Related Research Articles

Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types.

The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as parotid gland secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal adult human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27 mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3 mm.

The sublingual gland is a seromucous polystomatic exocrine gland. Located underneath the oral diaphragm, the sublingual gland is the smallest and most diffuse of the three major salivary glands of the oral cavity, with the other two being the submandibular and parotid. The sublingual gland provides approximately 3-5% of the total salivary volume.

The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segment of the bowel, it functions to regulate release of excrement by two muscular sphincter complexes. The anus is the aperture at the terminal portion of the anal canal.
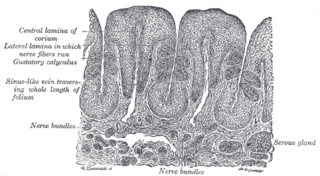
Serous glands secrete serous fluid. They contain serous acini, a grouping of serous cells that secrete serous fluid, isotonic with blood plasma, that contains enzymes such as alpha-amylase.
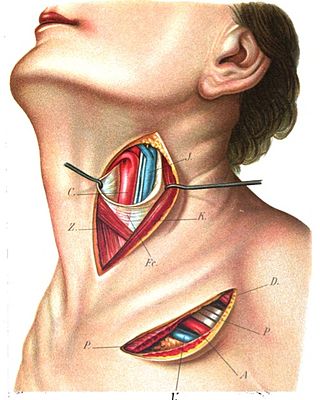
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.
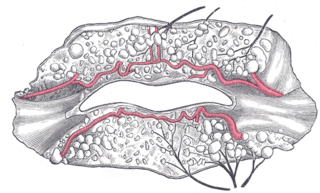
The inferior labial artery arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane.

The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of vagus nerve and additionally also receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.

The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands.
The mucous membrane of the soft palate is thin, and covered with stratified squamous epithelium on both surfaces, except near the pharyngeal ostium of the auditory tube, where it is columnar and ciliated.

The esophageal glands are glands that are part of the digestive system of various animals, including humans.
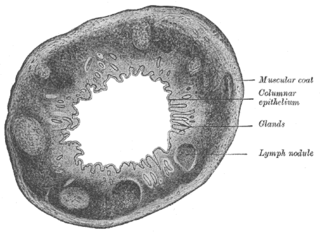
The Solitary lymphatic nodules are structures found in the small intestine and large intestine.

Mucous gland, also known as muciparous glands, are found in several different parts of the body, and they typically stain lighter than serous glands during standard histological preparation. Most are multicellular, but goblet cells are single-celled glands.

The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve, is the part of the facial nerve located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve. It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve. Upon reaching the facial canal, it joins with the motor root of the facial nerve at the geniculate ganglion. Alex Alfieri postulates that the intermediate nerve should be considered as a separate cranial nerve and not a part of the facial nerve.

Gastric pits are indentations in the stomach which denote entrances to 3-5 tubular shaped gastric glands. They are deeper in the pylorus than they are in the other parts of the stomach. The human stomach has several million of these pits which dot the surface of the lining epithelium. Surface mucous cells line the pits themselves but give way to a series of other types of cells which then line the glands themselves.
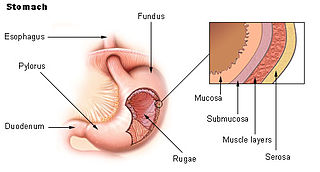
The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the glands and the gastric pits. In humans, it is about 1 mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. It consists of simple columnar epithelium, lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae.
The excretory ducts of the sublingual gland are from eight to twenty in number. Of the smaller sublingual ducts, some join the submandibular duct; others open separately into the mouth, on the elevated crest of mucous membrane, caused by the projection of the gland, on either side of the frenulum linguae. One or more join to form the major sublingual duct, which opens into the submandibular duct.

The labial glands are minor salivary glands situated between the mucous membrane and the orbicularis oris around the orifice of the mouth.

The laryngeal ventricle, is a fusiform fossa, situated between the vestibular and vocal folds on either side, and extending nearly their entire length. There is also a sinus of Morgagni in the pharynx.
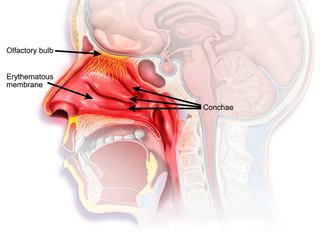
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous with the skin through the nostrils, and with the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx through the choanae. From the nasal cavity its continuity with the conjunctiva may be traced, through the nasolacrimal and lacrimal ducts; and with the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, through the several openings in the nasal meatuses. The mucous membrane is thickest, and most vascular, over the nasal conchae. It is also thick over the nasal septum where increased numbers of goblet cells produce a greater amount of nasal mucus. It is very thin in the meatuses on the floor of the nasal cavities, and in the various sinuses. It is one of the most commonly infected tissues in adults and children. Inflammation of this tissue may cause significant impairment of daily activities, with symptoms such as stuffy nose, headache, mouth breathing, etc.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1141 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1141 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)