
Heterobranchia, the heterobranchs, is a taxonomic clade of snails and slugs, which includes marine, aquatic and terrestrial gastropod mollusks.

Caenogastropoda is a taxonomic subclass of molluscs in the class Gastropoda. It is a large diverse group which are mostly sea snails and other marine gastropod mollusks, but also includes some freshwater snails and some land snails. The subclass is the most diverse and ecologically successful of the gastropods.

Neomphaloidea is a superfamily of deep-sea snails or limpets, marine gastropod mollusks. Neomphaloidea is the only superfamily in the order Neomphalida.

Neolepetopsidae is a family of small deep sea sea snails or true limpets, marine gastropod mollusks in the subclass Patellogastropoda.

Abyssochrysidae is a family of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Caenogastropoda.

Phenacolepadidae is a family of small sea snails or false limpets, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Cycloneritimorpha.

Seguenzioidea is a superfamily of minute to medium-sized sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Vetigastropoda.
The Hyalogyrinidae is a taxonomic family of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the informal group Lower Heterobranchia.

Alviniconcha is a genus of deep water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Provannidae. These snails are part of the fauna of the hydrothermal vents in the Indian and Western Pacific Ocean. These and another genus and species within the same family are the only known currently existing animals whose nutrition is derived from an endosymbiotic relationship with a member of bacteria from phylum Campylobacterota and Gammaproteobacteria, occurring as endosymbionts within the vacuoles of Alviniconcha ctenidia. All species of Alviniconcha are thought to be foundational species found near hydrothermal venting fluid supplying their bacterial endosymbionts with vent derived compounds such as hydrogen sulfide. These snails can withstand large variations in temperature, pH, and chemical compositions.

Abyssochrysoidea is a superfamily of deep-water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks unassigned in the orderCaenogastropoda.

Ifremeria nautilei is a species of large, deepwater hydrothermal vent sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae, and the only species in the genus Ifremeria. This species lives in the South Pacific Ocean

Provanna goniata is a species of deep-sea sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.
Provanna ios is a species of deep-sea sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.

Provanna laevis is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.

Provanna muricata is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.

Provanna sculpta is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.

Provanna segonzaci is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.
Provanna variabilis is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Provannidae.
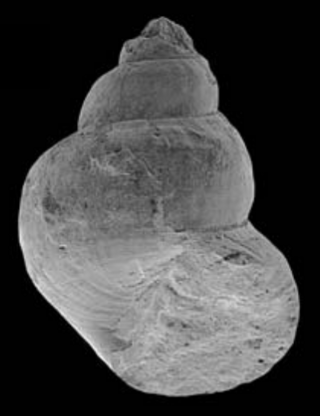
Provanna is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Provannidae.
This overview lists proposed changes in the taxonomy of gastropods at the family level and above since 2005, when the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi (2005) was published. In other words, these are recent updates in the way various groups of snails and slugs are classified.













