Related Research Articles
William Penton Sears, also referred to as Dr. Bill, is an American pediatrician and the author or co-author of parenting books. Sears is a celebrity doctor and has been a guest on various television talk shows. Sears is a proponent of the attachment parenting philosophy and is most well known for authoring The Baby Book, which popularized that style of parenting.

Internet fraud is a type of cybercrime fraud or deception which makes use of the Internet and could involve hiding of information or providing incorrect information for the purpose of tricking victims out of money, property, and inheritance. Internet fraud is not considered a single, distinctive crime but covers a range of illegal and illicit actions that are committed in cyberspace. It is differentiated from theft since, in this case, the victim voluntarily and knowingly provides the information, money or property to the perpetrator. It is also distinguished by the way it involves temporally and spatially separated offenders.
A pastebin or text storage site is a type of online content-hosting service where users can store plain text. The most famous pastebin is the eponymous pastebin.com. Other sites with the same functionality have appeared, and several open source pastebin scripts are available. Pastebins may allow commenting where readers can post feedback directly on the page. GitHub Gists are a type of pastebin with version control.

A lottery scam is a type of advance-fee fraud which begins with an unexpected email notification, phone call, or mailing explaining that "You have won!" a large sum of money in a lottery. The recipient of the message—the target of the scam—is usually told to keep the notice secret, "due to a mix-up in some of the names and numbers," and to contact a "claims agent." After contacting the agent, the target of the scam will be asked to pay "processing fees" or "transfer charges" so that the winnings can be distributed, but will never receive any lottery payment. Many email lottery scams use the names of legitimate lottery organizations or other legitimate corporations/companies, but this does not mean the legitimate organizations are in any way involved with the scams.

A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. The NICU is divided into several areas, including a critical care area for babies who require close monitoring and intervention, an intermediate care area for infants who are stable but still require specialized care, and a step down unit where babies who are ready to leave the hospital can receive additional care before being discharged.

Surrogacy is an adoption arrangement, often supported by a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to childbirth on behalf of another person(s) who will become the child's parent(s) after birth. People pursue surrogacy for a variety of reasons such as infertility, dangers or undesirable factors of pregnancy, or when pregnancy is a medical impossibility.
Egg donation is the process by which a woman donates eggs to enable another woman to conceive as part of an assisted reproduction treatment or for biomedical research. For assisted reproduction purposes, egg donation typically involves in vitro fertilization technology, with the eggs being fertilized in the laboratory; more rarely, unfertilized eggs may be frozen and stored for later use. Egg donation is a third-party reproduction as part of assisted reproductive technology.
A spoofed URL involves one website masquerading as another, often leveraging vulnerabilities in web browser technology to facilitate a malicious computer attack. These attacks are particularly effective against computers that lack up-to- security patches. Alternatively, some spoofed URLs are crafted for satirical purposes.
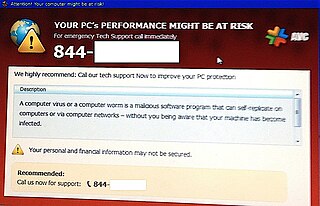
A computer virus hoax is a message warning the recipients of a non-existent computer virus threat. The message is usually a chain e-mail that tells the recipients to forward it to everyone they know, but it can also be in the form of a pop-up window.

The Faith Healers is a 1987 book by conjurer and skeptic James Randi. In this book, Randi documents his exploration of the world of faith healing, exposing the tricks that religious con artists use in their healing shows to fool the audience. Randi's expertise in performing stage magic and mentalism allowed him to easily identify the same techniques when used by con artists. Randi analyzes the methods used by A. A. Allen, Ernest Angley, Willard Fuller, WV Grant, Peter Popoff, Oral Roberts, Pat Robertson, Ralph DiOrio and others, exposing their tricks. Popoff was dramatically exposed as a fraud by Randi on The Tonight Show Starring Johnny Carson. Randi expended considerable effort contacting people who were supposedly cured by these faith-healers. He found there was a lot of disappointment and not a single verifiable case of healing. Randi describes the "calling out trick," the "wheelchair trick," the "leg-stretching trick," the "how many fingers trick," the "shotgun technique," as well as methods used to gain personal information about potential victims in the audience. He also describes methods used, often by mail, to convince people to make large donations.

Demonoid is a BitTorrent tracker and website founded in 2003 to facilitate file-sharing related discussion and provide a searchable index of torrent files. The site underwent intermittent periods of extended downtime in its history due to the occasional need to move the server, generally caused by cancellation of ISP service due to local political pressure.

A reborn doll is a hand made art doll created from a blank kit or a manufactured doll that has been transformed by an artist to resemble a human infant with as much realism as possible. The process of creating a reborn doll is referred to as reborning and the doll artists are referred to as reborners. Reborn dolls are also known as lifelike dolls or reborn baby dolls.
Koobface is a network worm that attacks Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux platforms. This worm originally targeted users of networking websites like Facebook, Skype, Yahoo Messenger, and email websites such as GMail, Yahoo Mail, and AOL Mail. It also targets other networking websites, such as MySpace, Twitter, and it can infect other devices on the same local network. Technical support scammers also fraudulently claim to their intended victims that they have a Koobface infection on their computer by using fake popups and using built-in Windows programs.
The Jessica Mydek hoax was a popular chain letter, circulated by hoaxsters, to play on the sympathy of credulous readers, and get them to respond, so as to build a sucker list. The letter was first observed in 1997.
PhotoDNA is a proprietary image-identification and content filtering technology widely used by online service providers.

Talking Angela is a videogame app, developed by Slovenian studio Outfit7 as part of the Talking Tom & Friends series. It was released on November 13, 2012 and January 2012 for iPhone, iPod and iPad, January 2013 for Android, and January 2014 for Google Play. The app's successor, the My Talking Angela app, was released in December 2014.
Annabelle Natalie Gibson is an Australian convicted scammer and pseudoscience advocate. She is the author of The Whole Pantry mobile app and its later companion cookbook. Throughout her career as a wellness guru, Gibson falsely claimed to have been diagnosed with multiple cancer pathologies, including malignant brain cancer, and that she was effectively managing them through diet, exercise, natural medicine, and alternative medicine therapies. She additionally alleged that she had donated significant proportions of her income and her company's profits to numerous charities.

Facebook's Feed, formerly known as the News Feed, is a web feed feature for the social network. The feed is the primary system through which users are exposed to content posted on the network. Feed highlights information that includes profile changes, upcoming events, and birthdays, among other updates. Using a proprietary method, Facebook selects a handful of updates to show users every time they visit their feed, out of an average of 2,000 updates they can potentially receive. Over two billion people use Facebook every month, making the network's Feed the most viewed and most influential aspect of the news industry. The feature, introduced in 2006, was renamed "Feed" in 2022.
Lydia Ann Reid was a Scottish activist. She advocated the cause of parents who lost a child as an infant, and may have had their child's remains inappropriately used for research, or disposed of, and without consent.
References
- 1 2 Patricia M. Wallace, The Internet in the workplace: how new technology is transforming work, 2004, ISBN 0521809312, p. 103
- ↑ Facebook hoax: this child's got a cancer
- ↑ Protalinski, Emil (5 February 2012). "Anti-scam websites beg facebook to remove Sick baby hoaxes". ZDNET. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ↑ Protalinski, Emil (6 February 2012). "Facebook removes sick baby hoaxes, urges users to report more". ZDNET. Retrieved 17 February 2023.