The Federated States of Micronesia, or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Micronesia, a subregion of Oceania. The federation consists of four states—from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae—that are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise around 607 islands that cover a longitudinal distance of almost 2,700 km (1,700 mi) just north of the equator. They lie northeast of Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, south of Guam and the Marianas, west of Nauru and the Marshall Islands, east of Palau and the Philippines, about 2,900 km (1,800 mi) north of eastern Australia, 3,400 km (2,100 mi) southeast of Japan, and some 4,000 km (2,485 mi) southwest of the main islands of the Hawaiian Islands.

The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. The territory consists of 29 coral atolls and five islands, divided across two island chains: Ratak in the east and Ralik in the west. 97.87% of its territory is water, the largest proportion of water to land of any sovereign state. The country shares maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and the Federated States of Micronesia to the west. The capital and largest city is Majuro, home to approximately half of the country's population.

Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples.
Nauru, officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Micronesia, part of Oceania in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba of Kiribati, about 300 km (190 mi) to the east.

The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994. The Imperial Japanese South Seas Mandate had been seized by the US during the Pacific War, as Japan had administered the territory since the League of Nations gave Japan mandate over the area from Imperial Germany after World War I. However, in the 1930s, Japan left the League of Nations, and then invaded additional lands. During World War II, military control of the islands was disputed, but by the end of the war the islands had come under control of the Allies. The Trust Territory of the Pacific was created to administer the islands as part of the United States, while still under the auspices of the United Nations. Most of the island groups in the territory became independent states, with some degree of ties kept with the United States: the Federated States of Micronesia, Marshall Islands and Palau are today independent states in a Compact of Free Association with the US, while the Northern Mariana Islands remain under US jurisdiction, as an unincorporated territory and commonwealth.

This is an overview of the postage stamps and postal history of Australia.

Early mail sent to and from the Caroline Islands was occasional and dependent on visiting ships.

The South Seas Mandate, officially the Mandate for the German Possessions in the Pacific Ocean Lying North of the Equator, was a League of Nations mandate in the "South Seas" given to the Empire of Japan by the League of Nations following World War I. The mandate consisted of islands in the north Pacific Ocean that had been part of German New Guinea within the German colonial empire until they were occupied by Japan during World War I. Japan governed the islands under the mandate as part of the Japanese colonial empire until World War II, when the United States captured the islands. The islands then became the United Nations–established Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands governed by the United States. The islands are now part of Palau, the Northern Mariana Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia, and the Marshall Islands.

European exploration and settlement of Oceania began in the 16th century, starting with the Spanish (Castilian) landings and shipwrecks in the Mariana Islands, east of the Philippines. This was followed by the Portuguese landing and settling temporarily in some of the Caroline Islands and Papua New Guinea. Several Spanish landings in the Caroline Islands and New Guinea came after. Subsequent rivalry between European colonial powers, trade opportunities and Christian missions drove further European exploration and eventual settlement. After the 17th century Dutch landings in New Zealand and Australia, with no settlement in these lands, the British became the dominant colonial power in the region, establishing settler colonies in what would become Australia and New Zealand, both of which now have majority European-descended populations. States including New Caledonia (Caldoche), Hawaii, French Polynesia, and Norfolk Island also have considerable European populations. Europeans remain a primary ethnic group in much of Oceania, both numerically and economically.

The Guam kingfisher is a species of kingfisher from the United States Territory of Guam. It is restricted to a captive breeding program following its extinction in the wild due primarily to predation by the introduced brown tree snake.

The postage stamps of New Guinea, part of present-day Papua New Guinea, were issued up to 1942.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Micronesia:

The postage stamps and postal history of Papua New Guinea originated in the two colonial administrations on the eastern part of the island of New Guinea and continued until their eventual merger, followed by independence in 1975.
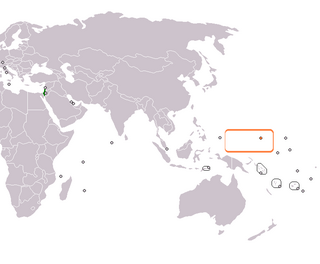
Israel – Micronesia relations are diplomatic and other relations between the State of Israel and the Federated States of Micronesia. Israel was among the first countries to establish formal diplomatic relations with Micronesia.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Tuvalu.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM).

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Palau.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Nauru.


















