This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2006) |
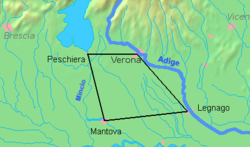
The Quadrilatero (English: Quadrilateral, for greater specificity often called the "Quadrilateral fortresses") is the traditional name of a defensive system of the Austrian Empire in the Lombardy-Venetia region of Italy, which connected the fortresses of Peschiera, Mantua, Legnago and Verona between the Mincio, the Po, and the Adige Rivers. The name refers to the fact that on a map the fortresses appear to form the vertices of a quadrilateral. In the period between the end of the Napoleonic Wars and the Revolutions of 1848, they were the only fully modernized and armed fortresses within the Empire. [1]
Contents
Starting from c. 1850, supplies and reinforcements were shipped to the positions through the new Venice-Milan railroad.
The experience of the Second Italian Independence War of 1859, in which rifled guns had been used for the first time by the Italian Army, pushed the Austrians to build a second line of eight forts, about 4 kilometers from the main line (completed in the spring of 1866), pivoting around Verona.



