Related Research Articles
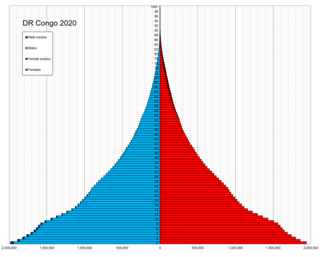
This article is about the demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo has declined drastically around the 1980s, despite being home to vast potential in natural resources and mineral wealth; their gross domestic product is $48.994 billion as of 2019.
Telecommunications in the Democratic Republic of the Congo include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a country in Central Africa bordered to the west by the South Atlantic Ocean. By area, the DRC is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 108 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the nation's economic center. The country is bordered to the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, and the Cabinda exclave of Angola.

The United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo or MONUSCO, an acronym based on its French name Mission de l'Organisation des Nations Unies pour la stabilisation en République démocratique du Congo, is a United Nations peacekeeping force in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) which was established by the United Nations Security Council in resolutions 1279 (1999) and 1291 (2000) to monitor the peace process of the Second Congo War, though much of its focus subsequently turned to the Ituri conflict, the Kivu conflict and the Dongo conflict. The mission was known as the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo or MONUC, an acronym of its French name Mission de l'Organisation des Nations Unies en République démocratique du Congo, until 2010.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the Democratic Republic of the Congo face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal for both males and females in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), although LGBT individuals may still be targeted for prosecution under public indecency provisions on occasion.
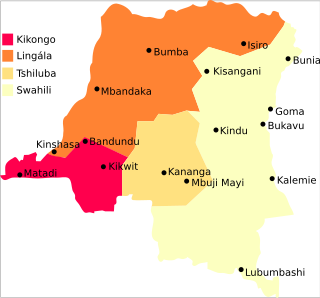
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a multilingual country where an estimated total of 242 languages are spoken. Ethnologue lists 215 living languages. The official language, inherited from the colonial period, is French. Four other languages, three of them indigenous, have the status of national language: Kikongo, Lingala, Swahili and Tshiluba.

Rugby Africa, is the administrative body for rugby union within the continent of Africa under the authority of World Rugby, which is the world governing body of rugby union. As of 2018, Rugby Africa has 37 member nations and runs several rugby tournaments for national teams, including the Africa Cup which is the main 15-a-side competition for African national teams.
Articles related to the Democratic Republic of the Congo include:

The Court of Cassation is the main court of last resort in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has its seat in the Kinshasa Palace of Justice.

The mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo produces copper, diamonds, tantalum, tin, gold, and more than 63% of global cobalt production. Minerals and petroleum are central to the DRC's economy, making up more than 95% of value of its exports.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo was a net energy exporter in 2008. Most energy was consumed domestically in 2008. According to the IEA statistics the energy export was in 2008 small and less than from the Republic of Congo. 2010 population figures were 3.8 million for the RC compared to CDR 67.8 Million.
Rugby union in Benin is a minor but growing sport.
Rugby union in the Republic of the Congo is a minor but growing sport

The African Nations Championship, known for sponsorship purposes as the TotalEnergies African Nations Championship and commonly abbreviated as CHAN, is a biennial African national association football tournament organized by the Confederation of African Football (CAF) since 2009 and first announced on 11 September 2007. The participating nations must consist of players playing in their national league competitions.
The 2014 Africa Cup was the fourteenth edition of the Africa Cup, an annual international rugby union tournament for African nations organised by the Confederation of African Rugby (CAR). The tournament, as well as the 2012 and 2013 editions of it, served as the qualifiers for the 2015 Rugby World Cup.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Democratic Republic of the Congo. The DRC is a strategic partner of Kenya in many areas, particularly trade and security.

General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 30 December 2018, to determine a successor to President Joseph Kabila, as well as for the 500 seats of the National Assembly and the 715 elected seats of the 26 provincial assemblies. Félix Tshisekedi (UDPS) won with 38.6% of the vote, defeating another opposition candidate, Martin Fayulu, and Emmanuel Ramazani Shadary, backed by the ruling party PPRD. Fayulu alleged that the vote was rigged against him in a deal made by Tshisekedi and outgoing President Kabila, challenging the result in the DRC's Constitutional Court. Different election observers, including those from the country's Roman Catholic Church, also cast doubt on the official result. Nonetheless on 20 January the Court rejected his appeal and declared Tshisekedi as the winner. Parties supporting President Kabila won the majority of seats in the National Assembly. Félix Tshisekedi was sworn in as the 5th President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 24 January 2019, making it the first peaceful transition of power in the country since it became independent from Belgium in 1960.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–Holy See relations refers to the current relationship between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Holy See. The two states have seen an increase in their cooperation in recent years, and due to the large number of Roman Catholics in the DRC, President Joseph Kabila has made an effort to maintain good relations with the Vatican.
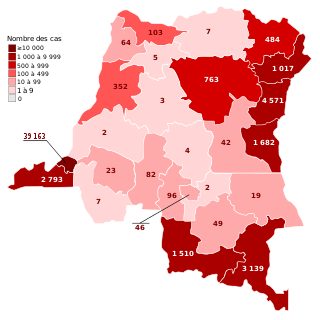
The COVID-19 pandemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 10 March 2020. The first few confirmed cases were all outside arrivals.