
Lipoxygenases are a family of (non-heme) iron-containing enzymes most of which catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4- pentadiene into cell signaling agents that serve diverse roles as autocrine signals that regulate the function of their parent cells, paracrine signals that regulate the function of nearby cells, and endocrine signals that regulate the function of distant cells.
SUNdomains are conserved C-terminal protein regions a few hundred amino acids long. SUN domains are usually found following a transmembrane domain and a less conserved region of amino acids. Most proteins containing SUN domains are thought to be involved in the positioning of the nucleus in the cell. It is thought that SUN domains interact directly with KASH domains in the space between the outer and inner nuclear membranes to bridge the nuclear envelope and transfer force from the nucleoskeleton to the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton which enables mechanosensory roles in cells. SUN proteins are thought to localize to the inner nuclear membrane. The S. pombe Sad1 protein localises at the spindle pole body. In mammals, the SUN domain is present in two proteins, Sun1 and Sun2. The SUN domain of Sun2 has been demonstrated to be in the periplasm.
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, also known as ALOX5, 5-lipoxygenase, 5-LOX, or 5-LO, is a non-heme iron-containing enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALOX5 gene. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. It transforms essential fatty acids (EFA) substrates into leukotrienes as well as a wide range of other biologically active products. ALOX5 is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases.

Polycystin 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKD1 gene. Mutations of PKD1 are associated with most cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, a severe hereditary disorder of the kidneys characterised by the development of renal cysts and severe kidney dysfunction.

Ras-related protein Rab-6A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB6A gene located in the eleventh chromosome. Its main function is the regulation of protein transport from the Golgi complex to the endoplasmic reticulum and the exocytosis along with the microtubules.
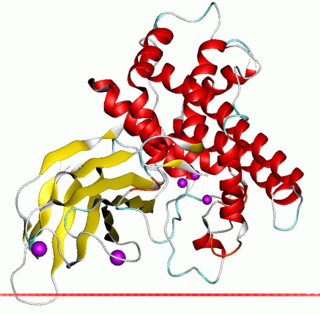
In molecular biology, zinc-dependent phospholipases C is a family of bacterial phospholipases C enzymes, some of which are also known as alpha toxins.

Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP6 gene. LRP6 is a key component of the LRP5/LRP6/Frizzled co-receptor group that is involved in canonical Wnt pathway.

Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAPRE1 gene.

Alpha-centractin (yeast) or ARP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTR1A gene.

H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GAR1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit gamma-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1G2 gene.

Protein SMG5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMG5 gene. This protein contains a PIN domain that appears to have mutated the residues in the active site.

Polycystic kidney disease 2-like 1 protein also known as transient receptor potential polycystic 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKD2L1 gene.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.
PKD domain was first identified in the polycystic kidney disease protein, polycystin-1, and contains an Ig-like fold consisting of a beta-sandwich of seven strands in two sheets with a Greek key topology, although some members have additional strands. Polycystin-1 is a large cell-surface glycoprotein involved in adhesive protein–protein and protein–carbohydrate interactions; however it is not clear if the PKD domain mediates any of these interactions.
This family contains acyltransferases involved in phospholipid biosynthesis and proteins of unknown function. This family also includes tafazzin, the Barth syndrome gene.
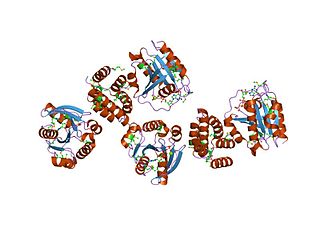
In molecular biology, the GRIP domain is a conserved protein domain. The GRIP domain is found in many large coiled-coil proteins. It has been shown to be sufficient for targeting to the Golgi. It contains a completely conserved tyrosine residue.
In molecular biology, the protein domain, WIF N-terminal refers to the N terminal domain of the protein, WIF. It stands for, Wnt-inhibitory factor, whereby wnt is a signalling molecule also known as wingless. Wnt is a molecule in the wnt signaling pathway. The WIF domain binds to the wnt ligand since it inhibits it.
The Polycystin Cation Channel (PCC) Family consists of several transporters ranging in size from 500 to over 4000 amino acyl residues (aas) in length and exhibiting between 5 and 18 transmembrane segments (TMSs). This family is a constituent of the Voltage-Gated Ion Channel (VIC) Superfamily. These transporters generally catalyze the export of cations. A representative list of proteins belonging to the PCC family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.












