
The New Year is the time or day at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system today, New Year occurs on January 1. This was also the first day of the year in the original Julian calendar and the Roman calendar.
A sidereal year, also called a sidereal orbital period, is the time that Earth or another planetary body takes to orbit the Sun once with respect to the fixed stars.

Thai New Year or Songkran, also known as Songkran Festival, Songkran Splendours, is the Thai New Year's national holiday. Songkran is on 13 April every year, but the holiday period extends from 14 to 15 April. In 2018 the Thai cabinet extended the festival nationwide to seven days, 9–16 April, to enable citizens to travel home for the holiday. In 2019, the holiday was observed 9–16 April as 13 April fell on a Saturday. In 2024, Songkran was extended to almost the entire month, starting on the first of April, and ending on the twenty-first, departing from the traditional 3-day format. And with the New Year of many calendars of Southeast and South Asia, in keeping with the Buddhist calendar and also coincides with New Year in Hindu calendar such as Vishu, Bihu, Pohela Boishakh, Pana Sankranti, Vaisakhi. The New Year takes place at around the same time as the new year celebrations of many regions of South Asia like China, India, Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, Nepal, and Sri Lanka.
The Hindu calendar, also called Panchanga, is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a similar underlying concept for timekeeping based on sidereal year for solar cycle and adjustment of lunar cycles in every three years, but differ in their relative emphasis to moon cycle or the sun cycle and the names of months and when they consider the New Year to start. Of the various regional calendars, the most studied and known Hindu calendars are the Shalivahana Shaka found in the Deccan region of Southern India and the Vikram Samvat (Bikrami) found in Nepal and the North and Central regions of India – both of which emphasize the lunar cycle. Their new year starts in spring. In regions such as Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the solar cycle is emphasized and this is called the Tamil calendar and Malayalam calendar and these have origins in the second half of the 1st millennium CE. A Hindu calendar is sometimes referred to as Panchangam (पञ्चाङ्गम्), which is also known as Panjika in Eastern India.

Makar(a) Sankranti, also referred to as Uttarayana, Makar, or simply Sankranti, is a Hindu observance and a festival. Usually falling on the date of 14 January annually, this occasion marks the transition of the sun from the zodiac of Sagittarius (dhanu) to Capricorn (makara). Since the sun has made this transition which vaguely coincides with moving from south to north, the festival is dedicated to the solar deity, Surya, and is observed to mark a new beginning. Many native multi-day festivals are organised on this occasion all over India.

Vishu is a Hindu festival celebrating the Malayali New Year in Kerala, Tulu Nadu, and Mahe of India. Vishu falls on the first day of the month of Medam in the Malayalam Calendar. It is the traditional new year, while the Kollam era calendar new year falls on the 1st Chingham.
Sankranti refers to the transmigration of the sun from one zodiac to another in Indian astronomy. In Saurmanavarsha, there are twelve Sankrantis corresponding with twelve months of a year. The Sankrantis can be broadly classified into four main categories: Ayan (Solstice), Vishuva (Equinox), Vishnupadi and Shadshitimukhi sankrantis.

Vaisakhi, also known as Baisakhi, marks the first day of the month of Vaisakh and is traditionally celebrated annually on 13 April and sometimes 14 April. It is seen as a spring harvest celebration primarily in Punjab and Northern India. Whilst it is culturally significant as a festival of harvest, in many parts of India, Vaisakhi is also the date for the Indian Solar New Year.
Vikram Samvat, also known as the Vikrami calendar is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent and still used in several states. It is a solar calendar, using twelve to thirteen lunar months each solar sidereal years. The year count of the Vikram Samvat calendar is usually 57 years ahead of the Gregorian calendar, except during January to April, when it is ahead by 56 years.
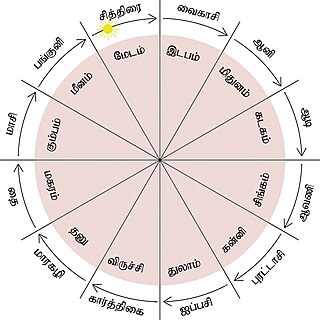
The Tamil calendar is a sidereal solar calendar used by the Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It is also used in Puducherry, and by the Tamil population in Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Singapore, and Mauritius.

Puthandu, also known as Tamil New Year, is the first day of year on the Tamil calendar that is traditionally celebrated as a festival by Tamils. The festival date is set with the solar cycle of the solar Hindu calendar, as the first day of the month of Chittirai. It falls on or about 14 April every year on the Gregorian calendar. The same day is observed elsewhere in South and South East Asia as the traditional new year, but it is known by other names such as Vishu in Kerala, and Vaisakhi or Baisakhi in central and northern India.
The term Uttarāyaṇa is derived from two different Sanskrit words – "uttaram" (North) and "ayanam" (movement) – thus indicating the northward movement of the Sun. In the Gregorian calendar, this pertains to the "actual movement of the sun with respect to the earth." Also known as the six month period that occurs between the winter solstice and summer solstice. According to the Indian solar calendar, it refers to the movement of the Sun through the zodiac. This difference is because the solstices continually precess at a rate of 50 arcseconds per year due to the precession of the equinoxes, i.e. this difference is the difference between the sidereal and tropical zodiacs. The Surya Siddhanta bridges this difference by juxtaposing the four solstitial and equinoctial points with four of the twelve boundaries of the rashis.

Thingyan is the Myanmar New Year festival that usually occurs in middle of April. It is a Buddhist festival celebrated over a period of four to five days, culminating in the New Year. The dates of the Thingyan Festival are calculated according to the Burmese calendar. The dates of the festival are observed as public holidays throughout Myanmar, and are part of the summer holidays at the end of the school year. Water-throwing or dousing one another from any shape or form of vessel or device that delivers water is the distinguishing feature of this festival and may be done on the first four days of the festival. The New Year takes place at virtually the same time as the new year celebrations of many countries in South Asia like China, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, Nepal, Bangladesh, India, and Sri Lanka.

Sinhalese New Year, generally known as Aluth Avurudda in Sri Lanka, is a Sri Lankan holiday that celebrates the traditional New Year of the Sinhalese people and Tamil population of Sri Lanka. It is a major anniversary celebrated by not only the Sinhalese and Tamil people but by most Sri Lankans. The timing of the Sinhala Tamil New Year coincides with the new year celebrations of many traditional calendars of South and Southeast Asia. The festival has close semblance to the Tamil New year and other South and Southeast Asian New Years. It is a public holiday in Sri Lanka. It is generally celebrated on 13 April or 14 April and traditionally begins at the sighting of the new moon.

Pana Sankranti,, also known as Maha Bishuba Sankranti, is the traditional new year day festival of Odia people in Odisha, India. The festival occurs in the solar Odia calendar on the first day of the traditional solar month of Meṣa, hence equivalent lunar month Baisakha. This falls on the Purnimanta system of the Indian Hindu calendar. It therefore falls on 13/14 April every year on the Gregorian calendar.
Jur Sital or Maithil New Year is the celebration of the first day of the Maithil new year also called Aakhar Bochhor. Maithils eat Bori with Bhaat and Sondesh on the day. This day which usually falls on 14th or 15th April on Gregorian calendar is celebrated by the Maithils and Tharu people of India and Nepal. This is also called Nirayana Mesh Sankranti and Tirhuta new year. The festive occasion is in keeping with the Tirhuta Panchang calendar used in the Mithila region.
Tirhuta Panchang is a calendar followed by the Maithili community of India and Nepal. This calendar is one of the many Hindu calendars. It is a tropical solar Hindu calendar in which the year begins on the first day of Baishakh month i.e. Mesh Sankranti. Every year, this day falls on 13/14 April of the Gregorian Calendar

Songkran is the water-splashing festival celebration of Tai peoples in traditional new year for Buddhist calendar widely celebrated across South and Southeast Asia in Bangladesh, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, parts of northeast India, parts of Vietnam and Xishuangbanna, China begins on 13th April of the year.

Mesha Sankranti refers to the first day of the solar cycle year, that is the solar New Year in the Hindu luni-solar calendar. The Hindu calendar also has a lunar new year, which is religiously more significant. The solar cycle year is significant in Assamese, Odia, Punjabi, Malayalam, Tamil, and Bengali calendars.

















