
The Levant is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of West Asia and core territory of the political term Middle East. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in western Asia: i.e. the historical region of Syria, which includes present-day Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the Palestinian territories and most of Turkey southwest of the middle Euphrates. Its overwhelming characteristic is that it represents the land bridge between Africa and Eurasia. In its widest historical sense, the Levant included all of the Eastern Mediterranean with its islands; that is, it included all of the countries along the Eastern Mediterranean shores, extending from Greece in Southern Europe to Cyrenaica, Eastern Libya in Northern Africa.
Arabic music is the music of the Arab world with all its diverse music styles and genres. Arabic countries have many rich and varied styles of music and also many linguistic dialects, with each country and region having their own traditional music.

The music of Palestine is one of many regional subgenres of Arabic music. While it shares much in common with Arabic music, both structurally and instrumentally, there are musical forms and subject matter that are distinctively Palestinian.
Regarding the music of Syria, there are certain musical traditions and practices that have been present in Syria longer than others. There have been musical influences introduced into Syria through multiple eras of conquest and influences from surrounding cultures in modern-day Syria. Lying near Egypt and Israel, and connected to southern Europe by the Mediterranean, Syria became host to many distinct cultural musics through trade and route. The music present in Syria is related greatly to poetry, influenced greatly by the Bedouin nomadic tribes, the maqam system in Arabic classical music, as well as influenced greatly by the geopolitical movement and conflict in the Middle East. Syrian music generally has a singer who is accompanied by three or four instruments. The texture is usually thin but can become denser depending on the use of each instrument. Music is tightly linked to poetry in Syria.
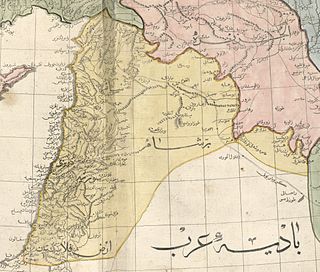
Southern Syria is the southern part of the Syria region, roughly corresponding to the Southern Levant. Typically it refers chronologically and geographically to the southern part of Ottoman Syria provinces.

In Arabic music, a mizmār is any single or double reed wind instrument. In Egypt, the term mizmar usually refers to the conical shawm that is called zurna in Turkey and Armenia.
The mijwiz is a traditional Middle East musical instrument popular in Syria, Palestine, Lebanon and Jordan. Its name in Arabic means "dual," because of its consisting of two, short, bamboo pipes with reed tips put together, making the mijwiz a double-pipe, single-reed woodwind instrument.
Over recorded history, there have been many names of the Levant, a large area in the Near East, or its constituent parts. These names have applied to a part or the whole of the Levant. On occasion, two or more of these names have been used at the same time by different cultures or sects. As a natural result, some of the names of the Levant are highly politically charged. Perhaps the least politicized name is Levant itself, which simply means "where the sun rises" or "where the land rises out of the sea", a meaning attributed to the region's easterly location on the shore of the Mediterranean Sea.

The various nations of the region include the Arabic-speaking countries of the Middle East, the Iranian traditions of Persia, the Jewish music of Israel and the diaspora, Armenian music. Azeri Music, the varied traditions of Cypriot music, the Turkish music of Turkey, traditional Assyrian music, Coptic ritual music in Egypt as well as other genres of Egyptian music in general. It is widely regarded that some Middle-Eastern musical styles have influenced Central Asia, as well as the Balkans and Spain.

Dabke is a Levantine folk dance. Dabke combines circle dance and line dancing and is widely performed at weddings and other joyous occasions. The line forms from right to left and the leader of the dabke heads the line, alternating between facing the audience and the other dancers. In English, it can be transcribed as dabka, dabki, dabkeh.

The culture of Palestinians is influenced by the many diverse cultures and religions which have existed in the historical region of Palestine and the state of Palestine. The cultural and linguistic heritage of Palestinian Arabs along with Lebanese, Syrians, and Jordanians is integral part of levantine Arab culture

Sunni Islam is a major religion in Palestine, being the religion of the majority of the Palestinian population. Muslims comprise 85% of the population of the West Bank, when including Israeli settlers, and 99% of the population of the Gaza Strip. The largest denomination among Palestinian Muslims are Sunnis, comprising 98–99% of the total Muslim population.

The Mashriq, also known as the Arab Mashriq, sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb sharaqa, from the sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises.

Syria or Sham is a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other synonyms are Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. In modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Syrian Arab Republic.
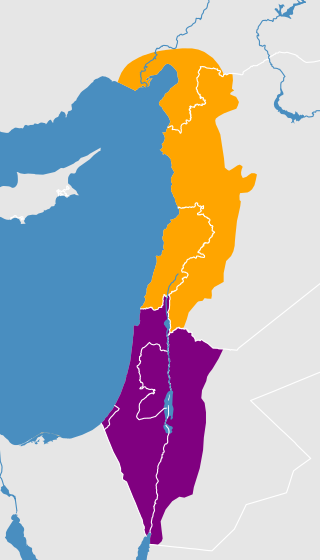
Palestinian Arabic is a dialect continuum of mutually intelligible varieties of Levantine Arabic spoken by most Palestinians in Palestine, Israel and in the Palestinian diaspora.

Electrowavez is an Arab psychedelic trance group formed in 2008, comprising two members, the brothers Charlie Shaabi and Richard Savo.
Mahragan, also Mahraganat or Egyptian electro, Egyptian street music, shaabi-electro, is a popular genre of Egyptian folk music. Mahraganat is a combination of working class popular Egyptian music (shaabi) played at weddings, EDM and hip-hop, with heavy autotune use. DJ Figo made the genre more well known with his team "set dyaba" released during the 2011 Egyptian Revolution. Although this may be the first ever track to go mainstream, Mahraganat was conceived early by several Egyptian underground artists as DJ Ahmed Figo, El Sadat, Feelo and Alaa Fifty in 2004. They shared their music via MP3 files and phones, and it could be heard playing everywhere in taxis, tuktuks and on the street, since Egyptian Shaabi music has always been considered as the true soul of Egypt, given how powerful it is. Another Mahragan mix was released by the same group of friends in 2006 and it was called "Mahragan Elsalam", named after their neighbourhood 'Elsalam' in northeastern Cairo, it talked about friendship and how to be mature.

Arab folk dances, also referred to as Oriental dance, Middle-Eastern dance and Eastern dance, are the traditional folk dances of the Arabs in Arab world. Arab dance has many different styles, including the three main types of folklore, classical, and contemporary. It is enjoyed and implemented throughout the Arab region, from North Africa to the Middle East.

47Soul is a Palestinian Jordanian electronic music group who are one of the main forces behind the Shamstep electronic dance music movement in the Middle East. The band's first album, Shamstep, was released in 2015.
Islam Said, stage name Islam Chipsy, is an Egyptian musician. His music incorporates elements of traditional Arabic wedding and electronic instruments. Their style is seen as part of a new wave of Shaabi music, referred to as electro-shaabi or Mahraganat.














