Cnidaria is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.

Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella-shaped bells and trailing tentacles, although a few are anchored to the seabed by stalks rather than being mobile. The bell can pulsate to provide propulsion for highly efficient locomotion. The tentacles are armed with stinging cells and may be used to capture prey and defend against predators. Jellyfish have a complex life cycle; the medusa is normally the sexual phase, which produces planula larvae that disperse widely and enter a sedentary polyp phase before reaching sexual maturity.
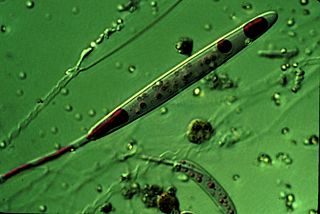
A cnidocyte is an explosive cell containing one large secretory organelle called a cnidocyst that can deliver a sting to other organisms. The presence of this cell defines the phylum Cnidaria. Cnidae are used to capture prey and as a defense against predators. A cnidocyte fires a structure that contains a toxin within the cnidocyst; this is responsible for the stings delivered by a cnidarian.

The Portuguese man o' war, also known as the man-of-war, is a marine hydrozoan found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Indian Ocean. It is considered to be the same species as the Pacific man o' war or blue bottle, which is found mainly in the Pacific Ocean. The Portuguese man o' war is the only species in the genus Physalia, which in turn is the only genus in the family Physaliidae.

Box jellyfish are cnidarian invertebrates distinguished by their box-like body. Some species of box jellyfish produce potent venom delivered by contact with their tentacles. Stings from some species, including Chironex fleckeri, Carukia barnesi, Malo kingi, and a few others, are extremely painful and often fatal to humans.

Hydrozoa are a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria.
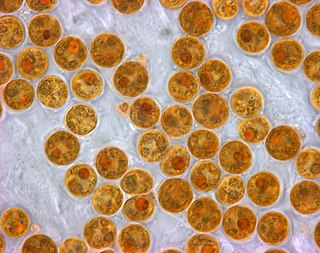
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus Symbiodinium, but some are known from the genus Amphidinium, and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true Zooxanthella K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian Collozoum inerme and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae.

Physalia is a genus of the order Siphonophorae, colonies of four specialized polyps and medusoids that drift on the surface of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans. Although these organisms look like a single multicellular organism, each specimen is actually a colony of minute organisms called zooids that have to work together for survival. A gas-filled bladder resembling a blue bottle provides buoyancy, and long tentacles of venomous cnidocytes provide a means of capturing prey. A sail on the float, which may be left or right-handed, propels Physalia about the sea, often in groups. These siphonophores sometimes become stranded on beaches, where their toxic nematocysts can remain potent for weeks or months in moist conditions. Both species of this siphonophore resemble a jellyfish in appearance, with their gas-filled float and cluster of polyps beneath, which can hang up to 30 or 165 feet below the surface of the sea.

Velella is a monospecific genus of hydrozoa in the Porpitidae family. Its only known species is Velella velella, a cosmopolitan free-floating hydrozoan that lives on the surface of the open ocean. It is commonly known by the names sea raft, by-the-wind sailor, purple sail, little sail, or simply Velella.

Medusozoa is a clade in the phylum Cnidaria, and is often considered a subphylum. It includes the classes Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Staurozoa and Cubozoa, and possibly the parasitic Polypodiozoa. Medusozoans are distinguished by having a medusa stage in their often complex life cycle, a medusa typically being an umbrella-shaped body with stinging tentacles around the edge. With the exception of some Hydrozoa, all are called jellyfish in their free-swimming medusa phase.

Glaucus atlanticus is a species of small, blue sea slug, a pelagic (open-ocean) aeolid nudibranch, a shell-less gastropod mollusk in the family Glaucidae.

Turritopsis dohrnii, also known as the immortal jellyfish, is a species of small, biologically immortal jellyfish found worldwide in temperate to tropic waters. It is one of the few known cases of animals capable of reverting completely to a sexually immature, colonial stage after having reached sexual maturity as a solitary individual. Others include the jellyfish Laodicea undulata and species of the genus Aurelia.

Fire corals (Millepora) are a genus of colonial marine organisms that exhibit physical characteristics similar to that of coral. The name coral is somewhat misleading, as fire corals are not true corals but are instead more closely related to Hydra and other hydrozoans, making them hydrocorals. They make up the only genus in the monotypic family Milleporidae.

Hydroidolina is a subclass of Hydrozoa and makes up 90% of the class. Controversy surrounds who the sister groups of Hydroidolina are, but research has shown that three orders remain consistent as direct relatives: Siphonophorae, Anthoathecata, and Leptothecata.

Turritopsis is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Oceaniidae.

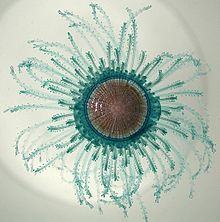
Porpita porpita, or blue button, is a marine organism consisting of a colony of hydroids found in the warmer, tropical and sub-tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, as well as the Mediterranean Sea and eastern Arabian Sea. It was first identified by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, under the basionym Medusa porpita. In addition, it is one of the two genera under the suborder Chondrophora, which is a group of cnidarians that also includes Velella. The chondrophores are similar to the better-known siphonophores, which includes the Portuguese man o' war, or Physalia physalis. Although it is superficially similar to a jellyfish, each apparent individual is actually a colony of hydrozoan polyps. The taxonomic class, Hydrozoa, falls under the phylum Cnidaria, which includes anemones, corals, and jellyfish, which explains their similar appearances.

Porpita prunella is a marine species of hydrozoan organisms within the family Porpitidae. It consists of colonies of zooids. Very little is known about this species, as there have been no confirmed sightings since its discovery in 1801 and naming by Haeckel in 1888. Being in the chondrophore group, it is likely that its behaviour is similar to the other species of the genera in the family. However there are also serious doubts as to its very existence as a separate species and may in fact be a synonym for Porpita porpita instead.

Polypodium is a genus of cnidarians that parasitizes in the eggs of sturgeon and similar fishes. It is one of the few metazoans (animals) that live inside the cells of other animals.

Zancleidae is a family of cnidarians belonging to the order Anthoathecata.