Related Research Articles

Essential tremor (ET), also called benign tremor, familial tremor, and idiopathic tremor, is a medical condition characterized by involuntary rhythmic contractions and relaxations of certain muscle groups in one or more body parts of unknown cause. It is typically symmetrical, and affects the arms, hands, or fingers; but sometimes involves the head, vocal cords, or other body parts. Essential tremor is either an action (intention) tremor—it intensifies when one tries to use the affected muscles during voluntary movements such as eating and writing—or it is a postural tremor, which occurs when holding arms outstretched and against gravity. This means that it is distinct from a resting tremor, such as that caused by Parkinson's disease, which is not correlated with movement. Unlike Parkinson's disease, essential tremor may worsen with action.

A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic muscle contraction and relaxation involving oscillations or twitching movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the hands, arms, eyes, face, head, vocal folds, trunk, and legs. Most tremors occur in the hands. In some people, a tremor is a symptom of another neurological disorder.

Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin, is a highly potent neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromuscular junction, thus causing flaccid paralysis. The toxin causes the disease botulism. The toxin is also used commercially for medical and cosmetic purposes. Botulinum toxin is an acetylcholine release inhibitor and a neuromuscular blocking agent.

Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular twitching of a muscle, a joint, or a group of muscles, different from clonus, which is rhythmic or regular. Myoclonus describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. It belongs to the hyperkinetic movement disorders, among tremor and chorea for example. These myoclonic twitches, jerks, or seizures are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions or brief lapses of contraction. The most common circumstance under which they occur is while falling asleep. Myoclonic jerks occur in healthy people and are experienced occasionally by everyone. However, when they appear with more persistence and become more widespread they can be a sign of various neurological disorders. Hiccups are a kind of myoclonic jerk specifically affecting the diaphragm. When a spasm is caused by another person it is known as a provoked spasm. Shuddering attacks in babies fall in this category.
Dystonia is a neurological hyperkinetic movement disorder in which sustained or repetitive muscle contractions occur involuntarily, resulting in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed postures. The movements may resemble a tremor. Dystonia is often intensified or exacerbated by physical activity, and symptoms may progress into adjacent muscles.
Dyskinesia refers to a category of movement disorders that are characterized by involuntary muscle movements, including movements similar to tics or chorea and diminished voluntary movements. Dyskinesia can be anything from a slight tremor of the hands to an uncontrollable movement of the upper body or lower extremities. Discoordination can also occur internally especially with the respiratory muscles and it often goes unrecognized. Dyskinesia is a symptom of several medical disorders that are distinguished by their underlying cause.
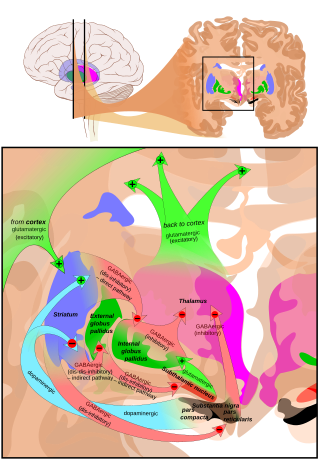
Hyperkinesia refers to an increase in muscular activity that can result in excessive abnormal movements, excessive normal movements, or a combination of both. Hyperkinesia is a state of excessive restlessness which is featured in a large variety of disorders that affect the ability to control motor movement, such as Huntington's disease. It is the opposite of hypokinesia, which refers to decreased bodily movement, as commonly manifested in Parkinson's disease.
Hemifacial spasm (HFS) is a rare neuromuscular disease characterized by irregular, involuntary muscle contractions (spasms) on one side (hemi-) of the face (-facial). The facial muscles are controlled by the facial nerve, which originates at the brainstem and exits the skull below the ear where it separates into five main branches.
Torsion dystonia, also known as dystonia musculorum deformans, is a disease characterized by painful muscle contractions resulting in uncontrollable distortions. This specific type of dystonia is frequently found in children, with symptoms starting around the ages of 11 or 12. It commonly begins with contractions in one general area such as an arm or a leg that continue to progress throughout the rest of the body. It takes roughly 5 years for the symptoms to completely progress to a debilitating state.
Blepharospasm is a neurological disorder characterized by intermittent, involuntary spasms and contractions of the orbicularis oculi (eyelid) muscles around both eyes. These result in abnormal twitching or blinking, and in the extreme, sustained eyelid closure resulting in functional blindness.

Spasmodic torticollis is an extremely painful chronic neurological movement disorder causing the neck to involuntarily turn to the left, right, upwards, and/or downwards. The condition is also referred to as "cervical dystonia". Both agonist and antagonist muscles contract simultaneously during dystonic movement. Causes of the disorder are predominantly idiopathic. A small number of patients develop the disorder as a result of another disorder or disease. Most patients first experience symptoms midlife. The most common treatment for spasmodic torticollis is the use of botulinum toxin type A.

Meige's syndrome is a type of dystonia. It is also known as Brueghel's syndrome and oral facial dystonia. It is actually a combination of two forms of dystonia, blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia (OMD).
Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) are symptoms that are archetypically associated with the extrapyramidal system of the brain's cerebral cortex. When such symptoms are caused by medications or other drugs, they are also known as extrapyramidal side effects (EPSE). The symptoms can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). They include movement dysfunction such as dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism characteristic symptoms such as rigidity, bradykinesia, tremor, and tardive dyskinesia. Extrapyramidal symptoms are a reason why subjects drop out of clinical trials of antipsychotics; of the 213 (14.6%) subjects that dropped out of one of the largest clinical trials of antipsychotics, 58 (27.2%) of those discontinuations were due to EPS.
Spasmodic dysphonia, also known as laryngeal dystonia, is a disorder in which the muscles that generate a person's voice go into periods of spasm. This results in breaks or interruptions in the voice, often every few sentences, which can make a person difficult to understand. The person's voice may also sound strained or they may be nearly unable to speak. Onset is often gradual and the condition is lifelong.

Geniospasm is movement disorder of the mentalis muscle.
Myoclonic dystonia or Myoclonus dystonia syndrome is a rare movement disorder that induces spontaneous muscle contraction causing abnormal posture. The prevalence of myoclonus dystonia has not been reported, however, this disorder falls under the umbrella of movement disorders which affect thousands worldwide. Myoclonus dystonia results from mutations in the SGCE gene coding for an integral membrane protein found in both neurons and muscle fibers. Those suffering from this disease exhibit symptoms of rapid, jerky movements of the upper limbs (myoclonus), as well as distortion of the body's orientation due to simultaneous activation of agonist and antagonist muscles (dystonia).

Basal ganglia disease is a group of physical problems that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly suppress unwanted movements or to properly prime upper motor neuron circuits to initiate motor function. Research indicates that increased output of the basal ganglia inhibits thalamocortical projection neurons. Proper activation or deactivation of these neurons is an integral component for proper movement. If something causes too much basal ganglia output, then the ventral anterior (VA) and ventral lateral (VL) thalamocortical projection neurons become too inhibited, and one cannot initiate voluntary movement. These disorders are known as hypokinetic disorders. However, a disorder leading to abnormally low output of the basal ganglia leads to reduced inhibition, and thus excitation, of the thalamocortical projection neurons which synapse onto the cortex. This situation leads to an inability to suppress unwanted movements. These disorders are known as hyperkinetic disorders.
Oromandibular dystonia(OMD) is an uncommon focal neurological condition affecting the jaws, face, and mouth. Oromandibular dystonia is characterized by involuntary spasms of the tongue, jaw, and mouth muscles that result in bruxism, or grinding of the teeth, and jaw closure. These conditions frequently lead to secondary dental wear as well as temporomandibular joint syndrome. In addition, problems with chewing, speaking, and swallowing may result from jaw opening, involuntary tongue movements, or jaw deviation.

Kufor–Rakeb syndrome (KRS) is an autosomal recessive disorder of juvenile onset also known as Parkinson disease-9 (PARK9). It is named after Kufr Rakeb in Irbid, Jordan. Kufor–Rakeb syndrome was first identified in this region in Jordan with a Jordanian couple's 5 children who had rigidity, mask-like face, and bradykinesia. The disease was first described in 1994 by Najim Al-Din et al. The OMIM number is 606693.
Alan Brown Scott was an American ophthalmologist specializing in eye muscles and their disorders, such as strabismus. He is best known for his work in developing and manufacturing the drug that became known as Botox, research described as "groundbreaking" by the ASCRS.
References
- 1 2 Park, S. N.; Park, K. H.; Kim, D. H.; Yeo, S. W. (Feb 7, 2011). "Palatal Myoclonus Associated with Orofacial Buccal Dystonia". Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology. 5 (1): 44–48. doi:10.3342/ceo.2012.5.1.44. PMC 3314805 . PMID 22468202.
Orofacial buccal dystonia is a focal dystonia with sustained spasms of the masticatory, facial or lingual muscles. The frequent symptoms of this disease have mainly been reported to be involuntary and possibly painful jaw opening, closing, deflecting and retruding, or a combination of the above. However, the subtle and unnoticeable involuntary movement of multiple facial muscles, which might be an infrequent symptom of orofacial buccal dystonia, makes this disease hard to diagnose.
- ↑ Kim, Jong S.; Caplan, Louis R. (2016). "26 Vertebrobasilar Disease". Stroke (Sixth ed.). Elsevier. pp. 413–448.e7. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-29544-4.00026-8. ISBN 9780323295444.
Occasionally, rhythmic, jerky movements are also observed in the face, eyeballs, tongue, jaw, vocal cord or extremities (mostly hands); they may not be synchronous with palatal movements. The movements of the palate vary in rate between 40 and 200 beats per minute. The movements may involve the Eustachian tube and make a click that the patient can hear.
- ↑ Zadikoff C, Lang AE, Klein C. (29 November 2005). "The 'essentials' of essential palatal tremor: a reappraisal of the nosology". Brain. 129 (4): 832–840. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh684 . PMID 16317025.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Saeed SR1, Brookes GB. (1993). "The use of clostridium botulinum toxin in palatal myclonus. A preliminary report". Journal of Laryngology & Otology. 107 (3): 208–210. doi:10.1017/S0022215100122650. PMID 8509697. S2CID 19052329.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)