
The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark, often shortened to Hamlet, is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts Prince Hamlet and his revenge against his uncle, Claudius, who has murdered Hamlet's father in order to seize his throne and marry Hamlet's mother.

William Shakespeare was an English playwright, poet and actor, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's greatest dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon". His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. His works continue to be studied and reinterpreted.

English Renaissance theatre, also known as Renaissance English theatre and Elizabethan theatre, refers to the theatre of England between 1558 and 1642.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1601.
The Ur-Hamlet is a play by an unknown author, thought to be either Thomas Kyd or William Shakespeare. No copy of the play, dated by scholars to the second half of 1587, survives today. The play was staged in London, more specifically at The Burbages' Shoreditch Playhouse as recalled by Elizabethan author Thomas Lodge. It includes a character named Hamlet; the only other known character from the play is a ghost who, according to Thomas Lodge in his 1596 publication Wits Misery and the Worlds Madnesse, cries, "Hamlet, revenge!"

This article presents a possible chronological listing of the composition of the plays of William Shakespeare.
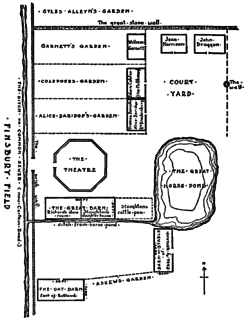
The Theatre was an Elizabethan playhouse in Shoreditch, just outside the City of London. It was the first permanent theatre ever built in England. It was built in 1576 after the Red Lion, and the first successful one. Built by actor-manager James Burbage, near the family home in Holywell Street, The Theatre is considered the first theatre built in London for the sole purpose of theatrical productions. The Theatre's history includes a number of important acting troupes including the Lord Chamberlain's Men, which employed Shakespeare as actor and playwright. After a dispute with the landlord, the theatre was dismantled and the timbers used in the construction of the Globe Theatre on Bankside.

Heiner Müller was a German dramatist, poet, writer, essayist and theatre director. His "enigmatic, fragmentary pieces" are a significant contribution to postmodern drama and postdramatic theatre.

Shakespeare's plays are a canon of approximately 39 dramatic works written by English poet, playwright, and actor William Shakespeare. The exact number of plays—as well as their classifications as tragedy, history, or comedy—is a matter of scholarly debate. Shakespeare's plays are widely regarded as being among the greatest in the English language and are continually performed around the world. The plays have been translated into every major living language.
Metatheatre, and the closely related term metadrama, describes the aspects of a play that draw attention to its nature as drama or theatre, or to the circumstances of its performance.
William Shakespeare (1564–1616) was an English poet and playwright. He wrote approximately 39 plays and 154 sonnets, as well as a variety of other poems.

From its premiere at the turn of the 17th century, Hamlet has remained Shakespeare's best-known, most-imitated, and most-analyzed play. The character of Hamlet played a critical role in Sigmund Freud's explanation of the Oedipus complex. Even within the narrower field of literature, the play's influence has been strong. As Foakes writes, "No other character's name in Shakespeare's plays, and few in literature, have come to embody an attitude to life ... and been converted into a noun in this way."

William Shakespeare's style of writing was borrowed from the conventions of the day and adapted to his needs.

Thousands of performances of William Shakespeare's plays have been staged since the end of the 16th century. While Shakespeare was alive, many of his greatest plays were performed by the Lord Chamberlain's Men and King's Men acting companies at the Globe and Blackfriars Theatres. Among the actors of these original performances were Richard Burbage, Richard Cowley, and William Kempe.

The "art of representation" is a critical term used by the seminal Russian theatre practitioner Konstantin Stanislavski to describe a method of acting. It comes from his acting manual An Actor Prepares (1936). Stanislavski defines his own approach to acting as "experiencing the role" and contrasts it with the "art of representation". It is on the basis of this formulation that the American Method acting teacher Uta Hagen defines her recommended Stanislavskian approach as 'presentational' acting, as opposed to 'representational' acting. This use, however, directly contradicts mainstream critical use of these terms. Despite the distinction, Stanislavskian theatre, in which actors 'experience' their roles, remains 'representational' in the broader critical sense.

The Moscow Art Theatre production of Hamlet in 1911–12, on which two of the 20th century's most influential theatre practitioners—Konstantin Stanislavski and Edward Gordon Craig—collaborated, is particularly important in the history of performances of Hamlet and of 20th-century theatre in general.

Naturalism is a movement in European drama and theatre that developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It refers to theatre that attempts to create an illusion of reality through a range of dramatic and theatrical strategies. Interest in naturalism especially flourished with the French playwrights of the time, but the most successful example is Strindberg's play Miss Julie, which was written with the intention to abide by both his own particular version of naturalism, and also the version described by the French novelist and literary theoretician, Émile Zola.

Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communicate this experience to the audience through combinations of gesture, speech, song, music, and dance. Elements of art, such as painted scenery and stagecraft such as lighting are used to enhance the physicality, presence and immediacy of the experience. The specific place of the performance is also named by the word "theatre" as derived from the Ancient Greek θέατρον, itself from θεάομαι.

Ophelia is a character in William Shakespeare's drama Hamlet. She is a young noblewoman of Denmark, the daughter of Polonius, sister of Laertes and potential wife of Prince Hamlet, who, due to Hamlet's actions, ends up in a state of madness that ultimately leads to her drowning.

Presentational acting and the related representational acting are opposing ways of sustaining the actor–audience relationship. With presentational acting, the actor acknowledges the audience. With representational acting, the audience is studiously ignored and treated as voyeurs.