A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions, thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.
A supermajority, supra-majority, qualified majority, or special majority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but they can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises in the times action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. Parliamentary procedure requires that any action of a deliberative assembly that may alter the rights of a minority have a supermajority requirement, such as a two-thirds vote.

In California, a ballot proposition is a referendum or an initiative measure that is submitted to the electorate for a direct decision or direct vote. If passed, it can alter one or more of the articles of the Constitution of California, one or more of the 29 California Codes, or another law in the California Statutes by clarifying current or adding statute(s) or removing current statute(s).
In the politics of the United States, the process of initiatives and referendums allow citizens of many U.S. states to place new legislation, or to place legislation that has recently been passed by a legislature on a ballot for a popular vote. Initiatives and referendums, along with recall elections and popular primary elections, are signature reforms of the Progressive Era; they are written into several state constitutions, particularly in the West. It is a form of direct democracy.

Proposition 1F of 2009 was a measure approved by California voters relating to the salaries of state officers. It was an amendment of the Constitution of California prohibiting pay raises for members of the State Legislature, the Governor, and other state officials during deficit years. It was proposed by the legislature and approved in a referendum held as part of the May 19, 2009 special election ballot, in which the California electorate also voted on five other propositions.

The Moldovan referendum of 2010 was a nationwide referendum in Moldova held on 5 September on whether or not the country should amend the Constitution of Moldova to return to direct popular election of the president. Since 2001, the president had been indirectly elected by Parliament, with a supermajority of 61 seats required for election. The voters are asked to answer the following question "Would you agree with the Constitutional amendment, which would allow the election of the President of the Republic of Moldova by the entire population?", voting for one of the proposed options: “Yes (for)” or “No (against)”. Of those who had cast their vote, 87.83% chose "Yes". However, the referendum did not pass because only 30.29% of voters turned out, short of the necessary 33% for the referendum to be considered valid.
Pensions in Norway fall into three major divisions; State Pensions, Occupational Pensions and Individual or personal Pensions.
Twelve national referendums were held in Switzerland during 2012. On 11 March voters across the country were asked five questions on employment leave, second houses, building society savings, the Fixed Book Price Agreement and gambling revenues. On 17 June there were three questions on healthcare, foreign policy and home buying. On 23 September there were three on a smoking ban, secure housing in old age and music lessons at school. A final referendum was held on 25 November on the Animal Diseases Act.

A constitutional referendum was held in Uruguay on 29 November 1942, alongside general elections. The new constitution was approved by 77.17% of voters.

The Michigan ballot proposals in 2012 included a referendum on a law passed by the Michigan Legislature and five proposed amendments to the Michigan Constitution. All six proposals were defeated.

A constitutional referendum was held in Uruguay on 27 November 1966 alongside general elections. Four proposals for amending the constitution were put to voters, with one option receiving 65% of the vote. As a result, the colegiado system was abolished in favour of returning to the presidential system.
Eleven national referendums were held in Switzerland during 2013. Voters approved six proposals related to spatial planning, executive pay, family policy, amendments to the laws on asylum and epidemics and an increase in the length of petrol station shop opening hours. The other five proposals on directly electing the Federal Council, abolishing compulsory military service, limiting salaries in a company to 12 times the lowest paid worker, tax credits for stay-at-home parents and an increase in road tax were rejected.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.

The sixth Constitution of Uruguay came into force in 1967.

The Illinois Fair Tax was a proposed amendment to the Illinois state constitution that would have effectively changed the state income tax system from a flat tax to a graduated income tax. The proposal, formally titled the "Allow for Graduated Income Tax Amendment", appeared on the ballot in the November 3, 2020 election in Illinois as a legislatively referred constitutional amendment striking language from the Constitution of Illinois requiring a flat state income tax. Concurrent with the proposed constitutional amendment, the Illinois legislature passed legislation setting a new set of graduated income tax rates that would have taken effect had the amendment been approved by voters.
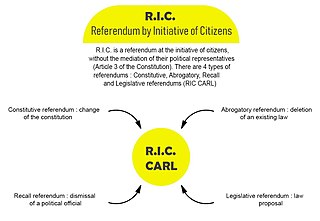
The Référendum d'initiative Citoyenne is the name given to the proposal for a constitutional amendment in France to permit consultation of the citizenry by referendum concerning the proposition or abrogation of laws, the revocation of politicians' mandates, and constitutional amendment.

The 2019 Uruguayan constitutional referendum, officially referred to as the referendum for constitutional reform on security matters, took place alongside general election of that year, on 27 October 2019, to ask the electorate whether a constitutional reform in public security should be approved. The proposed amendments to the Constitution would create a national guard, forbid early release for some serious crimes, introduce life sentences for crimes of rape, sexual abuse or homicide of minors as well as aggravated homicide of adults, and allow the police to conduct night raids. The referendum resulted in 46.8% of the votes cast in favor of amending the Constitution; however, not reaching the necessary 50%, the amendment was not approved, being rejected by 53.7% of the votes.

The Pension reform in Brazil was a proposal by the Brazilian government to amend the Constitution for the reform of the social security system of the country. By changing the country's constitution, it had to be approved in both houses of the National Congress by an absolute majority. The reform was created to combat the giant deficit in the pension system, of more than R$194 billion in 2018, and the rapid aging of the Brazilian population.

The Illinois Public Pension Amendment was a proposed amendment to the Illinois state constitution. On November 6, 2012, Illinois voters rejected it in a statewide referendum.







