
A bicycle, also called a bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A bicycle rider is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.

A hybrid vehicle uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.

A bicycle-sharing system, public bicycle scheme, or public bike share (PBS) scheme, is a service in which bicycles are made available for shared use to individuals on a short term basis for a price or free. Many bike share systems allow people to borrow a bike from a "dock" and return it at another dock belonging to the same system. Docks are special bike racks that lock the bike, and only release it by computer control. The user enters payment information, and the computer unlocks a bike. The user returns the bike by placing it in the dock, which locks it in place. Other systems are dockless.

A brushless DC electric motor, also known as electronically commutated motor and synchronous DC motors, are synchronous motors powered by direct current (DC) electricity via an inverter or switching power supply which produces electricity in the form of alternating current (AC) to drive each phase of the motor via a closed loop controller. The controller provides pulses of current to the motor windings that control the speed and torque of the motor. This control system replaces the commutator (brushes) used in many conventional electric motors.

A stationary bicycle is a device used as exercise equipment. It includes a saddle, pedals, and some form of handlebars arranged as on a (stationary) bicycle.

ZF Sachs AG, also known as Fichtel & Sachs was founded in Schweinfurt in 1895 and was a well-known German family business. At its last point as an independent company, the company name was Fichtel & Sachs AG.

In automobile engineering, electric vehicle conversion is the replacement of a car's combustion engine and connected components with an electric motor and batteries, to create an all-electric vehicle. Another option is to replace a large combustion engine with an electric motor and a small combustion engine, creating a hybrid electric vehicle or a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.

A bicycle trainer is a piece of equipment that makes it possible to ride a bicycle while it remains stationary. They are commonly used to warm up before races, or when riding conditions outside are not favorable.

An electric bicycle also known as an e-bike is a bicycle with an integrated electric motor which can be used to assist propulsion. Many kinds of e-bikes are available worldwide, from e-bikes that only have a small motor to assist the rider's pedal-power to more powerful e-bikes which are closer to moped-style functionality. All retain the ability to be pedalled by the rider and are therefore not electric motorcycles.

A belt-driven bicycle is a chainless bicycle that uses a toothed synchronous belt to transmit power from the pedals to the wheel.

A motorized scooter is a powered stand-up scooter using a small utility internal combustion engine or, more commonly, an electric motor. Classified as a form of micro-mobility, these scooters are generally designed with a large deck in the center on which the rider stands. The first production scooter, the "Sport", was released by Go-Ped in 1985.
Hybrid vehicle drive trains transmit power to the driving wheels for hybrid vehicles. A hybrid vehicle has multiple forms of motive power.

Electric motorcycles and scooters are plug-in electric vehicles with two or three wheels. The electricity is stored on board in a rechargeable battery, which drives one or more electric motors. Electric scooters have a step-through frame.

ZAP is an American electric vehicle company that designs, produces and markets vehicles including automobiles, motorcycles, bicycles, scooters, personal watercraft, hovercraft, ATVs, neighborhood electric vehicles and commercial vehicles. The name stands for Zero Air Pollution. The company headquarters are located in Santa Rosa, California.

A Goldsprint is a bicycle rollers racing and social event. Riders on stationary bikes compete against each other in front of spectators.
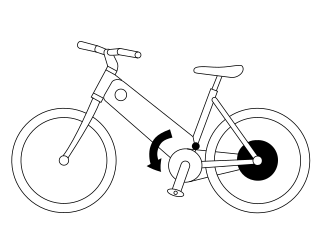
A pedelec is a type of electric bicycle where the rider's pedalling is assisted by a small electric motor; thus it is a type of low-powered e-bike. However, unlike some other types of e-bikes, pedelecs are classified as conventional bicycles in many countries by road authorities rather than as a type of electric moped. Pedelecs include an electronic controller which cuts power to the motor when the rider is not pedalling or when a certain speed – usually 25 km/h (16 mph) or 32 km/h (20 mph) – is reached. Pedelecs are useful for people who ride in hilly areas or in strong headwinds. While a pedelec can be any type of bicycle, a pedelec city bike is very common. A conventional bicycle can be converted to a pedelec with the addition of the necessary parts, e.g., motor, battery, etc.
Quality Bicycle Products (QBP) is the largest distributor of bicycle parts and accessories in the bicycle industry, with revenues of $150 million in 2008. In addition to wholesaling bicycles and components from other manufacturers, QBP owns and manufactures several brands of its own. QBP also participates in activities which support its community through cycling advocacy and green building.

An electronic gear-shifting system is a method of changing gears on a bicycle, which enables riders to shift with electronic switches instead of using conventional control levers and mechanical cables. The switches are connected by wire or wirelessly to a battery pack and to a small electric motor that drives the derailleur, switching the chain from cog to cog. An electronic system can switch gears faster, and because the system does not use Bowden cables and can calibrate itself, it may require less maintenance.

Motor doping, or mechanical doping, in competitive cycling terminology, is a method of cheating by using a hidden motor to help propel a racing bicycle. The term is an analogy to chemical doping in sport, cheating by using performance-enhancing drugs. As a form of "technological fraud" it is banned by the Union Cycliste Internationale, the international governing body of cycling.

















