Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ; two smaller, inhabited islands ; and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands. Samoa is located 64 km (40 mi) west of American Samoa, 889 km (552 mi) northeast of Tonga, 1,152 km (716 mi) northeast of Fiji, 483 km (300 mi) east of Wallis and Futuna, 1,151 km (715 mi) southeast of Tuvalu, 519 km (322 mi) south of Tokelau, 4,190 km (2,600 mi) southwest of Hawaii, and 610 km (380 mi) northwest of Niue. The capital and largest city is Apia. The Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan cultural identity.
Queen Salamasina was a powerful and high-ranking woman in Samoan social history. She held the four papā (district) titles which gave her the paramount status of Tafa‘ifā on the western islands of Samoa. Contrary to popular belief she was not the first Tafa'ifā, as these titles were willed to her by their previous possessor, Nafanua. She is the titular ancestor of two of the four paramount titles of Samoa, Tupua Tamasese of Falefa and Salani and the Amaile Mataafa line.

Samoa is made up of eleven itūmālō. These are the traditional eleven districts that were established well before European arrival. Each district has its own constitutional foundation (faavae) based on the traditional order of title precedence found in each district's faalupega.

Aʻana is a district of Samoa. It is on the western third of Upolu island, with a small exclave surrounded by Aiga-i-le-Tai. It has an area of 193 km² and a population of 23,265. The main centre is Leulumoega.

Ātua is an ancient political district of Samoa, consisting of most of the eastern section of Upolu and the island Tutuila. Within Samoa’s traditional polity, Ātua is ruled by the Tui Ātua together with the group of six senior orators of Lufilufi and 13 senior matai from throughout Ātua, comprising the Fale Ātua. The fono (meeting) of Atua's rulers takes place in Lufilufi on the great malae of Lalogafu'afu'a.
Tuamāsaga is a district of Samoa, with a population of 95,907. The geographic area of Tuamasaga covers the central part of Upolu island.

Tui Ātua Tupua Tamasese Tupuola Tufuga Efi is a Samoan political leader and as holder of the maximal lineage Tama-a-'āiga title of Tupua Tamasese, is one of the four paramount chiefs of Samoa. He also holds the royal pāpā title of Tui Atua.

Susuga Malietoa Laupepa was the ruler (Malietoa) of Samoa in the late 19th century.

Tupua (known as Tupua Tamasese) is a state dynasty and one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa, known as the Tama-a-Aiga or 'Sons of the Great Families'). It is the titular head of one of Samoa's two great royal families - Sā Tupua, the lineage of Queen Salamasina. The 'Tupua' refers to Salamasina's descendant, King Tupua Fuiavailili, who was the first to unite both of Salamasina's descent lines in his personage and ascended to the Kingship of Samoa in c.1550, upon the death of his adoptive father, King Muagututi'a. Tupua Fuiavailili was adopted by his aunt, Fenunu'ivao (daughter of Leutele and wife of King Muagututi'a) and named as the King's successor. Tupua's rise also led to the first usage of the term "Tama-a-'aiga" by the orator polity of Leulumoega and Lufilufi, in reference to his many genealogical connections to the great families of Ātua. The 'Tamasese' part refers to his descendant Tupua Tamasese Titimaea, whose prowess in battle and generosity won favour with many of his followers and whose actions restored the Salamasina line's prestige. All subsequent Tupua title holders have thus carried the two names together since then.

Susuga Malietoa Tanumafili I was the Malietoa in Samoa from 1898 until his death in 1939.

The O le Ao o le Malo is the head of state of Samoa. The position is described in Part III of the 1960 Samoan constitution. At the time the constitution was adopted, it was anticipated that future heads of state would be chosen from among the four Tama a 'Aiga "matai" paramount chiefs in line with customary protocol. This is not a constitutional requirement, so Samoa can be considered a parliamentary republic rather than a constitutional monarchy. The government Press Secretariat describes Head of State as a "ceremonial president". The holder is given the formal style of Highness, as are the heads of the four paramount chiefly dynasties.

Falefā is located on the north eastern coast of Upolu island in Samoa. It was the ancient capital during the ‘Malo’ (‘government’) of Tupu Tafa'ifa (King) Fonoti. After having defeated his siblings Va'afusuaga and Samalaulu for control of Samoa, King Fonoti chose to rule from his new seat in Falefa, an honour remembered in its faalupega to this day.

General elections were held in Samoa on 31 March 2006 to determine the composition of the 14th Parliament. The main contesting parties were that of incumbent Prime Minister Tuilaʻepa Saʻilele Malielegaoi, of the Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP); and the Samoan Democratic United Party (SDUP). In addition, three other parties, the Christian Party (SCP), the Samoa Party (SP), and the Samoa Progressive Party (SPP), competed in the election. The result was a landslide victory for the HRPP, which won 33 of the 49 seats. The newly founded SDUP secured ten seats, and the remaining six were won by independents. After the election, three independents joined the HRPP, increasing the party's seat count to 36.
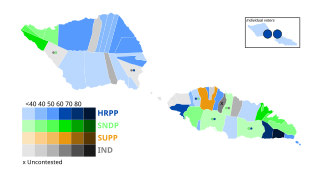
General elections were held in Samoa on 2 March 2001 to determine the composition of the 13th Parliament. Prime minister Tuilaʻepa Saʻilele Malielegaoi led the Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP) into the election. Opposition leader and former prime minister and future head of state, Tui Ātua Tupua Tamasese Efi led the Samoan National Development Party (SNDP) into the election. The HRPP won 23 seats, but initially fell short of a majority. The SNDP won 13 seats, the Samoan United People's Party secured one seat and the remaining 12 were won by independents. Following the election, all 12 independents joined the HRPP, giving the party a majority in parliament and allowing Tuila'epa to remain prime minister.

Fa'amatai is the indigenous political ('chiefly') system of Samoa, central to the organization of Samoan society. It is the traditional indigenous form of governance in both Samoas, comprising American Samoa and the Independent State of Samoa. The term comprises the prefix fa'a and the word matai.

Matāʻafa is one of the four paramount tama-a-ʻaiga titles of Samoa. It is one of two such titles originating from the Atua district at the east end of Upolu island and has its historical seat in the village of Amaile. Prominent holders of the title include Matā'afa Iosefo of Falefa, one of the three rival candidates for the kingship of Samoa during the early colonial period, Matāʻafa Faumuina Fiame Mulinuʻu I of Lepea and Lotofaga, who became leader of Samoa's pro-independence Mau movement after Tupua Tamasese Lealofi III's assassination; and his son Fiame Matāʻafa Faumuina Mulinuʻu II (1921–1975), the first Prime Minister of Samoa.

General elections were held in Samoa on 4 March 2011, to determine the composition of the 15th Parliament. Two parties contested the election, the ruling Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP), which had been in power for most of the time since 1982, led by Prime Minister Tuilaʻepa Saʻilele Malielegaoi and the newly founded Tautua Samoa Party (TSP) led by Vaʻai Papu Vailupe, which several minor parties had merged into. The election occurred following amendments to the electoral act in 2009, including the introduction of the Monotoga law, a requirement for aspiring candidates to dedicate traditional village service and commitments. As a result, three TSP aspiring candidates, including a challenger for the prime minister's seat, were disqualified by the Supreme Court for failing to satisfy this law.

Tuimaleali'ifano is one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa, known as the Tama-a-Aiga. Samoa's other three paramount chiefs are Malietoa, Mata'afa and Tupua Tamasese. The seat of the Tuimaleali'ifano title is at Falelatai in the Aʻana district.

Vailoatai is a village in southwestern Tutuila, the main island of American Samoa. It is located on the eastern end of Leone Bay. The village is known for its beautiful malae, nested along the island's rugged southern coast and lined by the fale tali mālō of its village chiefs.

Faʻatuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi is a political party in Samoa. It was founded by MP La'auli Leuatea Polataivao and is currently led by Prime Minister Fiamē Naomi Mataʻafa.