
Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. It contains manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re) and bohrium (Bh). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table, and are hence transition metals. This group is sometimes called the manganese group or manganese family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.
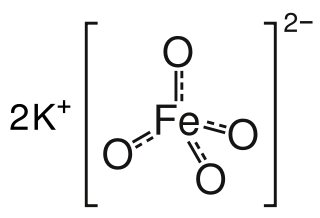
Potassium ferrate is an inorganic compound with the formula K2FeO4. It is the potassium salt of ferric acid. Potassium ferrate is a powerful oxidizing agent with applications in green chemistry, organic synthesis, and cathode technology.

Hydrazoic acid, also known as hydrogen azide, azic acid or azoimide, is a compound with the chemical formula HN3. It is a colorless, volatile, and explosive liquid at room temperature and pressure. It is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, and is therefore a pnictogen hydride. It was first isolated in 1890 by Theodor Curtius. The acid has few applications, but its conjugate base, the azide ion, is useful in specialized processes.

Perrhenic acid is the chemical compound with the formula Re2O7(H2O)2. It is obtained by evaporating aqueous solutions of Re2O7. Conventionally, perrhenic acid is considered to have the formula HReO4, and a species of this formula forms when rhenium(VII) oxide sublimes in the presence of water or steam. When a solution of Re2O7 is kept for a period of months, it breaks down and crystals of HReO4·H2O are formed, which contain tetrahedral ReO−4. For most purposes, perrhenic acid and rhenium(VII) oxide are used interchangeably. Rhenium can be dissolved in nitric or concentrated sulfuric acid to produce perrhenic acid.
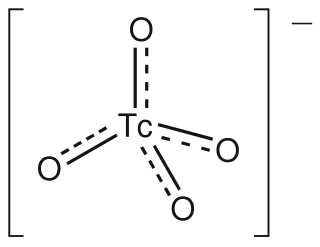
The pertechnetate ion is an oxyanion with the chemical formula TcO−
4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.
A salt metathesis reaction is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations. This reaction is represented by the general scheme:
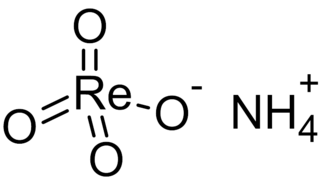
Ammonium perrhenate (APR) is the ammonium salt of perrhenic acid, NH4ReO4. It is the most common form in which rhenium is traded. It is a white salt; soluble in ethanol and water, and mildly soluble in NH4Cl. It was first described soon after the discovery of rhenium.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the name used for a series of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)n. Most common is the nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)9. The hydrates are all pale colored, water-soluble paramagnetic salts.
Osmium compounds are compounds containing the element osmium (Os). Osmium forms compounds with oxidation states ranging from −2 to +8. The most common oxidation states are +2, +3, +4, and +8. The +8 oxidation state is notable for being the highest attained by any chemical element aside from iridium's +9 and is encountered only in xenon, ruthenium, hassium, iridium, and plutonium. The oxidation states −1 and −2 represented by the two reactive compounds Na
2[Os
4(CO)
13] and Na
2[Os(CO)
4] are used in the synthesis of osmium cluster compounds.

Sodium permanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaMnO4. It is closely related to the more commonly encountered potassium permanganate, but it is generally less desirable, because it is more expensive to produce. It is mainly available as the monohydrate. This salt absorbs water from the atmosphere and has a low melting point. Being about 15 times more soluble than KMnO4, sodium permanganate finds some applications where very high concentrations of MnO4− are sought.

Dirhenium decacarbonyl is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Re2(CO)10. Commercially available, it is used as a starting point for the synthesis of many rhenium carbonyl complexes. It was first reported in 1941 by Walter Hieber, who prepared it by reductive carbonylation of rhenium. The compound consists of a pair of square pyramidal Re(CO)5 units joined via a Re-Re bond, which produces a homoleptic carbonyl complex.

Potassium nonahydridorhenate(VII) is an inorganic compound having the formula K2[ReH9]. This colourless salt is soluble in water but only poorly soluble in most alcohols. This salt contains the nonahydridorhenate(VII) anion, [ReH9]2−, which is a rare example of a coordination complex bearing only hydride ligands.
The perrhenate ion is the anion with the formula ReO−
4, or a compound containing this ion. The perrhenate anion is tetrahedral, being similar in size and shape to perchlorate and the valence isoelectronic permanganate. The perrhenate anion is stable over a broad pH range and can be precipitated from solutions with the use of organic cations. At normal pH, perrhenate exists as metaperrhenate, but at high pH mesoperrhenate forms. Perrhenate, like its conjugate acid perrhenic acid, features rhenium in the oxidation state of +7 with a d0 configuration. Solid perrhenate salts takes on the color of the cation.
Organorhenium chemistry describes the compounds with Re−C bonds. Because rhenium is a rare element, relatively few applications exist, but the area has been a rich source of concepts and a few useful catalysts.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of +6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.

Manganese(II) molybdate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MnMoO4. α-MnMoO4 has a monoclinic crystal structure. It is also antiferromagnetic at low temperatures.
Sodium cyanate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaOCN. A white solid, it is the sodium salt of the cyanate anion.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.















