
A ventilator is a type of breathing apparatus, a class of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators may be computerized microprocessor-controlled machines, but patients can also be ventilated with a simple, hand-operated bag valve mask. Ventilators are chiefly used in intensive-care medicine, home care, and emergency medicine and in anesthesiology.

A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen is added to replenish the amount metabolised by the user. This differs from open-circuit breathing apparatus, where the exhaled gas is discharged directly into the environment. The purpose is to extend the breathing endurance of a limited gas supply, while also eliminating the bubbles otherwise produced by an open circuit system. The latter advantage over other systems is useful for covert military operations by frogmen, as well as for undisturbed observation of underwater wildlife. A rebreather is generally understood to be a portable apparatus carried by the user. The same technology on a vehicle or non-mobile installation is more likely to be referred to as a life-support system.

A diving regulator or underwater diving regulator is a pressure regulator that controls the pressure of breathing gas for underwater diving. The most commonly recognised application is to reduce pressurized breathing gas to ambient pressure and deliver it to the diver, but there are also other types of gas pressure regulator used for diving applications. The gas may be air or one of a variety of specially blended breathing gases. The gas may be supplied from a scuba cylinder carried by the diver, in which case it is called a scuba regulator, or via a hose from a compressor or high-pressure storage cylinders at the surface in surface-supplied diving. A gas pressure regulator has one or more valves in series which reduce pressure from the source, and use the downstream pressure as feedback to control the delivered pressure, or the upstream pressure as feedback to prevent excessive flow rates, lowering the pressure at each stage.

Positive airway pressure (PAP) is a mode of respiratory ventilation used in the treatment of sleep apnea. PAP ventilation is also commonly used for those who are critically ill in hospital with respiratory failure, in newborn infants (neonates), and for the prevention and treatment of atelectasis in patients with difficulty taking deep breaths. In these patients, PAP ventilation can prevent the need for tracheal intubation, or allow earlier extubation. Sometimes patients with neuromuscular diseases use this variety of ventilation as well. CPAP is an acronym for "continuous positive airway pressure", which was developed by Dr. George Gregory and colleagues in the neonatal intensive care unit at the University of California, San Francisco. A variation of the PAP system was developed by Professor Colin Sullivan at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney, Australia, in 1981.

Oxygen therapy, also referred to as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Supplemental oxygen can also refer to the use of oxygen enriched air at altitude. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia, carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactically given to maintain blood oxygen levels during the induction of anesthesia. Oxygen therapy is often useful in chronic hypoxemia caused by conditions such as severe COPD or cystic fibrosis. Oxygen can be delivered via nasal cannula, face mask, or endotracheal intubation at normal atmospheric pressure, or in a hyperbaric chamber. It can also be given through bypassing the airway, such as in ECMO therapy.
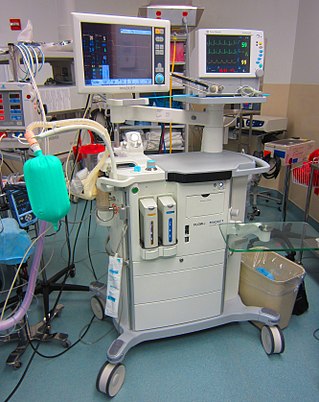
An anaesthetic machine or anesthesia machine is a medical device used to generate and mix a fresh gas flow of medical gases and inhalational anaesthetic agents for the purpose of inducing and maintaining anaesthesia.
A resuscitator is a device using positive pressure to inflate the lungs of an unconscious person who is not breathing, in order to keep them oxygenated and alive. There are three basic types: a manual version consisting of a mask and a large hand-squeezed plastic bulb using ambient air, or with supplemental oxygen from a high-pressure tank. The second type is the expired air or breath powered resuscitator. The third type is an oxygen powered resuscitator. These are driven by pressurized gas delivered by a regulator, and can either be automatic or manually controlled. The most popular type of gas powered resuscitator are time cycled, volume constant ventilators. In the early days of pre-hospital emergency services, pressure cycled devices like the Pulmotor were popular but yielded less than satisfactory results. Most modern resuscitators are designed to allow the patient to breathe on his own should he recover the ability to do so. All resuscitation devices should be able to deliver more than 85% oxygen when a gas source is available.

A breathing apparatus or breathing set is equipment which allows a person to breathe in a hostile environment where breathing would otherwise be impossible, difficult, harmful, or hazardous, or assists a person to breathe. A respirator, medical ventilator, or resuscitator may also be considered to be breathing apparatus. Equipment that supplies or recycles breathing gas other than ambient air in a space used by several people is usually referred to as being part of a life-support system, and a life-support system for one person may include breathing apparatus, when the breathing gas is specifically supplied to the user rather than to the enclosure in which the user is the occupant.
A breathing mask is a mask that covers the mouth, nose, and optionally other parts of the face or head, designed to constrain and direct the wearer's breath to and/or from a particular breathing apparatus. It may mean, or be part of, one of these types:

An oxygen mask is a mask that provides a method to transfer breathing oxygen gas from a storage tank to the lungs. Oxygen masks may cover only the nose and mouth or the entire face. They may be made of plastic, silicone, or rubber. In certain circumstances, oxygen may be delivered via a nasal cannula instead of a mask.

The nasal cannula (NC) is a device used to deliver supplemental oxygen or increased airflow to a patient or person in need of respiratory help. This device consists of a lightweight tube which on one end splits into two prongs which are placed in the nostrils curving toward the sinuses behind the nose, and from which a mixture of air and oxygen flows. The other end of the tube is connected to an oxygen supply such as a portable oxygen generator, or a wall connection in a hospital via a flowmeter. The cannula is generally attached to the patient by way of the tube hooking around the patient's ears or by an elastic headband, and the prongs curve toward the paranasal sinuses. The earliest, and most widely used form of adult nasal cannula carries 1–3 litres of oxygen per minute.
An oxygen tank is an oxygen storage vessel, which is either held under pressure in gas cylinders, referred to in the industry as high pressure oxygen cylinders, or as liquid oxygen in a cryogenic storage tank.
The venturi mask, also known as an air-entrainment mask, is a medical device to deliver a known oxygen concentration to patients on controlled oxygen therapy. The mask was invented by Moran Campbell at McMaster University Medical School as a replacement for intermittent oxygen treatment. Dr. Campbell was fond of quoting John Scott Haldane's description of intermittent oxygen treatment; "bringing a drowning man to the surface – occasionally". By contrast the venturi mask offered a constant supply of oxygen at a much more precise range of concentrations.

A non-rebreather mask is a device used in medicine to assist in the delivery of oxygen therapy. A NRB requires that the patient can breathe unassisted, but unlike a low-flow nasal cannula, the NRB allows for the delivery of higher concentrations of oxygen. An ideal non-rebreather mask does not permit air from the surrounding environment to be inhaled, hence an event of a source gas failure is life-threatening.

A portable oxygen concentrator (POC) is a device used to provide oxygen therapy to people that require greater oxygen concentrations than the levels of ambient air. It is similar to a home oxygen concentrator (OC), but is smaller in size and more mobile. They are small enough to carry and many are now FAA-approved for use on airplanes.

An orinasal mask, oro-nasal mask or oral-nasal mask is a breathing mask that covers the mouth and the nose only. It may be a complete independent item, as an oxygen mask, or on some anaesthetic apparatuses, or it may be fitted as a component inside a fullface mask on underwater breathing apparatus, a gas mask or an industrial respirator to reduce the amount of dead space. It may be designed for its lower edge to seal on the front of the lower jaw or to go under the chin.

Heated humidified high-flow therapy, often simply called high flow therapy, is a type of respiratory support that delivers a flow of medical gas to a patient of up to 60 liters per minute and 100% oxygen through a large bore or high flow nasal cannula. Primarily studied in neonates, it has also been found effective in some adults to treat hypoxemia and work of breathing issues. The key components of it are a gas blender, heated humidifier, heated circuit, and cannula.

A built-in breathing system is a source of breathing gas installed in a confined space where an alternative to the ambient gas may be required for medical treatment, emergency use, or to minimise a hazard. They are found in diving chambers, hyperbaric treatment chambers, and submarines.

High altitude breathing apparatus is a breathing apparatus which allows a person to breathe more effectively at an altitude where the partial pressure of oxygen in the ambient atmospheric air is insufficient for the task or to sustain consciousness or human life over the long or short term.

A breathing apparatus or breathing set is equipment which allows a person to breathe in a hostile environment where breathing would otherwise be impossible, difficult, harmful, or hazardous, or assists a person to breathe. A respirator, medical ventilator, or resuscitator may also be considered to be breathing apparatus. Equipment that supplies or recycles breathing gas other than ambient air in a space used by several people is usually referred to as being part of a life-support system, and a life-support system for one person may include breathing apparatus, when the breathing gas is specifically supplied to the user rather than to the enclosure in which the user is the occupant.














