
Crinoids are marine invertebrates that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their juvenile form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms, called feather stars or comatulids, are members of the largest crinoid order, Comatulida. Crinoids are echinoderms in the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes the starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. They live in both shallow water and in depths as great as 9,000 meters (30,000 ft).

The Rickettsiales, informally called rickettsias, are an order of small Alphaproteobacteria. They are obligate intracellular parasites, and some are notable pathogens, including Rickettsia, which causes a variety of diseases in humans, and Ehrlichia, which causes diseases in livestock. Another genus of well-known Rickettsiales is the Wolbachia, which infect about two-thirds of all arthropods and nearly all filarial nematodes. Genetic studies support the endosymbiotic theory according to which mitochondria and related organelles developed from members of this group.

Articulata are a subclass or superorder within the class Crinoidea, including all living crinoid species. They are commonly known as sea lilies or feather stars. The Articulata are differentiated from the extinct subclasses by their lack of an anal plate in the adult stage and the presence of an entoneural system. Articulata first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic period although other, now extinct crinoid groups, originated in the Ordovician.

The Polypodiidae, commonly called leptosporangiate ferns, formerly Leptosporangiatae, are one of four subclasses of ferns, the largest of these being the largest group of living ferns, including some 11,000 species worldwide. The group has also been treated as the class Pteridopsida or Polypodiopsida, although other classifications assign them a different rank. Older names for the group include Filicidae and Filicales, although at least the "water ferns" were then treated separately.

Crinozoa is a subphylum of mostly sessile echinoderms, of which the crinoids, or sea lilies and feather stars, are the only extant members. Crinozoans have an extremely extensive fossil history, which may or may not extend into the Precambrian.

Taxonomy of commonly fossilised invertebrates is a complex and evolving field that combines both traditional and modern paleozoological terminology. This article provides an overview of various invertebrate taxa found in the fossil record, ranging from protists to arthropods. The taxonomy discussed is not exhaustive, but rather emphasizes invertebrates that are either frequently collected as fossils or are extinct. This includes groups that are significant in paleontological contexts, notably abundant in the fossil record, or have a high proportion of extinct species. For better understanding, special notations used in this context are explained below:
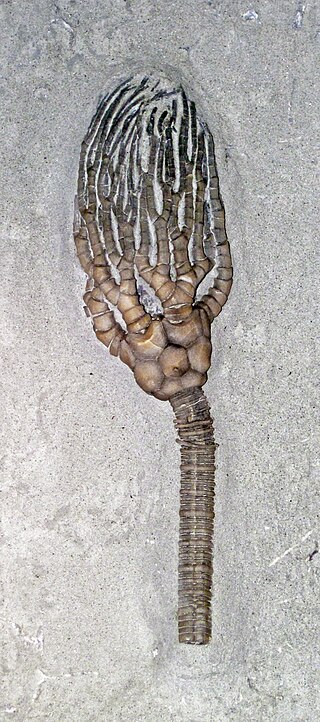
Cyathocrinites is an extinct genus of crinoids that lived from the Early Silurian to the Late Permian in Europe and North America.

Echmatocrinus is a Cambrian animal which resembles a crinoid or an octocoral. Its exact taxonomy is still a subject of debate. It is known only from the Burgess shale. Around 20 specimens of Echmatocrinus are known; these comprise < 0.02% of the community.

Scincosaurus is an extinct genus of nectridean lepospondyl within the family Scincosauridae.

Comatulida is an order of crinoids. Members of this order are known as feather stars and mostly do not have a stalk as adults. The oral surface with the mouth is facing upwards and is surrounded by five, often divided rays with feathery pinnules. Comatulids live on the seabed and on reefs in tropical and temperate waters.

Cupressocrinitidae is an extinct family of crinoid from the Middle to Late Devonian. Cupressocrinites is a representative of this family.

Cladida is a major subgroup of crinoids with a complicated taxonomic history. Cladida was originally applied to a wide assortment of extinct crinoids with a dicyclic calyx. Under this original definition, cladids would represent a paraphyletic order ancestral to several other major crinoid groups, particularly the living Articulata. More recently, Cladida has been redefined as a monophyletic parvclass of pentacrinoids which encompasses articulates and the extinct Flexibilia (flexibles). Cladids also include various minor taxa such as the hybocrinids and "cyathocrines". As flexibles were not originally considered cladids, the new subgroup Eucladida has been erected for cladids which are more derived than flexibles. Cladida is the sister group to Disparida, another large group of extinct crinoids.

The Camerata or camerate crinoids are an extinct subclass of Paleozoic stalked crinoids. They were some of the earliest crinoids to originate during the Early Ordovician, reached their maximum diversity during the Mississippian, and became extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Camerates are the sister group of Pentacrinoidea, which contains all other crinoids. The two largest camerate subgroups are the orders Diplobathrida and Monobathrida.
Petalocrinidae is an extinct family of cladid crinoids from the Early Ordovician to Lower Devonian. Fossils of petalocrinoids have been found in China, Europe and the United States.
Cyrtura is a dubious genus of extinct Testudinata from the Late Jurassic of the Solnhofen Formation of Bavaria, Germany. Cyrtura was originally described as a temnospondyl amphibian by Otto Jaekel in 1904 on the basis of MNB 1890, the distal portion of a tail with 14 caudal vertebrae. Most authors overlooked the genus, although those who mentioned Cyrtura dismissed it as either undiagnostic or referable to Testudines rather than Temnospondyli. Warren and Hutchinson (1983) rejected the temnospondyl classification of the genus based on examination of a cast of the holotype, and subsequent studies showed that Cyrtura is actually a marine turtle, although the lack of diagnostic characters renders it a nomen dubium.

Comatulidae is a family of comatulid crinoids. Since 2015, it replaces the family Comasteridae.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2018.
Disparida is an parvclass of extinct marine animals in the class Crinoidea. Disparids are a speciose and morphologically diverse group of crinoids distinguished by their monocyclic calyx and slender arms without pinnules. They range from the Early Ordovician (Tremadocian) to Middle Permian, reaching their highest diversity during the Late Ordovician.

Flexibilia is a superorder of specialized Paleozoic crinoids. They exhibited a conserved body plan and consistent suite of characteristics throughout their long history. Previously considered a subclass with unclear affinities, later investigation determined that flexibles are well-nested within Cladida, a broad group ancestral to living articulate crinoids. The Ordovician cladid Cupulocrinus acts as an intermediate form linking the generalized anatomy of other early cladids with the distinctive anatomy of flexibles, and several studies have considered it to be ancestral to the rest of the group. Although flexibles never reached the same abundance or diversity as many other crinoid groups, they remained a reliable component of crinoid faunas, particularly from the Silurian onwards. Flexible fossils are very rare in the Ordovician, but the Late Ordovician appears to have been an interval of rapid diversification for the group.














