The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.

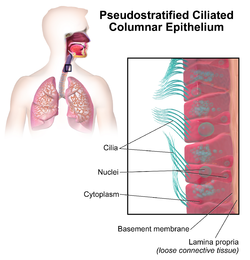
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.

A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.

The bronchioles or bronchioli are the smaller branches of the bronchial airways in the lower respiratory tract. They include the terminal bronchioles, and finally the respiratory bronchioles that mark the start of the respiratory zone delivering air to the gas exchanging units of the alveoli. The bronchioles no longer contain the cartilage that is found in the bronchi, or glands in their submucosa.

The epididymis is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is present in all male reptiles, birds, and mammals. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, 6 to 7 meters in length connecting the efferent ducts from the rear of each testicle to its vas deferens.

The vas deferens, or ductus deferens, is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.

The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract.

The olfactory epithelium is a specialized epithelial tissue inside the nasal cavity that is involved in smell. In humans, it measures 9 cm2 and lies on the roof of the nasal cavity about 7 cm above and behind the nostrils. The olfactory epithelium is the part of the olfactory system directly responsible for detecting odors.

The efferent ducts connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.

Metaplasia is the transformation of one differentiated cell type to another differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abnormal stimulus. In simplistic terms, it is as if the original cells are not robust enough to withstand their environment, so they transform into another cell type better suited to their environment. If the stimulus causing metaplasia is removed or ceases, tissues return to their normal pattern of differentiation. Metaplasia is not synonymous with dysplasia, and is not considered to be an actual cancer. It is also contrasted with heteroplasia, which is the spontaneous abnormal growth of cytologic and histologic elements. Today, metaplastic changes are usually considered to be an early phase of carcinogenesis, specifically for those with a history of cancers or who are known to be susceptible to carcinogenic changes. Metaplastic change is thus often viewed as a premalignant condition that requires immediate intervention, either surgical or medical, lest it lead to cancer via malignant transformation.

Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple columnar epithelium lines most organs of the digestive tract including the stomach, and intestines. Simple columnar epithelium also lines the uterus.

Respiratory epithelium, or airway epithelium, is a type of ciliated columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract as respiratory mucosa, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It is not present in the vocal cords of the larynx, or the oropharynx and laryngopharynx, where instead the epithelium is stratified squamous. It also functions as a barrier to potential pathogens and foreign particles, preventing infection and tissue injury by the secretion of mucus and the action of mucociliary clearance.

Stratified columnar epithelium is a rare type of epithelial tissue composed of column-shaped cells arranged in multiple layers. It is found in the conjunctiva, pharynx, anus, and male urethra. It also occurs in embryo.

In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or organ.

Simple cuboidal epithelium is a type of epithelium that consists of a single layer of cuboidal (cube-like) cells which have large, spherical and central nuclei.
Histology is the study of the minute structure, composition, and function of tissues. Mature human vocal cords are composed of layered structures which are quite different at the histological level.

Bronchogenic cysts are small, solitary cysts or sinuses, most typically located in the region of the suprasternal notch or behind the manubrium.
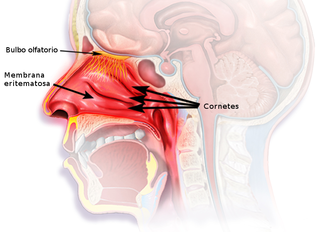
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous with the skin through the nostrils, and with the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx through the choanae. From the nasal cavity its continuity with the conjunctiva may be traced, through the nasolacrimal and lacrimal ducts; and with the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, through the several openings in the nasal meatuses. The mucous membrane is thickest, and most vascular, over the nasal conchae. It is also thick over the nasal septum where increased numbers of goblet cells produce a greater amount of nasal mucus. It is very thin in the meatuses on the floor of the nasal cavities, and in the various sinuses. It is one of the most commonly infected tissues in adults and children. Inflammation of this tissue may cause significant impairment of daily activities, with symptoms such as stuffy nose, headache, mouth breathing, etc.

Anatomical terminology is used to describe microanatomical structures. This helps describe precisely the structure, layout and position of an object, and minimises ambiguity. An internationally accepted lexicon is Terminologia Histologica.
The monotremes represent the order of extant mammals most distantly related to humans. The platypus is indigenous to eastern Australia; the short-beaked echidna is indigenous to Australia and Papua New Guinea; whereas the long-beaked echidna is restricted to Papua New Guinea and Irian Jaya. Since monotremes exhibit characteristics common with both reptiles and therian mammals, they are of great interest for the study of mammalian evolution.