Related Research Articles

The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael, is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001.

The Data Encryption Standard is a symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of digital data. Although its short key length of 56 bits makes it too insecure for modern applications, it has been highly influential in the advancement of cryptography.
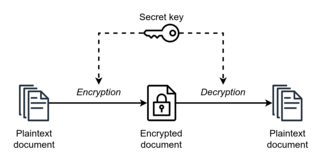
Symmetric-key algorithms are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys. The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link. The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to public-key encryption. However, symmetric-key encryption algorithms are usually better for bulk encryption. With exception of the one-time pad they have a smaller key size, which means less storage space and faster transmission. Due to this, asymmetric-key encryption is often used to exchange the secret key for symmetric-key encryption.
In cryptography, Lucifer was the name given to several of the earliest civilian block ciphers, developed by Horst Feistel and his colleagues at IBM. Lucifer was a direct precursor to the Data Encryption Standard. One version, alternatively named DTD-1, saw commercial use in the 1970s for electronic banking.
In cryptography, Skipjack is a block cipher—an algorithm for encryption—developed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA). Initially classified, it was originally intended for use in the controversial Clipper chip. Subsequently, the algorithm was declassified.

The GOST block cipher (Magma), defined in the standard GOST 28147-89, is a Soviet and Russian government standard symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 64 bits. The original standard, published in 1989, did not give the cipher any name, but the most recent revision of the standard, GOST R 34.12-2015, specifies that it may be referred to as Magma. The GOST hash function is based on this cipher. The new standard also specifies a new 128-bit block cipher called Kuznyechik.
In cryptography, Camellia is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits. It was jointly developed by Mitsubishi Electric and NTT of Japan. The cipher has been approved for use by the ISO/IEC, the European Union's NESSIE project and the Japanese CRYPTREC project. The cipher has security levels and processing abilities comparable to the Advanced Encryption Standard.
MARS is a block cipher that was IBM's submission to the Advanced Encryption Standard process. MARS was selected as an AES finalist in August 1999, after the AES2 conference in March 1999, where it was voted as the fifth and last finalist algorithm.

In cryptography, LOKI97 is a block cipher which was a candidate in the Advanced Encryption Standard competition. It is a member of the LOKI family of ciphers, with earlier instances being LOKI89 and LOKI91. LOKI97 was designed by Lawrie Brown, assisted by Jennifer Seberry and Josef Pieprzyk.
In cryptography, MISTY1 is a block cipher designed in 1995 by Mitsuru Matsui and others for Mitsubishi Electric.
In cryptography, SAFER is the name of a family of block ciphers designed primarily by James Massey on behalf of Cylink Corporation. The early SAFER K and SAFER SK designs share the same encryption function, but differ in the number of rounds and the key schedule. More recent versions — SAFER+ and SAFER++ — were submitted as candidates to the AES process and the NESSIE project respectively. All of the algorithms in the SAFER family are unpatented and available for unrestricted use.
In cryptography, Khufu and Khafre are two block ciphers designed by Ralph Merkle in 1989 while working at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center. Along with Snefru, a cryptographic hash function, the ciphers were named after the Egyptian Pharaohs Khufu, Khafre and Sneferu.
In cryptography, impossible differential cryptanalysis is a form of differential cryptanalysis for block ciphers. While ordinary differential cryptanalysis tracks differences that propagate through the cipher with greater than expected probability, impossible differential cryptanalysis exploits differences that are impossible at some intermediate state of the cipher algorithm.
In cryptography, DFC is a symmetric block cipher which was created in 1998 by a group of researchers from École Normale Supérieure, CNRS, and France Télécom and submitted to the AES competition.
In cryptography, Hierocrypt-L1 and Hierocrypt-3 are block ciphers created by Toshiba in 2000. They were submitted to the NESSIE project, but were not selected. Both algorithms were among the cryptographic techniques recommended for Japanese government use by CRYPTREC in 2003, however, both have been dropped to "candidate" by CRYPTREC revision in 2013.
In cryptography, ARIA is a block cipher designed in 2003 by a large group of South Korean researchers. In 2004, the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards selected it as a standard cryptographic technique.
In cryptography, CIPHERUNICORN-A is a block cipher created by NEC in 2000. It was among the cryptographic techniques recommended for Japanese government use by CRYPTREC in 2003. However, it has been dropped to "candidate" level by the CRYPTREC revision of 2013.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cryptography:

In cryptography, Twofish is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes up to 256 bits. It was one of the five finalists of the Advanced Encryption Standard contest, but it was not selected for standardization. Twofish is related to the earlier block cipher Blowfish.
In cryptography, a round or round function is a basic transformation that is repeated (iterated) multiple times inside the algorithm. Splitting a large algorithmic function into rounds simplifies both implementation and cryptanalysis.
References
- ↑ Lars Knudsen, Håvard Raddum (7 March 2001). "A first report on Whirlpool, NUSH, SC2000, Noekeon, Two-Track-MAC and RC6" (PDF). Retrieved 8 February 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Hitoshi Yanami, Takeshi Shimoyama, Orr Dunkelman (2000). Differential and Linear Cryptanalysis of a Reduced-Round SC2000 (PDF/PostScript). Proceedings of Second Open NESSIE Workshop. Retrieved 8 February 2007.
{{cite conference}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Jiqiang Lu (July 2011). "Differential Attack on Five Rounds of the SC2000 Block Cipher" (PDF). Journal of Computer Science and Technology. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
- ↑ Alex Biryukov; Ivica Nikolić (10 November 2014). "Colliding Keys for SC2000-256" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)