
The California Zephyr was a passenger train that ran between Chicago, Illinois, and Oakland, California, via Omaha, Denver, Salt Lake City, Winnemucca, Oroville and Pleasanton in the United States. It was operated by the Chicago, Burlington & Quincy (CB&Q), Denver & Rio Grande Western (D&RGW) and Western Pacific (WP) railroads, all of which dubbed it "the most talked about train in America" on March 19, 1949, with the first departure the following day. The train was scheduled to pass through the most spectacular scenery on its route in the daylight. The original train ceased operation in 1970, though the D&RGW continued to operate its own passenger service, the Rio Grande Zephyr, between Salt Lake City and Denver, using the original equipment until 1983. In 1983 a second iteration of the California Zephyr, an Amtrak service, was formed. The current version of the California Zephyr operates partially over the route of the original Zephyr and partially over the route of its former rival, the City of San Francisco.
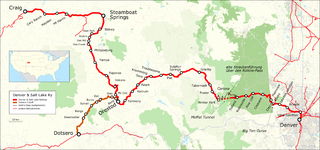
The Denver and Salt Lake Railway (D&SL) was a U.S. railroad company located in Colorado. Originally incorporated in 1902 as the Denver, Northwestern and Pacific (DN&P) Railway, it had as a goal a direct connection of Denver, Colorado, with Salt Lake City, Utah. It underwent numerous reorganizations throughout its financially troubled history and by the time the company was acquired in 1931 by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, it had advanced only as far as Craig, Colorado. After the acquisition the line was connected to the D&RGW main, and the eastern half of the line was used to give the D&RGW a more direct route to Denver. The portions of the railroad still in use today are known as the Moffat Tunnel Subdivision of Union Pacific Railroad's Central Corridor. Amtrak’s California Zephyr service from Denver to Glenwood Springs follows much of the old D&SL route.

The Nevada Northern Railway was a railroad in the U.S. state of Nevada, built primarily to reach a major copper producing area in White Pine County, Nevada. The railway, constructed in 1905–06, extended northward about 140 miles (230 km) from Ely to connections with the Western Pacific Railroad at Shafter and Southern Pacific Railroad at Cobre. In 1967 NN reported 40 million net ton-miles of revenue freight on 162 miles (261 km) of line.

The Nevada Northern Railway Museum is a railroad museum and heritage railroad located in Ely, Nevada, owned by the State of Nevada and operated by a historic foundation dedicated to the preservation of the Nevada Northern Railway.

Interstate 80 (I-80) traverses the northern portion of the US state of Nevada. The freeway serves the Reno metropolitan area and passes through the towns of Fernley, Lovelock, Winnemucca, Battle Mountain, Carlin, Elko, Wells, and West Wendover on its way through the state.

State Route 233 (SR 233) is a 34.256-mile (55.130 km) state highway in rural eastern Elko County, Nevada, United States. The highway follows the route of the First transcontinental railroad from Interstate 80 (I-80) to the Utah state line. The highway was formerly numbered State Route 30.

The Los Angeles and Salt Lake Railroad was a rail company in California, Nevada, and Utah in the United States, that completed and operated a railway line between its namesake cities, via Las Vegas, Nevada. Incorporated in Utah in 1901 as the San Pedro, Los Angeles and Salt Lake Railroad, the line was largely the brainchild of William Andrews Clark, a Montana mining baron and United States Senator. Clark enlisted the help of Utah's U.S. Senator Thomas Kearns, mining magnate and newspaper man, to ensure the success of the line through Utah. Construction of the railroad's main line was completed in 1905. Company shareholders adopted the LA&SL name in 1916. The railway was also known by its official nickname, "The Salt Lake Route", and was sometimes informally referred to as "The Clark Road". The tracks are still in use by the modern Union Pacific Railroad, as the Cima, Caliente, Sharp, and Lynndyl Subdivisions.

The Feather River Route is a rail line that was built and operated by the Western Pacific Railroad. It was constructed between 1906 and 1909, and connects the cities of Oakland, California, and Salt Lake City, Utah. The line was built to compete with the Central Pacific Railroad, which at the time held a nearly complete monopoly on Northern California rail service. The route derives its name from its crossing of the Sierra Nevada, where it follows both the North and Middle Forks of the Feather River. The route is famous for its impressive engineering qualities and its considerable scenic value. All of the route is now owned and operated by the Union Pacific Railroad; however, the Union Pacific has transferred significant portions of the route to other lines. The portion still called the Feather River Route by the Union Pacific runs from the California Central Valley to Winnemucca, Nevada and has been divided into three subdivisions named the Sacramento, Canyon and Winnemucca subdivisions.

Interstate 80 (I-80) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey. The portion of the highway in the US state of Utah is 197.51 miles (317.86 km) long through the northern part of the state. From west to east, I-80 crosses the state line from Nevada in Tooele County and traverses the Bonneville Salt Flats—which are a part of the larger Great Salt Lake Desert. It continues alongside the Wendover Cut-off—the corridor of the former Victory Highway—US Route 40 (US-40) and the Western Pacific Railroad Feather River Route. After passing the Oquirrh Mountains, I-80 enters the Salt Lake Valley and Salt Lake County. A short portion of the freeway is concurrent with I-15 through Downtown Salt Lake City. At the Spaghetti Bowl, I-80 turns east again into the mouth of Parleys Canyon and Summit County, travels through the mountain range, and intersects the eastern end of I-84 near Echo Reservoir before turning northeast toward the Wyoming border near Evanston. I-80 was built along the corridor of the Lincoln Highway and the Mormon Trail through the Wasatch Range. The easternmost section also follows the historical routes of the first transcontinental railroad and US-30S.

The Carlin Tunnel is a collective name for a set of four tunnel bores in the Humboldt River's Carlin Canyon, east of Carlin in Elko County, Nevada, United States. The two railroad bores were constructed for different purposes at different times, while the two highway bores were constructed concurrently, all with the goal of bypassing a sharp bend in the river. Currently, two of the bores carry Interstate 80, while the other two bores carry Union Pacific Railroad's Overland Route and Central Corridor. Bridges over the Humboldt River are adjacent to both portals of three tubes, including the two freeway bores and one of the railroad bores.

U.S. Route 6 (US-6) is an east–west United States Numbered Highway through the central part of the U.S. state of Utah. Although it is only about 40 miles (64 km) longer than US-50, it serves more populated areas and, in fact, follows what had been US-50's routing until it was moved to follow Interstate 70 (I-70) in 1976. In 2009, the Utah State Legislature named part of the route the "Mike Dmitrich Highway", named after the Utah state senator, which generated controversy, as the state of Utah had previously joined with all the other states through which US-6 passes in naming all of US-6 the Grand Army of the Republic Highway.

The Utah Division of the former Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad (D&RGW) is a rail line that connects Grand Junction, Colorado and Salt Lake City, Utah in the Western United States. It is now incorporated into the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) system as part of the Central Corridor. The modern Union Pacific has split the line into two subdivisions for operational purposes, the Green River Subdivision between Grand Junction and Helper, Utah and the Provo Subdivision from Helper to Salt Lake City. Daily passenger service is provided by Amtrak's California Zephyr; the BNSF Railway and Utah Railway have trackage rights over the line.
The Lynndyl Subdivision is a rail line owned and operated by the Union Pacific Railroad in the U.S. state of Utah, running from Salt Lake City southwest to Milford, where the Caliente Subdivision continues towards Los Angeles. It was formerly part of the Los Angeles and Salt Lake Railroad and a section currently forms a segment of Union Pacific's Central Corridor. The subdivision is named for Lynndyl, a small community along the rail line. The highest elevation attained on the line is 6,061 feet (1,847 m) at Tintic. As of 2003 the line sees 16 trains daily between Lynndyl and Smelter.

The Overland Route was a train route operated jointly by the Union Pacific Railroad and the Central Pacific Railroad / Southern Pacific Railroad, between Council Bluffs, Iowa / Omaha, Nebraska, and the San Francisco Bay Area, over the grade of the first transcontinental railroad which had been opened on May 10, 1869. Passenger trains that operated over the line included the Overland Flyer, later renamed the Overland Limited, which also included a connection to Chicago. Although these passenger rail trains are no longer in operation, the Overland Route remains a common name for the line from Northern California to Chicago, now owned entirely by the Union Pacific. Although now primarily used for freight, a few portions still provide the route for the California Zephyr passenger train.
The Utah Southern Railroad was built by members of the church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints in 1871-2 to connect Salt Lake City to points south. The line was acquired by the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) in 1875. The Utah Southern Railroad name was initially kept as a separate division of the UP, but over time the line was moved around and divided among different UP subsidiaries. While most of the corridor is still used today it is no longer contiguous. The southern portion of the line, from Provo to Lynndyl, remains under UP ownership and is today known as the Sharp Subdivision. The portion through the Salt Lake Valley is today owned by the Utah Transit Authority and used for the TRAX light rail system, primarily the Blue Line. The portion between the end of the Blue line and Provo has had the rails removed, however UTA has retained the right to extend the TRAX system to Provo along the former Utah Southern right of way.

The Central Corridor is a rail line operated by the Union Pacific Railroad from near Winnemucca, Nevada to Denver, Colorado in the western United States. The line was created after the merger with the Southern Pacific Transportation Company by combining portions of lines built by former competitors. No portion of the line was originally built by the Union Pacific; in fact, some portions were built specifically to compete with the Union Pacific's Overland Route. The line is known for significant feats of engineering while crossing the Wasatch Mountains of Utah and the Rocky Mountains of Colorado. The line features numerous tunnels, the longest and highest of these is the Moffat Tunnel.

The California Zephyr is a long-distance passenger train operated by Amtrak between Chicago and the San Francisco Bay Area, via Omaha, Denver, Salt Lake City, and Reno. At 2,438 miles (3,924 km), it is Amtrak's longest daily route, and second-longest overall after the Texas Eagle's triweekly continuation from San Antonio to Los Angeles, with travel time between the termini taking approximately 511⁄2 hours. Amtrak claims the route as one of its most scenic, with views of the upper Colorado River valley in the Rocky Mountains, and the Sierra Nevada. The modern train is the second iteration of a train named California Zephyr; the original train was privately operated and ran on a different route through Nevada and California.
The Elko Subdivision is a railway line in Nevada owned and operated by the Union Pacific Railroad running from Weso to the freight yard in Elko. It is part of both the Overland Route and the Central Corridor. The line generally follows the Humboldt River and has several small tunnels while traversing the Palisade and Carlin Canyons, the longest tunnel is called the Carlin Tunnel.
















