Politics of Gabon takes place in a framework of a republic whereby the President of Gabon is head of state and in effect, also the head of government, since he appoints the prime minister and his cabinet. The government is divided into three branches: the Executive headed by the prime minister, the legislative that is formed by the two chambers of parliament. The judicial branch, like other two branches, is technically independent and equal to other three branches, although in practice, since its judges are appointed by the president, it is beholden to the same president. Since independence the party system is dominated by the conservative Gabonese Democratic Party.

The politics of Kenya take place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Kenya is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system in accordance with a new constitution passed in 2010.

The politics of Russia take place in the framework of the federal semi-presidential republic of Russia. According to the Constitution of Russia, the President of Russia is head of state, and of a multi-party system with executive power exercised by the government, headed by the Prime Minister, who is appointed by the President with the parliament's approval. Legislative power is vested in the two houses of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, while the President and the government issue numerous legally binding by-laws. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union at the end of 1991, Russia has seen serious challenges in its efforts to forge a political system to follow nearly seventy-five years of Soviet governance. For instance, leading figures in the legislative and executive branches have put forth opposing views of Russia's political direction and the governmental instruments that should be used to follow it. That conflict reached a climax in September and October 1993, when President Boris Yeltsin used military force to dissolve the parliament and called for new legislative elections. This event marked the end of Russia's first constitutional period, which was defined by the much-amended constitution adopted by the Supreme Soviet of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic in 1978. A new constitution, creating a strong presidency, was approved by referendum in December 1993.

Nursultan Abishuly Nazarbayev or Nursultan Abishevich Nazarbayev is a Kazakh politician who served as the first President of Kazakhstan, in office from 1990 until his formal resignation in 2019, and as the Chairman of the Security Council of Kazakhstan from 1991 to 2022. He held the special title as Elbasy from 2010 to 2022. Nazarbayev was one of the longest-ruling non-royal leaders in the world, having led Kazakhstan for nearly three decades, excluding chairmanship in the Security Council after the end of his presidency. He was named First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Kazakh SSR in 1989 and was elected as the nation's first president shortly before its independence from the Soviet Union.
Albania is a unitary parliamentary constitutional republic, where the President of Albania is the head of state and the Prime Minister of Albania the head of government in a multi-party system. The executive power is exercised by the Government and the Prime Minister with its Cabinet. Legislative power is vested in the Parliament of Albania. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The political system of Albania is laid out in the 1998 constitution. The Parliament adopted the current constitution on 28 November 1998. Due to political instability, the country has had many constitutions during its history. Albania was initially constituted as a monarchy in 1913, briefly a republic in 1925, then it returned to a democratic monarchy in 1928. It later became a socialist republic until the restoration of capitalism and democracy in 1992.

The Politics of Azerbaijan takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential republic, with the President of Azerbaijan as the head of state, and the Prime Minister of Azerbaijan as head of government. Executive power is exercised by the president and the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The Judiciary is nominally independent of the executive and the legislature.

The politics of Barbados function within a framework of a parliamentary republic with strong democratic traditions; constitutional safeguards for nationals of Barbados include: freedom of speech, press, worship, movement, and association.

The Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan oversees a presidential republic. The President of Kazakhstan, currently Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, is head of state and nominates the Prime Minister of Kazakhstan, the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament.
The Government of Poland takes place in the framework of a unitary parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the President is the head of state and the Prime Minister is the head of government. However, its form of government has also been identified as semi-presidential.

Kassym-Jomart Kemeluly Tokayev is a Kazakh politician and diplomat who is currently serving as the President of Kazakhstan since 12 June 2019. He became acting president on 20 March 2019 after the resignation of Nursultan Nazarbayev, who resigned on 19 March 2019 after 29 years in office.

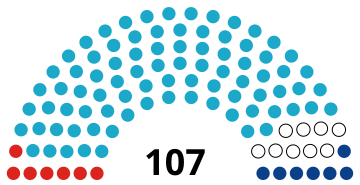
The Parliament of the Republic of Kazakhstan is the bicameral legislature of Kazakhstan. The lower house is the Mazhilis, with 107 seats, which are elected to five-year terms. The upper house is the Senate, which has 47 members.

Elections in Kazakhstan are held on a national level to elect a President and the Parliament, which is divided into two bodies, the Majilis and the Senate. Local elections for maslihats are held every five years.

The president of the Republic of Kazakhstan is the head of state of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The president is the holder of the highest office within the Republic of Kazakhstan. The powers of this position are described in a special section of the Constitution of Kazakhstan.

The Senate of Kazakhstan is the upper house of two chambers in Kazakhstan's legislature, known as the Parliament (Parlamenti). The Senate is composed of elected members: two from each region and two from three municipalities which are Almaty, Nur-Sultan, and Shymkent.

The 2007 amendment to the Constitution of Kazakhstan modified Kazakhstan's basic law, on May 18, 2007. The changes followed the conclusion of the activities of the 'State Commission on Democratization' formed two years previously.
The National Election Commission is independent constitutional institution in South Korea, established to manage free and fair elections, national referendums and other administrative affairs concerning political parties and funds. The agency was established in accordance with Article 114 of the Constitution of South Korea. The NEC has equal status as highest constitutional institution as National Assembly, the Executive Ministries, the Supreme Court and the Constitutional Court. This highly independent status of NEC reflects national will to overcome past histories such as election rigging of South Korea in 1960.

Snap presidential elections were held in Kazakhstan on 26 April 2015 to elect the President of Kazakhstan. This was the fifth presidential election held and second without having any formal opposition candidates. With the highest-ever nationwide turnout of 95.2%, the result was a victory for long-term incumbent President Nursultan Nazarbayev of Nur Otan who received 97.8% of the vote, the largest since 1991, thus winning a fifth term in office while his closest challenger, Turgyn Syzdyqov, received only 1.6% of the votes.
Events of 2019 in Kazakhstan.

Snap presidential elections were held in Kazakhstan on 9 June 2019 to elect the President of Kazakhstan following the resignation of long-term President Nursultan Nazarbayev in March 2019. This was the sixth presidential election held since Kazakhstan's independence. The elections were not free and fair, and were widely denounced as a sham. Acting president Kassym-Jomart Tokayev of Nur Otan won the election.

A constitutional referendum in Kazakhstan, locally called the Republican referendum, was held on 5 June 2022. It was the third referendum since Kazakhstan's independence in 1991, and the first since the 1995 referendum that established the current constitution. The amendments followed violent civil unrest in early January caused by worsening economic conditions and subsequent calls for rapid political reform. The referendum changed 33 of the document's 98 articles. Political commentators assessed that amendments would lessen the influence of the executive branch, grant more powers to the Parliament, and eliminate the powers that former president Nursultan Nazarbayev had retained after resigning from office in 2019.