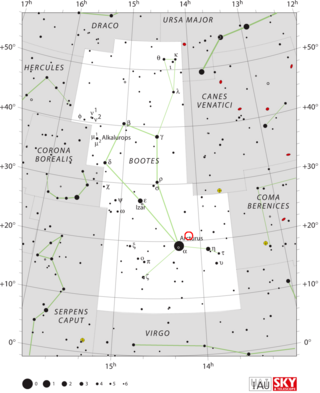
AB Boötis, also known as Nova Boötis 1877 and occasionally Nova Comae Berenices 1877, is an object that may have undergone a nova outburst in 1877. It was discovered by Friedrich Schwab at Technische Universität Ilmenau in 1877. He reported observing the star as a 5th magnitude object, visible to the naked eye, on 14 nights during the period from 30 May 1877 through 14 July 1877. The star was lost, and despite several searches in subsequent years, no other 19th century observations of the nova were reported. Downes et al. estimate that Schwab's reported coordinates for the star may have had a precision no better than 1/2 degree. In 1971, A. Sh. Khatisov suggested that the star Schwab saw was BD +21°2606, but that identification may be incorrect.

OY Arae, also known as Nova Arae 1910, is a nova in the constellation Ara. It was discovered by Williamina Fleming on a Harvard Observatory photographic plate taken on April 4, 1910. At that time it had a magnitude of 6.0, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal observing conditions. Examination of earlier plates showed that before the outburst it was a magnitude 17.5 object, and by March 19, 1910, it had reached magnitude 12.




















