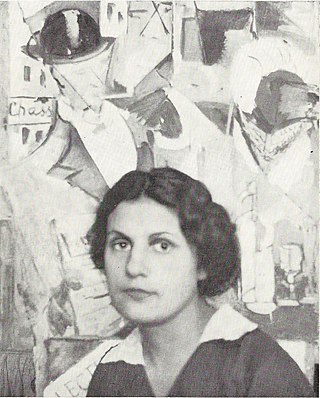Kazimir Severinovich Malevich was a Russian avant-garde artist and art theorist, whose pioneering work and writing influenced the development of abstract art in the 20th century. He was born in Kiev, modern-day Ukraine, to an ethnic Polish family. His concept of Suprematism sought to develop a form of expression that moved as far as possible from the world of natural forms (objectivity) and subject matter in order to access "the supremacy of pure feeling" and spirituality. Active primarily in Russia, Malevich was a founder of the artists collective UNOVIS and his work has been variously associated with the Russian avant-garde and the Ukrainian avant-garde, and he was a central figure in the history of modern art in Central and Eastern Europe more broadly.
Alexander Davidovich Brener, is a Russian performance artist and a self-described political activist. He is considered one of the main figures of Moscow Actionism along with Oleg Kulik.

Suprematism is an early twentieth-century art movement focused on the fundamentals of geometry, painted in a limited range of colors. The term suprematism refers to an abstract art based upon "the supremacy of pure artistic feeling" rather than on visual depiction of objects.

Aleksander Mikhailovich Rodchenko was a Russian and Soviet artist, sculptor, photographer, and graphic designer. He was one of the founders of constructivism and Russian design; he was married to the artist Varvara Stepanova.

UNOVIS was a short-lived but influential group of artists, founded and led by Kazimir Malevich at the Vitebsk Art School in 1919.

Among the collections of the Russian Museum in Saint Petersburg in Russia are some of the greatest pieces of Russian art in the world.

Cubo-Futurism or Kubo-Futurizm was an art movement, developed within Russian Futurism, that arose in early 20th century Russian Empire, defined by its amalgamation of the artistic elements found in Italian Futurism and French Analytical Cubism. Cubo-Futurism was the main school of painting and sculpture practiced by the Russian Futurists. In 1913, the term "Cubo-Futurism" first came to describe works from members of the poetry group "Hylaeans", as they moved away from poetic Symbolism towards Futurism and zaum, the experimental "visual and sound poetry of Kruchenykh and Khlebninkov". Later in the same year the concept and style of "Cubo-Futurism" became synonymous with the works of artists within Ukrainian and Russian post-revolutionary avant-garde circles as they interrogated non-representational art through the fragmentation and displacement of traditional forms, lines, viewpoints, colours, and textures within their pieces. The impact of Cubo-Futurism was then felt within performance art societies, with Cubo-Futurist painters and poets collaborating on theatre, cinema, and ballet pieces that aimed to break theatre conventions through the use of nonsensical zaum poetry, emphasis on improvisation, and the encouragement of audience participation.

Red Square is a crime novel by Martin Cruz Smith, primarily set in Moscow, Munich and Berlin between August 6 and August 21, 1991. It is a sequel to Gorky Park and Polar Star and features the Investigator Arkady Renko, taking place during the period of the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Nadezhda Andreevna Udaltsova was a Russian avant-garde artist, painter and teacher.

Productivism is an early twentieth-century art movement that is characterized by its spare geometry, limited color palette, and Cubist and Futurist influences. Aesthetically, it also looks similar to work by Kazimir Malevich and the Suprematists.

Lazar Markovich Lissitzky, better known as El Lissitzky, was a Russian artist, designer, photographer, typographer, polemicist and architect. He was an important figure of the Russian avant-garde, helping develop suprematism with his mentor, Kazimir Malevich, and designing numerous exhibition displays and propaganda works for the Soviet Union. His work greatly influenced the Bauhaus and constructivist movements, and he experimented with production techniques and stylistic devices that would go on to dominate 20th-century graphic design.

Ivan Vasilievich Kliun, or Klyun, born Klyunkov was a Russian Avant-Garde painter, sculptor and art theorist, associated with the Suprematist movement.

Suprematist Composition (blue rectangle over the red beam) is a 1916 painting by Kazimir Malevich, Ukrainian painter of Polish origin.

Soviet art is the visual art style produced after the Russian Revolution of 1917 and during the existence of the Soviet Union, until its collapse in 1991. The Russian Revolution led to an artistic and cultural shift within Russia and the Soviet Union as a whole, including a new focus on socialist realism in officially approved art.

Ukrainian avant-garde is the avant-garde movement in Ukrainian art from the end of 1890s to the middle of the 1930s along with associated artists in sculpture, painting, literature, cinema, theater, stage design, graphics, music, and architecture. Some well-known Ukrainian avant-garde artists include: Kazimir Malevich, Alexander Archipenko, Vladimir Tatlin, Sonia Delaunay, Vasyl Yermylov, Alexander Bogomazov, Aleksandra Ekster, David Burliuk, Vadym Meller, and Anatol Petrytsky. All were closely connected to the Ukrainian cities of Kyiv, Kharkiv, Lviv, and Odesa by either birth, education, language, national traditions or identity. Since it originated when Ukraine was part of the Russian Empire, Ukrainian avant-garde has been commonly lumped by critics into the Russian avant-garde movement.

The Last Futurist Exhibition of Paintings 0,10 was an exhibition presented by the Dobychina Art Bureau at Marsovo Pole, Petrograd, from 19 December 1915 to 17 January 1916. The exhibition was important in inaugurating a form of non-objective art called Suprematism, introducing a daring visual vernacular composed of geometric forms of varying colour, and in signifying the end of Russia's previous leading art movement, Cubo-Futurism, hence the exhibition's full name. The sort of geometric abstraction relating to Suprematism was distinct in the apparent kinetic motion and angular shapes of its elements.

Painterly Realism of a Peasant Woman in Two Dimensions, also known as Red Square, is a 1915 painting by Kazimir Malevich. Red Square was part of Malevich's Suprematist art movement (1915-1919), which aimed to create artworks that were universally understood.

Black Square is a 1915 oil on linen canvas painting by the Kyiv-born artist Kazimir Malevich. The first version was completed in 1915 and was described by the artist as his breakthrough work and the inception for the launch of his Suprematist art movement (1915–1919). In his manifesto for the Suprematist movement, Malevich said the works were intended as "desperate struggle to free art from the ballast of the objective world" by focusing only on pure form. He sought to create paintings that could be understood by all, that would have an emotional impact comparable to religious works.

An Englishman in Moscow, is a 1914 oil on canvas painting by Russian avant-garde artist and art theorist Kazimir Malevich.
Anna Aleksandrovna Leporskaya was a Soviet avant-garde artist. She was a recipient of several awards, including Honored Artist of the RSFSR and the Repin State Prize.