
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity ; the sustainable use of its components; and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. Its objective is to develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, and it is often seen as the key document regarding sustainable development.

A treaty is a formal, legally binding written contract between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons.

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of May 2023, 168 countries and the European Union are parties.

The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 is an international treaty that defines a framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. Its aim is to facilitate "the development of friendly relations" among governments through a uniform set of practices and principles; most notably, it codifies the longstanding custom of diplomatic immunity, in which diplomatic missions are granted privileges that enable diplomats to perform their functions without fear of coercion or harassment by the host country. The Vienna Convention is a cornerstone of modern international relations and international law and is almost universally ratified and observed; it is considered one of the most successful legal instruments drafted under the United Nations.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. It was adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966 and entered into force on 23 March 1976 after its thirty-fifth ratification or accession. As of June 2022, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification, most notably the People's Republic of China and Cuba; North Korea is the only state that has tried to withdraw.

The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, Sudan, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.

The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) is a subsidiary body of the U.N. General Assembly (UNGA) responsible for helping to facilitate international trade and investment.
The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) is an international arbitration institution established in 1966 for legal dispute resolution and conciliation between international investors and States. ICSID is part of and funded by the World Bank Group, headquartered in Washington, D.C., in the United States. It is an autonomous, multilateral specialized institution to encourage international flow of investment and mitigate non-commercial risks by a treaty drafted by the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development's executive directors and signed by member countries. As of May 2016, 153 contracting member states agreed to enforce and uphold arbitral awards in accordance with the ICSID Convention.

The Brussels Regime is a set of rules regulating which courts have jurisdiction in legal disputes of a civil or commercial nature between individuals resident in different member states of the European Union (EU) and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA). It has detailed rules assigning jurisdiction for the dispute to be heard and governs the recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments.
International arbitration is arbitration between companies or individuals in different states, usually by including a provision for future disputes in a contract.

Arbitration is a formal method of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) involving a neutral third party who makes a binding decision. The dispute will be decided by one or more persons, which renders the 'arbitration award'. An arbitration decision or award is legally binding on both sides and enforceable in the courts, unless all parties stipulate that the arbitration process and decision are non-binding.
International law is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes norms for states across a broad range of domains, including war and diplomacy, economic relations, and human rights. International law differs from state-based domestic legal systems in that it is primarily, though not exclusively, applicable to states, rather than to individuals, and operates largely through consent, since there is no universally accepted authority to enforce it upon sovereign states. States may choose to not abide by international law, and even to breach a treaty but such violations, particularly of peremptory norms, can be met with disapproval by others and in some cases coercive action ranging from diplomatic and economic sanctions to war.

EUCLID, also called Pôle Universitaire Euclide or Euclid University, is an international intergovernmental organization with a university charter established in 2008. It has official headquarters in The Gambia and in the Central African Republic, but also maintains an executive office in Washington, D.C. Its primary mandate is to train officials for its Participating States but its programs are also offered to the general public. The institution's current Secretary-General is Winston Dookeran.
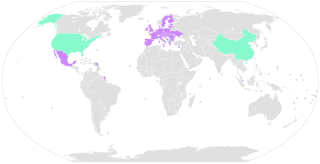
The Hague choice of court convention, formally the Convention of 30 June 2005 on Choice of Court Agreements, is an international treaty concluded within the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It was concluded in 2005, and entered into force on 1 October 2015. The European Union, Denmark, Mexico, Moldova, Montenegro, Singapore, Ukraine and the United Kingdom are parties to the convention. Albania, China, Israel, North Macedonia and the United States signed the convention, but did not ratify.

The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is a free trade agreement among the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population and 30% of global GDP, making it the largest trade bloc in history. Signed in November 2020, RCEP is the first free trade agreement among the largest economies in Asia, including China, Indonesia, Japan, and South Korea.

The Council of Europe Convention on Laundering, Search, Seizure and Confiscation of the Proceeds from Crime and on the Financing of Terrorism, also known as the Warsaw Convention or CETS 198, is a Council of Europe convention which aims to facilitate international co-operation and mutual assistance in investigating crime and tracking down, seizing and confiscating the proceeds thereof.

Singapore International Mediation Centre (SIMC) is an independent not-for-profit organisation in Singapore providing mediation services, through its panel of international mediators, to parties wishing to resolve their cross-border commercial disputes amicably. The centre is housed at Maxwell Chambers.

The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), also known as TPP11 or TPP-11, is a trade agreement between Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, and Vietnam. It evolved from the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), which was never ratified due to the withdrawal of the United States. The eleven members have combined economies representing 13.4 percent of global gross domestic product, at approximately US$13.5 trillion, making the CPTPP one of the world's largest free-trade areas by GDP, along with the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement, the European single market, and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership. The United Kingdom and the present members formally signed an accession protocol on 16 July 2023 and will join the agreement when it has been ratified by all parties, or after 15 months if the UK and a majority of CPTPP parties have ratified it.

The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is a free trade area encompassing most of Africa. It was established in 2018 by the African Continental Free Trade Agreement, which has 43 parties and another 11 signatories, making it the largest free-trade area by number of member states, after the World Trade Organization, and the largest in population and geographic size, spanning 1.3 billion people across the world's second largest continent.

The Hague Judgments Convention, formally the Convention of 2 July 2019 on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Judgments in Civil or Commercial Matters is an international treaty concluded within the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It was concluded in 2019, and entered into force on 1 September 2023 for the European Union and Ukraine. The convention governs the recognition of judgements in civil and commercial matters.

















