Related Research Articles
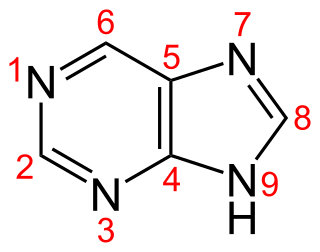
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature.
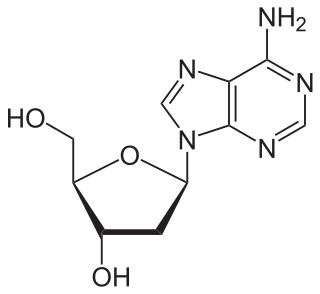
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase and a five-carbon sugar whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building blocks of DNA and RNA.

In biochemistry, a ribonucleotide is a nucleotide containing ribose as its pentose component. It is considered a molecular precursor of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Ribonucleotides themselves are basic monomeric building blocks for RNA. Deoxyribonucleotides, formed by reducing ribonucleotides with the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), are essential building blocks for DNA. There are several differences between DNA deoxyribonucleotides and RNA ribonucleotides. Successive nucleotides are linked together via phosphodiester bonds.
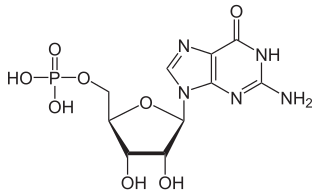
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5′-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine; hence it is a ribonucleoside monophosphate. Guanosine monophosphate is commercially produced by microbial fermentation.

Cytidine monophosphate, also known as 5'-cytidylic acid or simply cytidylate, and abbreviated CMP, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside cytidine. CMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase cytosine; hence, a ribonucleoside monophosphate. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix cytidylyl-.

Depurination is a chemical reaction of purine deoxyribonucleosides, deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine, and ribonucleosides, adenosine or guanosine, in which the β-N-glycosidic bond is hydrolytically cleaved releasing a nucleic base, adenine or guanine, respectively. The second product of depurination of deoxyribonucleosides and ribonucleosides is sugar, 2'-deoxyribose and ribose, respectively. More complex compounds containing nucleoside residues, nucleotides and nucleic acids, also suffer from depurination. Deoxyribonucleosides and their derivatives are substantially more prone to depurination than their corresponding ribonucleoside counterparts. Loss of pyrimidine bases occurs by a similar mechanism, but at a substantially lower rate.
In molecular biology, a polynucleotide is a biopolymer composed of 13 nucleotide monomers, covalently bonded in a chain. DNA and RNA are examples of polynucleotides with distinct biological functions. DNA consists of two chains of polynucleotides, with each chain in the form of a helix.

Taribavirin is an antiviral drug in Phase III human trials, but not yet approved for pharmaceutical use. It is a prodrug of ribavirin, active against a number of DNA and RNA viruses. Taribavirin has better liver-targeting than ribavirin, and has a shorter life in the body due to less penetration and storage in red blood cells. It is expected eventually to be the drug of choice for viral hepatitis syndromes in which ribavirin is active. These include hepatitis C and perhaps also hepatitis B and yellow fever.
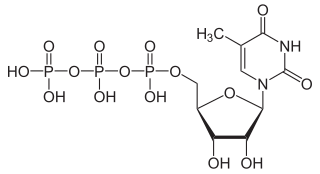
5-Methyluridine triphosphate or m5UTP is one of five nucleoside triphosphates. It is the ribonucleoside triphosphate of thymidine, but the nomenclature with "5-methyluridine" is used because the term thymidine triphosphate is used for the deoxyribonucleoside by convention.
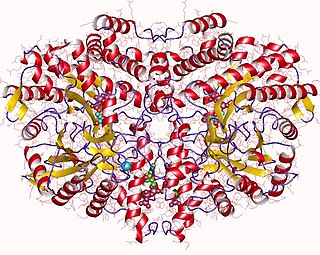
Ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase (EC 1.17.4.2, ribonucleotide reductase, 2'-deoxyribonucleoside-triphosphate:oxidized-thioredoxin 2'-oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name 2'-deoxyribonucleoside-triphosphate:thioredoxin-disulfide 2'-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Deoxycytidine diphosphate is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is related to the common nucleic acid CTP, or cytidine triphosphate, with the -OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose removed, and with one fewer phosphoryl group than CTP.
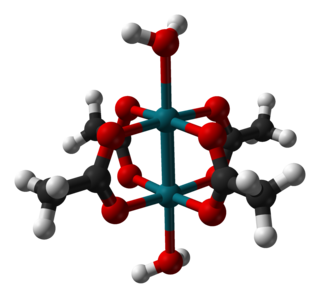
Rhodium(II) acetate is the coordination compound with the formula Rh2(AcO)4, where AcO− is the acetate ion (CH
3CO−
2). This dark green powder is slightly soluble in polar solvents, including water. It is used as a catalyst for cyclopropanation of alkenes. It is a widely studied example of a transition metal carboxylate complex.
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.

Xanthosine monophosphate also called Xanthylate is an intermediate in purine metabolism. It is a ribonucleoside monophosphate. It is formed from IMP via the action of IMP dehydrogenase, and it forms GMP via the action of GMP synthase. Also, XMP can be released from XTP by enzyme deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase containing (d)XTPase activity.
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors are a family of anti-cancer drugs that interfere with the growth of tumor cells by blocking the formation of deoxyribonucleotides.
Synthesis of nucleosides involves the coupling of a nucleophilic, heterocyclic base with an electrophilic sugar. The silyl-Hilbert-Johnson reaction, which employs silylated heterocyclic bases and electrophilic sugar derivatives in the presence of a Lewis acid, is the most common method for forming nucleosides in this manner.

Deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) is one of the four nucleoside triphosphates that are used in the in vivo synthesis of DNA. Unlike the other deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, thymidine triphosphate does not always contain the "deoxy" prefix in its name. The corresponding ribonucleoside triphosphate is called uridine triphosphate.
A riboside is any glycoside of ribose. Ribosides in the form of ribonucleosides and ribonucleotides play an important role in biochemistry.
Ribonuclease T2 is an enzyme. It is a type of endoribonuclease. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Vanadyl ribonucleoside is a potent transition-state analog of ribonucleic acid and potent inhibitor of many species of ribonuclease formed from a vanadium coordination complex and one ribonucleoside. Vanadium's [Ar] 3d3 4s2 electron configuration allows it to make five sigma bonds and two pi bonds with adjacent atoms.
References
- ↑ Ribonucleosides at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ "Ribonucleoside". Science Direct . 2007. Retrieved February 3, 2022.