| Schwannoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | neurilemoma, [1] : 621 neuroma, [2] neurolemoma, [2] Schwann cell tumor [2] |
 | |
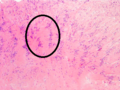
| Micrograph of a schwannoma showing both a cellular Antoni A area (top) and a loose paucicellular Antoni B area (bottom). HE stain. | |
| Specialty | Neuro-oncology |
A schwannoma (or neurilemmoma) is a usually benign nerve sheath tumor comprising Schwann cells, which normally produce the insulating myelin sheath covering peripheral nerves.
Contents
Schwannomas are homogeneous tumors, consisting only of Schwann cells. The tumor cells always stay on the outside of the nerve, but the tumor itself may either push the nerve aside and/or up against a bony structure (thereby possibly causing damage). Schwannomas are relatively slow-growing. For reasons not yet understood, schwannomas are mostly benign and less than 1% become malignant, degenerating into a form of cancer known as neurofibrosarcoma. These masses are generally contained within a capsule, so surgical removal is often successful. [3]
Schwannomas can be associated with neurofibromatosis type II, which may be due to a loss-of-function mutation in the protein merlin. [4] They are universally S-100 positive, which is a marker for cells of neural crest cell origin.
Schwannomas of the head and neck are a fairly common occurrence and can be found incidentally in 3–4% of patients at autopsy. [4] Most common of these is a vestibular schwannoma, a tumor of the vestibulocochlear nerve that may lead to tinnitus and hearing loss on the affected side. Outside the cranial nerves, schwannomas may present on the flexor surfaces of the limbs. Rare occurrences of these tumors in the penis have been documented in the literature. [5]
Verocay bodies are seen histologically in schwannomas.