
Transport in Belgium is facilitated with well-developed road, air, rail and water networks. The rail network has 2,950 km (1,830 mi) of electrified tracks. There are 118,414 km (73,579 mi) of roads, among which there are 1,747 km (1,086 mi) of motorways, 13,892 km (8,632 mi) of main roads and 102,775 km (63,861 mi) of other paved roads. There is also a well-developed urban rail network in Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent and Charleroi. The ports of Antwerp and Bruges-Zeebrugge are two of the biggest seaports in Europe. Brussels Airport is Belgium's biggest airport.

Dover is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel, and lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. The surrounding chalk cliffs are known as the White Cliffs of Dover.

Ostend is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the largest on the Belgian coast.

Ramsgate is a seaside town in the district of Thanet in east Kent, England. It was one of the great English seaside towns of the 19th century. In 2001 it had a population of about 40,000. Ramsgate’s main attraction is its coastline, and its main industries are tourism and fishing. The town has one of the largest marinas on the English south coast, and the Port of Ramsgate provided cross-channel ferries for many years.

Stena Line is one of the largest ferry operators in the world. It services Denmark, Germany, Ireland, Latvia, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Sweden and the United Kingdom, Stena Line is a major unit of Stena AB, itself a part of the Stena Sphere. Stena Line also owns the Swedish vessels of the otherwise German- and Danish-owned Scandlines.
Hoverspeed was a ferry company that operated on the English Channel from 1981 until 2005. It was formed in 1981 by the merger of Seaspeed and Hoverlloyd. Its last owners were Sea Containers; the company ran a small fleet of two high-speed SeaCat catamaran ferries in its final year.

Sealink was a ferry company based in the United Kingdom from 1970 to 1984, operating services to France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Channel Islands, Isle of Wight and Ireland.

The Ashford to Ramsgate line is a railway that runs through Kent from Ashford to Ramsgate via Canterbury West. Its route mostly follows the course of the River Great Stour.
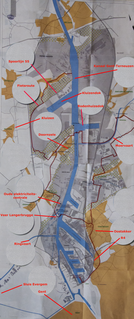
The Port of Ghent is the second busiest seaport in Belgium, located in Ghent, East Flanders in the Flemish Region. The first port of Ghent was situated at the Scheldt river and later on at the river Leie. Since the Middle Ages Ghent has sought for a connection to the sea. In the 13th century via the Lieve canal to the Zwin near Damme, in the 16th century via the Sassevaart, in the 17th century via the Ghent-Bruges Canal. Since the 19th century by the Ghent–Terneuzen Canal which connects via the Western Scheldt to the North Sea. The port of Ghent is accessible by ships of the Panamax size, and in February 2015 the construction of a new lock at Terneuzen was announced, which will maintain near-parity with those of the Panama Canal expansion project.

MS Pride of Calais was a cross-channel ferry owned and operated by P&O Ferries. She operated the Dover–Calais route between 1987 and 2012. In early 2013, under bareboat charter to Transeuropa Ferries, she served on their Ramsgate–Ostend route and was re-named MS Ostend Spirit. After further lay-up in the Port of Tilbury she was sold for scrap and finally beached at a salvage yard in Turkey on 13 November 2013.

MS Calais Seaways is a passenger and vehicle ferry operated jointly by LD Lines and DFDS Seaways between Dover and Calais.

The Port of Dover is the cross-channel port situated in Dover, Kent, south-east England. It is the nearest English port to France, at just 34 kilometres (21 mi) away, and is one of the world's busiest passenger ports, with 11.7 million passengers, 2.6 million lorries, 2.2 million cars and motorcycles and 80,000 coaches passing through it in 2017, with an annual turnover of £58.5 million a year. The Channel Tunnel in nearby Cheriton now takes an estimated 20 million passengers and 1.6 million trucks.

TransEuropa Ferries was a freight and passenger ferry company operating between Ramsgate, Kent, UK and Ostend, West Flanders, Belgium from 1998 to 2013, with three or more ships. The company suspended operations on 18 April 2013, and on 25 April 2013 the line filed to initiate bankruptcy procedures.
The Channel Ports are seaports in southern England and the facing continent, which allow for short crossings of the English Channel. There is no formal definition, but there is a general understanding of the term. Some ferry companies divide their routes into "short" and "long" crossings. The broadest definition might be from Plymouth east to Kent and from Roscoff to Zeebrugge although a tighter definition would exclude ports west of Newhaven and Dieppe. A historic group of such ports is the Cinque Ports of south-east England, most of which have ceased to be commercial ports.

Regie voor Maritiem Transport was the Belgian state-owned ferry service and operated ferries on the Ostend-Dover route under the name Oostende Lines. For the last few years until its demise in February 1997, the ferries from Ostend went to Ramsgate instead of Dover in partnership with Sally Line.
The MV Al Arabia was a roro-ferry which has seen service on several routes. The ship was built for the Belgium state-owner operator Regie voor Maritiem Transport België as the Prinses Maria Esmeralda. She sailed on the Ostend-Dover route.
Transport in Flanders is run in two levels regarding the federal nature of Belgium with certain functions run on behalf of the national Cabinet of Belgium and other functions run on behalf of Flemish Government. Therefore, the railways are run at national level by NMBS and are under the auspices of the Cabinet of Belgium, whilst the light railways are run at regional level by De Lijn under the auspices of the Flemish Government. The railway infrastructure is managed by Infrabel and thus is under the auspices of the Cabinet of Belgium.

M/F Sherbatskiy was a RORO Passenger and Freight ferry operating services between Almeria and Nador on a time-charter basis to the Spanish ferry operator Acciona Trasmediterranea. The ship was formerly called the M/F Oleander (2001-2013), P&OSL Picardy (1999-2001), Pride of Bruges (1987-1999) and Pride of Free Enterprise (1980-1987). She was operated by FerriMaroc and Comarit between 2010 and 2011 and previously owned and operated by TransEuropa Ferries between Ramsgate and Ostend. FerriMaroc owned the ferry between 2001 and 2013 and operated her between 2001 and 2010 before placing her on charter. She was scrapped at Alang in late 2015 under the name Sher.

The port of Brussels is an inland port, which is accessible for ships up to 4,500 tons and push towing convoys up to 9,000 tonnes. Via the Brussels–Scheldt Maritime Canal even sea-going vessels can reach the outer port, and through the Brussels–Charleroi Canal the transit to the Walloon region is assured. The port is located in the City of Brussels in the Brussels Capital Region.
Seaborne Freight (UK) Limited is a company that plans to run roll-on roll-off (ro-ro) ferries between the Port of Ramsgate, England and Port of Ostend, Belgium. It was formed in April 2017 and announced its plans in October 2017. It was awarded a £13.8 million contract by the UK Department for Transport in December 2018 in the case of a no-deal Brexit but there was controversy and doubts about the company's ability to provide the service and the contract was cancelled on 9 February 2019.














