
The Chaetothyriales are an order of ascomycetous fungi in the class Eurotiomycetes and within the subclass Chaetothyriomycetidae. The order was circumscribed in 1987 by mycologist Margaret Elizabeth Barr-Bigelow.

The Lecanoraceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Lecanorales. Species of this family have a widespread distribution.
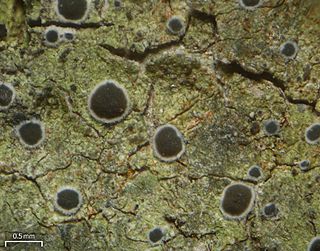
The Pilocarpaceae are a family of crustose lichens in the order Lecanorales. The species of this family have a cosmopolitan distribution and have been found in a variety of climatic regions. Pilocarpaceae was circumscribed by Alexander Zahlbruckner in Adolf Engler's influential 1905 work Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien.

The Sphaerophoraceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Lecanorales. Species of this family have a widespread distribution, especially in southern temperate regions. Sphaerophoraceae was circumscribed by mycologist Elias Magnus Fries in 1831.

Bacidia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Ramalinaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Giuseppe De Notaris in 1846. Species in the genus are crust-like lichens with stemless apothecia; they have green algae as photobionts. Their asci have 8 colourless, cylindrical to acicular, multiseptate spores, with curved and thread-like conidia.

The Pertusariaceae are a family of lichen-forming fungi in the order Pertusariales.

Anisomeridium is a genus of lichens in the family Monoblastiaceae. The type species was originally named Arthopyrenia xylogena by Swiss botanist Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1883; in 1928, Maurice Choisy defined the genus Anisomeridium, designating A. xylogena the type species.
Clavascidium is a genus of lichens in the family Verrucariaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1996 by Austrian lichenologist Othmar Breuss. Because the type species of the genus, Clavascidium umbrinum, has been shown using molecular phylogenetics to belong to genus Placidium, Cécile Gueidan and colleagues proposed to unite Clavascidium with Placidium in a 2009 publication. Despite this, the genus has been retained in recent publications of fungal classification.

Rhizocarpon is a genus of crustose, saxicolous, lecideoid lichens in the family Rhizocarpaceae. The genus is common in arctic-alpine environments, but also occurs throughout temperate, subtropical, and even tropical regions. They are commonly known as map lichens because of the prothallus forming border-like bands between colonies in some species, like the common map lichen.

Lepraria is a genus of leprose crustose lichens that grows on its substrate like patches of granular, caked up, mealy dust grains. Members of the genus are commonly called dust lichens. The main vegetative body (thallus) is made of patches of soredia. There are no known mechanisms for sexual reproduction, yet members of the genus continue to speciate. Some species can form marginal lobes and appear squamulose. Because of the morphological simplicity of the thallus and the absence of sexual structures, the composition of lichen products are important characters to distinguish between similar species in Lepraria.

Chrysothrix is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Chrysothricaceae. They are commonly called gold dust lichens or sulfur dust lichens, because they are bright yellow to greenish-yellow, sometimes flecked with orange, and composed entirely of powdery soredia. Apothecia are never present in North American specimens.

Bunodophoron is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Sphaerophoraceae.

The Trypetheliales are an order of fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. Most of the species in the order form lichens, although some are lichenicolous fungi. Trypetheliales contains two families, Polycoccaceae and Trypetheliaceae. The order was circumscribed in 2008 by lichenologists Robert Lücking, André Aptroot, and Harrie Sipman.

Mycoblastus is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Tephromelataceae. Members of the genus are commonly called blood lichens.

Caliciales is an order of mostly lichenized fungi in the class Lecanoromycetes. It consists of two families: Caliciaceae and Physciaceae, which together contain 54 genera and more than 1200 species. The order was circumscribed by American botanist Charles Edwin Bessey in 1907.

Rhizocarpales are an order of lichen-forming fungi in the subclass Lecanoromycetidae of the class Lecanoromycetes. It has two families, Rhizocarpaceae and Sporastatiaceae, which contain mostly crustose lichens.
Apatoplaca is a fungal genus in the family Teloschistaceae. It is monotypic, containing a single species, the rare crustose lichen Apatoplaca oblongula, found in the United States.

Megalospora is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Megalosporaceae.

Chrysothrix xanthina is a widely distributed species of leprose lichen in the family Arthoniaceae. It has a bright yellow to bright greenish-yellow, thin, granular thallus, and typically grows on bark, although it is infrequently found growing on rock.
Pyrenidium is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi. It is the only genus in the family Pyrenidiaceae. It has 13 species.

















