
Deception Pass is a strait separating Whidbey Island from Fidalgo Island, in the northwest part of the U.S. state of Washington. It connects Skagit Bay, part of Puget Sound, with the Strait of Juan de Fuca. A pair of bridges known collectively as Deception Pass Bridge cross Deception Pass. The bridges were added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

Captain George Vancouver was a British officer of the Royal Navy best known for his 1791–95 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are now the American states of Alaska, Washington, and Oregon, as well as the Canadian province of British Columbia. He also explored the Hawaiian Islands and the southwest coast of Australia.

The Pacific Northwest (PNW), sometimes referred to as Cascadia, is a geographic region in western North America bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and (loosely) by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the Canadian province of British Columbia (BC) and the U.S. states of Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. Broader conceptions reach north into Southeast Alaska and Yukon, south into northern California, and east to the Continental Divide to include Western Montana and parts of Wyoming. Narrower conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade and Coast mountains. The variety of definitions can be attributed to partially overlapping commonalities of the region's history, culture, geography, society, and other factors.

The Alexander Archipelago is a 300-mile (480 km) long archipelago, or group of islands, of North America off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, which are the tops of the submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the islands and cut them off from the mainland. The northern part of the Inside Passage is sheltered by the islands as it winds its way among them.

Queen Charlotte Sound is a sound of the Pacific Ocean in British Columbia, Canada, between Vancouver Island in the south and Haida Gwaii in the north. It merges with Hecate Strait in the north and Queen Charlotte Strait in the south.

John Meares was a navigator, explorer, and maritime fur trader, best known for his role in the Nootka Crisis, which brought Britain and Spain to the brink of war.

Admiralty Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago in Southeast Alaska, at 57°44′N134°20′W. It is 145 km (90 mi) long and 56 km (35 mi) wide with an area of 4,264.1 km2 (1,646.4 sq mi), making it the seventh-largest island in the United States and the 132nd largest island in the world. It is one of the ABC islands in Alaska. The island is nearly cut in two by the Seymour Canal; to its east is the long, narrow Glass Peninsula. Most of Admiralty Island—more than 955,000 acres (3,860 km2)—is occupied by the Admiralty Island National Monument - a federally protected wilderness area administered by the Tongass National Forest. The Kootznoowoo Wilderness encompasses vast stands of old-growth temperate rainforest. These forests provide some of the best habitat available to species such as brown bears, bald eagles, and Sitka black-tailed deer.

HMS Discovery was a Royal Navy ship launched in 1789 and best known as the lead ship in George Vancouver's exploration of the west coast of North America in his famous 1791-1795 expedition. She was converted to a bomb vessel in 1798 and participated in the Battle of Copenhagen. Thereafter she served as a hospital ship and later as a convict ship until 1831. She was broken up in 1834.

Queen Charlotte Strait is a strait between Vancouver Island and the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It connects Queen Charlotte Sound with Johnstone Strait and Discovery Passage and via them to the Strait of Georgia and Puget Sound. It forms part of the Inside Passage from Washington to Alaska. The term Queen Charlotte Strait is also used to refer to the general region and its many communities, notably of the Kwakwakaʼwakw peoples. Despite its name, Queen Charlotte Strait does not lie between Haida Gwaii and the mainland; that body of water is named Hecate Strait.

Discovery Bay is a small bay connected to the Strait of Juan de Fuca on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington state; it was also historically called Port Discovery. An unincorporated community also named Discovery Bay lies in Jefferson County at the southern end of the bay.

Lincoln Island is a wooded island in Lynn Canal in Alaska, United States. Located at 58°29′41″N134°59′40″W, the island is one kilometer northwest of larger Shelter Island and some 200 meters southeast of smaller Ralston Island. It is part of the Juneau City and Borough. The first European to sight the island was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–1795 expedition, in 1794. It was named in 1868 by Commander R. W. Meade, USN, presumably for Abraham Lincoln.
Zarembo Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies directly south of Mitkof Island and northwest of Etolin Island. To the northwest is Kupreanof Island and to the southwest is Prince of Wales Island. It has a land area of 183.14 square miles, making it the 34th largest island in the United States. It has no permanent resident population. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. He only charted its north, west, and south coasts, not realizing it was an island. The island is named after Dionysius Zarembo, a Polish employee of the Russian American Company and explorer of Alaska. Usually known as Dionysius Zarembo, he was captain of the Russian-American Company ship Chichagof during the foundation of the Redoubt San Dionisio, named for his name-saint, a fortification at present-day Wrangell which was established to forestall encroachment on the Stikine region by the Hudson's Bay Company.
HMS Chatham was a Royal Navy survey brig that accompanied HMS Discovery on George Vancouver's exploration of the west coast of North America in his 1791–1795 expedition. Chatham was built by King, of Dover and launched in early 1788. She was purchased for navy service on 12 February 1788.

Joseph Whidbey FRS was a member of the Royal Navy who served on the Vancouver Expedition 1791–95, and later achieved renown as a naval engineer. He is notable for having been the first European to discover and chart Admiralty Island in the Alexander Archipelago in 1794.

The Vancouver Expedition (1791–1795) was a four-and-a-half-year voyage of exploration and diplomacy, commanded by Captain George Vancouver of the Royal Navy. The British expedition circumnavigated the globe and made contact with five continents. The expedition at various times included between two and four vessels, and up to 153 men, all but six of whom returned home safely.
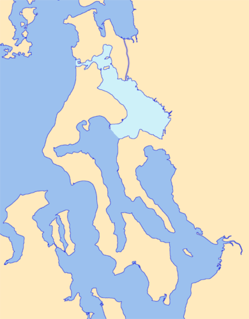
Skagit Bay is a bay and strait located in the U.S. state of Washington. It is part of the Whidbey Island Basin of Puget Sound. The Skagit River empties into Skagit Bay. To the south, Skagit Bay connects with the rest of Puget Sound via Saratoga Passage and Possession Sound. The boundary between Saratoga Passage and Skagit Bay is between Polnell Point on Whidbey Island and Rocky Point on Camano Island. To the northwest, Skagit Bay connects to the Strait of Juan de Fuca via the narrow strait of Deception Pass. A third waterway, the Swinomish Channel, connects Skagit Bay with Padilla Bay to the north.
James Johnstone was a British naval officer and explorer. He is noted for having served as sailing master of the armed tender HMS Chatham and later acting lieutenant during George Vancouver's 1791–1795 expedition to the Pacific Northwest. Johnstone Strait in British Columbia is named after him.
Favorite Channel is a channel in Southeast Alaska, northwest of Juneau, Alaska, United States. It is 25 kilometres (16 mi) long, extending northwest from Stephens Passage to Lynn Canal, separating Lincoln and Shelter islands from the mainland to the east. It was named in 1880 by U.S. Navy officers after the 80-foot (24 m) steamboat Favorite, which was chartered by the Navy for surveying work in Alaska, later being used to carry out trading and fishing for the herring plant at Killisnoo. The first European to traverse and chart the channel was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–95 expedition, in 1794.
Ralston Island is a small island in the Alexander Archipelago, northwest of Lincoln Island and northwest of Juneau, Alaska, United States. It was named in 1868 by Commander R. W. Meade, USN, for W. C. Ralston; the name was published by the U. S. Coast and Geodetic Survey in the 1883 Coast Pilot. The first European to sight the island was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–95 expedition, in 1794.
















