
A cereal is any grass cultivated for its edible grain, which is composed of an endosperm, a germ, and a bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food energy worldwide than any other type of crop and are therefore staple crops. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize. Edible grains from other plant families, such as buckwheat, quinoa, and chia, are referred to as pseudocereals.

Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diet. It is one of the oldest human-made foods, having been of significance since the dawn of agriculture, and plays an essential role in both religious rituals and secular culture.

Porridge is a food made by heating or boiling ground, crushed or chopped starchy plants, typically grain, in milk or water. It is often cooked or served with added flavourings such as sugar, honey, fruit, or syrup to make a sweet cereal, or it can be mixed with spices, meat, or vegetables to make a savoury dish. It is usually served hot in a bowl, depending on its consistency. Oat porridge, or oatmeal, is one of the most common types of porridge. Gruel is a thinner version of porridge and congee is a savoury variation of porridge of Asian origin.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities.

A bagel is a bread roll originating in the Jewish communities of Poland. Bagels are traditionally made from yeasted wheat dough that is shaped by hand into a torus or ring, briefly boiled in water, and then baked. The result is a dense, chewy, doughy interior with a browned and sometimes crisp exterior.

Soda bread is a variety of quick bread traditionally made in a variety of cuisines in which sodium bicarbonate is used as a leavening agent instead of the traditional yeast. The ingredients of traditional soda bread are flour, baking soda, salt, and buttermilk. The buttermilk in the dough contains lactic acid, which reacts with the baking soda to form tiny bubbles of carbon dioxide. Other ingredients can be added, such as butter, egg, raisins, or nuts. An advantage of quick breads is their ability to be prepared quickly and reliably, without requiring the time-consuming skilled labor and temperature control needed for traditional yeast breads.

White bread typically refers to breads made from wheat flour from which the bran and the germ layers have been removed from the whole wheatberry as part of the flour grinding or milling process, producing a light-colored flour.
Wheat flour is a powder made from the grinding of wheat used for human consumption. Wheat varieties are called "soft" or "weak" if gluten content is low, and are called "hard" or "strong" if they have high gluten content. Hard flour, or bread flour, is high in gluten, with 12% to 14% gluten content, and its dough has elastic toughness that holds its shape well once baked. Soft flour is comparatively low in gluten and thus results in a loaf with a finer, crumbly texture. Soft flour is usually divided into cake flour, which is the lowest in gluten, and pastry flour, which has slightly more gluten than cake flour.
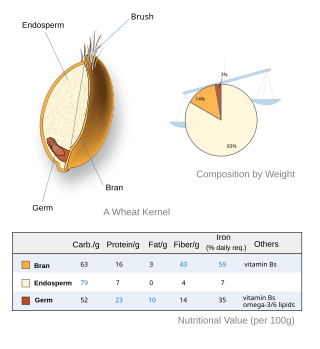
A whole grain is a grain of any cereal and pseudocereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm.

A flatbread is a bread made with flour; water, milk, yogurt, or other liquid; and salt, and then thoroughly rolled into flattened dough. Many flatbreads are unleavened, although some are leavened, such as pita bread.

Rye bread is a type of bread made with various proportions of flour from rye grain. It can be light or dark in color, depending on the type of flour used and the addition of coloring agents, and is typically denser than bread made from wheat flour. Compared to white bread, it is higher in fiber, darker in color, and stronger in flavor. The world's largest exporter of rye bread is Poland.

A teacake in England is generally a light yeast-based sweet bun containing dried fruit, typically served toasted and buttered. In the U.S. teacakes can be cookies or small cakes. In Sweden, they are soft, round, flat wheat breads made with milk and a little sugar, and used to make buttered ham or cheese sandwiches. In India and Australia, a teacake is more like a butter cake. Tea refers to the popular beverage to which these baked goods are an accompaniment.

Kama or talkkuna or tolokno, talqan is a traditional Estonian, Finnish, Russian, Turkic finely milled flour mixture. The kama or talkkuna powder is a mixture of roasted barley, rye, oat and pea flour. The oat flour may be completely replaced by wheat flour, or kibbled black beans may be added to the mixture. In Finland talkkuna is made by first steaming grains, then grinding them up and finally roasting them into talkkuna.
Traditional Estonian cuisine has substantially been based on meat and potatoes, and on fish in coastal and lakeside areas, but now bears influence from many other cuisines, including a variety of international foods and dishes, with a number of contributions from the traditions of nearby countries. Scandinavian, German, Russian, Latvian, Lithuanian and other influences have played their part. The most typical foods in Estonia have been rye bread, pork, potatoes and dairy products. Estonian eating habits have historically been closely linked to the seasons. In terms of staples, Estonia belongs firmly to the beer, vodka, rye bread and pork "belt" of Europe.
Bread is a staple food throughout Europe. Throughout the 20th century, there was a huge increase in global production, mainly due to a rise in available, developed land throughout Europe, North America and Africa.

Udmurt cuisine consists of the cuisine of Udmurtia and the Udmurt people, and is characterized by the rich use of local foods. Old traditions include foods made from grains and flour, especially milled rye, barley, wheat, and buckwheat. Meat, vegetables and black bread are staple foods in Udmurt cuisine. Additional foods include pelmeni, pancakes, pastries and small tarts. Milk is a scarce commodity, and that which exists is often made into ayran, a type of sour milk.

Barley flour is a flour prepared from dried and ground barley. Barley flour is used to prepare barley bread and other breads, such as flat bread and yeast breads.















