This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2018) |

Spanish Baroque is a strand of Baroque architecture that evolved in Spain, its provinces, and former colonies.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2018) |

Spanish Baroque is a strand of Baroque architecture that evolved in Spain, its provinces, and former colonies.
The development of the style passed through three phases. Between 1680 and 1720, the Churriguera popularized Guarini's blend of Solomonic columns and Composite order, known as the "supreme order". Between 1720 and 1760, the Churrigueresque column, or estipite, in the shape of an inverted cone or obelisk, was established as a central element of ornamental decoration. The years from 1760 to 1780 saw a gradual shift of interest away from twisted movement and excessive ornamentation toward a neoclassical balance and sobriety.
In contrast to the art of Northern Europe, the Spanish art of the period appealed to the emotions rather than seeking to please the intellect. The Churriguera family, which specialized in designing altars and retables, revolted against the sobriety of the Herreresque classicism and promoted an intricate, exaggerated, almost capricious style of surface decoration known as the Churrigueresque. Within half a century, they transformed Salamanca into an exemplary Churrigueresque city.

As Italian Baroque influences penetrated across the Pyrenees, they gradually superseded in popularity the restrained classicizing approach of Juan de Herrera, which had been in vogue since the late sixteenth century. As early as 1667, the façades of Granada Cathedral (by Alonso Cano) and Jaén Cathedral (by Eufrasio López de Rojas) suggest the artists' fluency in interpreting traditional motifs of Spanish cathedral architecture in the Baroque aesthetic idiom.
In Madrid, a vernacular Baroque with its roots in Herrerian and in traditional brick construction was developed in the Plaza Mayor and in the Royal Buen Retiro Palace, which was destroyed during the French invasion by Napoleon's troops. Its gardens still remain as Parque del Buen Retiro . This sober brick Baroque of the 17th century is still well represented in the streets of the capital in palaces and squares.

Three of the most eye-catching creations of Spanish Baroque are the energetic façades of the University of Valladolid (Diego Tome and Fray Pedro de la Visitación, 1719), the western façade (or Fachada del Obradoiro) of the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela (Fernando de Casas y Novoa, 1750), and the Hospicio de San Fernando in Madrid (Pedro de Ribera, 1722), whose curvilinear extravagance seems to herald Antonio Gaudí and Modernisme . In this case as in many others, the design involves a play of tectonic and decorative elements with little relation to structure and function. The focus of the florid ornamentation is an elaborately sculptured surround to a main doorway. If we remove the intricate maze of broken pediments, undulating cornices, stucco shells, inverted tapers and garlands from the rather plain wall it is set against, the building's form would not be affected in the slightest. However, Churrigueresque Baroque offered some of the most impressive combinations of space and light with buildings like Granada Charterhouse (sacristy by Francisco Hurtado Izquierdo), considered to be the apotheosis of Churrigueresque styles applied to interior spaces, or El Transparente of the Cathedral of Toledo by Narciso Tomé, where sculpture and architecture are integrated to achieve notable light dramatic effects.[ opinion ]
The Royal Palace of Madrid and the interventions of Paseo del Prado (Salón del Prado and Alcalá Doorgate) in the same city, deserve special mention. They were constructed in a sober Baroque international style, often mistaken for neoclassical, by the kings Philip V and Charles III. The Royal Palace of La Granja de San Ildefonso in Segovia and the Royal Palace of Aranjuez in Aranjuez are good examples of Baroque integration of architecture and gardening, with noticeable French influence (La Granja is known as the "Spanish Versailles"), but with local spatial conceptions which in some ways display the heritage of the Moorish occupation.

In the richest imperial province of 17th-century Spain, Flanders, florid decorative detailing was more tightly knit to the structure, thus precluding concerns of superfluity. A remarkable convergence of Spanish, French and Dutch Baroque aesthetics may be seen in the Abbey of Averbode (1667). Another characteristic example is the Church of St. Michel at Louvain (1650–70), with its exuberant two-storey façade, clusters of half-columns, and the complex aggregation of French-inspired sculptural detailing.
Six decades later, the architect Jaime Bort y Meliá was the first to introduce Rococo to Spain (Cathedral of Murcia, west façade, 1733). The greatest practitioner of the Spanish Rococo style was a native master, Ventura Rodríguez, responsible for the dazzling interior of the Basilica of Our Lady of the Pillar in Zaragoza (1750).

In the north, the richest province of 18th-century New Spain – Mexico – produced some fantastically extravagant and visually frenetic architecture known as Mexican Churrigueresque. This ultra-Baroque approach culminates in the works of Lorenzo Rodriguez, whose masterpiece is the Sagrario Metropolitano in Mexico City (1718–69). Other fine examples of the style may be found in the remote silver-mining towns. For instance, the Sanctuary at Ocotlán (begun in 1745) is a top-notch Baroque cathedral surfaced in bright red tiles, which contrast delightfully with a plethora of compressed ornament lavishly applied to the main entrance and the slender flanking towers (exterior, interior). The Church of Santa Prisca de Taxco (1758), and San Martín at San Luis Potosí (1764) are other excellent examples of Churrigueresque in Mexico.
The true capital of Mexican Baroque is Puebla, where a ready supply of hand-painted figurines (talavera) and vernacular gray stone led to its evolving further into a personalised and highly localised art form with a pronounced Indian flavour. There are about sixty churches whose façades and domes display glazed tiles of many colours, often arranged in Arabic designs. Their interiors are densely saturated with elaborate gold leaf ornamentation. In the 18th century, local artisans developed a distinctive brand of white stucco decoration, named "alfeñique" after a Pueblan candy made from egg whites and sugar.

The combination of the Native American and Moorish decorative influences with an extremely expressive interpretation of the Churrigueresque idiom may account for the full-bodied and varied character of the Baroque in the American colonies of Spain. Even more than its Spanish counterpart, American Baroque developed as a style of stucco decoration. Twin-towered façades of many American cathedrals of the seventeenth century had medieval roots and the full-fledged Baroque did not appear until 1664, when the Jesuit shrine on Plaza des Armas in Cusco was built. Even then, the new style hardly affected the structure of churches.
The Peruvian Baroque was particularly lush, as evidenced by the monastery of San Francisco in Lima (1673), which has a dark intricate façade sandwiched between the yellow twin towers. Followed the model of Il Gesù (also the case of the Jesuit Basilica and Convent of San Pedro, Lima, provincial "mestizo" (crossbred) styles emerged in Arequipa, Potosí and La Paz. In the eighteenth century, the architects of the region turned for inspiration to the Mudéjar art of medieval Spain. The late Baroque type of Peruvian façade first appears in the Church of Our Lady of Mercy, Lima (1697–1704). Similarly, the Iglesia de La Compañia, Quito (1722–65) suggests a carved altarpiece with its richly sculpted façade and a surfeit of Solomonic column.

The Baroque or Baroquism is a Western style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from the early 17th century until the 1750s. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well.

Rococo, less commonly Roccoco, also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and trompe-l'œil frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement.

Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia, the Ottoman Empire and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. In about 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe.

The Metropolitan Cathedral of Morelia is a religious site that is the seat of the Archdiocese of Morelia of the Catholic church in Mexico. It is located as its name itself says in the city of Morelia, capital of the state of Michoacán, Mexico. The cathedral is located in the first square of the city, forming the trace of the Historic Center of Morelia. The building was built in the 18th century at the time of the viceroyalty, it is Baroque in style and is made of pink stone that gives it a peculiar and characteristic color. An important family group headed by Sebastián de Guedea collaborated in its construction for a long period; They were Andrés, Pedro, Diego, Miguel, Anastacio, Lorenzo and Joseph, all with the surname Guedea.

Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes.
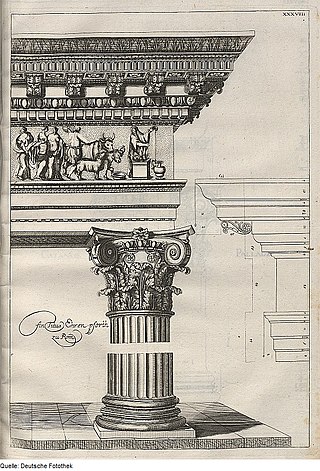
The Composite order is a mixed order, combining the volutes of the Ionic order capital with the acanthus leaves of the Corinthian order. In many versions the composite order volutes are larger, however, and there is generally some ornament placed centrally between the volutes. The column of the composite order is typically ten diameters high, though as with all the orders these details may be adjusted by the architect for particular buildings. The Composite order is essentially treated as Corinthian except for the capital, with no consistent differences to that above or below the capital.

Plateresque, meaning "in the manner of a silversmith", was an artistic movement, especially architectural, developed in Spain and its territories, which appeared between the late Gothic and early Renaissance in the late 15th century, and spread over the next two centuries. It is a modification of Gothic spatial concepts and an eclectic blend of Mudéjar, Flamboyant Gothic and Lombard decorative components, as well as Renaissance elements of Tuscan origin.

The Catedral de la Asunción de la Virgen, popularly known as New Cathedral is, together with the Old Cathedral, one of the two cathedrals of Salamanca, Castile and León, Spain. It is the seat of the diocese of Salamanca. It was constructed between 1533 and 1733 mixing late Gothic, Plateresque and Baroque styles. It was commissioned by Ferdinand V of Castile. It is one of the largest cathedrals in Spain in size and its bell tower, at 92 meters high, is also one of the tallest.

Churrigueresque, also but less commonly "Ultra Baroque", refers to a Spanish Baroque style of elaborate sculptural architectural ornament which emerged as a manner of stucco decoration in Spain in the late 17th century and was used until about 1750, marked by extreme, expressive and florid decorative detailing, normally found above the entrance on the main façade of a building.

The Metropolitan Cathedral of the Assumption of the Most Blessed Virgin Mary into Heaven is the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Mexico. It is situated on top of the former Aztec sacred precinct near the Templo Mayor on the northern side of the Plaza de la Constitución (Zócalo) in the historic center of Mexico City. The cathedral was built in sections from 1573 to 1813 around the original church that was constructed soon after the Spanish conquest of Tenochtitlan, eventually replacing it entirely. Spanish architect Claudio de Arciniega planned the construction, drawing inspiration from Gothic cathedrals in Spain.

Spanish architecture refers to architecture in any area of what is now Spain, and by Spanish architects worldwide. The term includes buildings which were constructed within the current borders of Spain prior to its existence as a nation, when the land was called Iberia, Hispania, or was divided between several Christian and Muslim kingdoms. Spanish architecture demonstrates great historical and geographical diversity, depending on the historical period. It developed along similar lines as other architectural styles around the Mediterranean and from Central and Northern Europe, although some Spanish constructions are unique.

José Benito de Churriguera was a Spanish architect, sculptor and urbanist of the late-Baroque or Rococo style. He was born in Madrid to a Catalan cabinetmaker, gilder and altarpiece joiner, Josep Simó Xoriguera i Elies and to doña Maria de Ocaña, and studied under his father along with two of his brothers.

The architecture of Mexico reflects the influences of various cultures, regions, and periods that have shaped the country's history and identity. In the pre-Columbian era, distinct styles emerged that reflected the distinct cultures of the indigenous peoples of Mexico, particularly in the architecture of Mesoamerica. During the colonial era, the region was transformed by successive styles from Europe. With the foremost style during this era being Mexican Baroque.

The estipite column is a type of pilaster typical of the Churrigueresque Baroque style of Spain and Spanish America used in the 18th century. In the late Baroque period, many classical architectural elements lost their simple shapes and became increasingly complex, offering variety of forms and exuberant decoration. Therefore, the column has the shape of an inverted cone or obelisk. The shaft is always wider in its middle part than the base and capital. The column combines features of both late Baroque and Mannerist. It was widely used between 1720 and 1780.

The Parroquia de Santa Prisca y San Sebastían, commonly known as the Church of Santa Prisca, is a colonial monument located in the city of Taxco de Alarcón, in the southern state of Guerrero, Mexico, built between 1751 and 1759. It is located on the east side of the main plaza of Taxco.

The Peruvian colonial architecture, developed in the Viceroyalty of Peru between the 16th and 19th centuries, was characterized by the importation and adaptation of European architectural styles to the Peruvian reality, yielding an original architecture.

The Church and Convent of San Ignacio de Loyola de la Compañía de Jesús de Quito, also known in the Ecuadorian people simply as La Compañía, is a Catholic clerical complex located on the corner formed by calles García Moreno and Sucre, in the Historic Center of the city of Quito, capital of Ecuador. The façade of its main temple is entirely carved in volcanic stone. Over time, this church has also been called: "Temple of Solomon of South America". Father Bernardo Recio, a traveling Jesuit, called it "Golden Ember".

The Spanish Rococo style of the 18th century is relatively unexplored and bears little resemblance to its French equivalent. Under the reign of Philip V of the Bourbon Dynasty, architectural commissions were primarily awarded to Italian architects, rather than the French who were the pioneers of the rococo style. This is largely due to the influence of his second wife, Elisabeth Farnese of Parma, who aimed to transcend French influence through the promotion of the Italians. Consequently, Rococo was left to be discovered by the Spanish school and therefore evolved separately from French and other variations of Rococo.

Elizabethan Baroque is a term for the Russian Baroque architectural style, developed during the reign of Elizabeth of Russia between 1741 and 1762. It is also called style Rocaille or Rococo style. The Italian architect Francesco Bartolomeo Rastrelli is the key figure of this trend, which is still given the name 'Rastrellian Baroque'. The Russian architect Savva Chevakinsky is also a renowned figure representing this style.

Ephemeral architecture had a special relevance in the Spanish Baroque, as it fulfilled diverse aesthetic, political, religious and social functions. On the one hand, it was an indispensable component of support for architectural achievements, carried out in a perishable and transitory way, which allowed a cheapening of materials and a way to capture new designs and more daring and original solutions of the new Baroque style, which could not be done in conventional constructions. On the other hand, its volubility made possible the creation of a wide range of productions designed according to their diverse functionality: triumphal arches for the reception of kings and aristocratic personages, catafalques for religious ceremonies, burial mounds for funerary ceremonies and diverse scenarios for social or religious events, such as the feast of Corpus Christi or Holy Week.