
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area Rio dos Camarões, which became Cameroon in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in the north in the 19th century, and various ethnic groups of the west and northwest established powerful chiefdoms and fondoms.

Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.

A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.

Prefect is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
The provinces of Thailand are administrative divisions of the government of Thailand. The country is divided into 76 provinces proper, with one additional special administrative area. They are the primary local government units and act as juristic persons. They are divided into amphoe (districts) which are further divided into tambon, the next lower level of local government.

Manica is a province of Mozambique. It has an area of 62,272 km² and a population of 1,945,994. The province is surrounded by Zimbabwe to the west, Tete Province to the northwest, Sofala Province to the east, the Save River to the south, and the Zambezi river to the northeast. Chimoio is the capital of the province. The highest mountain in Mozambique, Mount Binga, lies in this province near the border with Zimbabwe. The Manica province is divided into nine districts and 34 administrative regions.

The Northwest Region, or North-West Region is one of ten regions of Cameroon. Its regional capital is Bamenda. The Northwest Region was part of the Southern Cameroons, found in the western highlands of Cameroon. It is bordered to the southwest by the Southwest Region, to the south by the West Region, to the east by the Adamawa Region, and to the north by Nigeria. Various Ambazonian nationalist and separatist factions regard the region as being distinct as a polity from Cameroon.

Departments of Ivory Coast are currently the third-level administrative subdivision of the country. Each of the 31 second-level regions of Ivory Coast is divided into two or more departments. Each department is divided into two or more sub-prefectures. Since 2020, there are 109 departments of Ivory Coast.
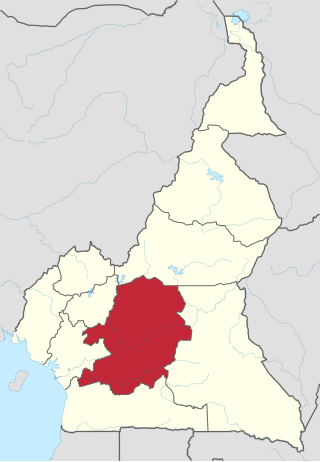
The Centre Region occupies 69,000 km2 of the central plains of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the north by the Adamawa Region, to the south by the South Region, to the east by the East Region, and to the West by the Littoral and West Regions. It is the second largest of Cameroon's regions in land area. Major ethnic groups include the Bassa, Ewondo, and Vute.
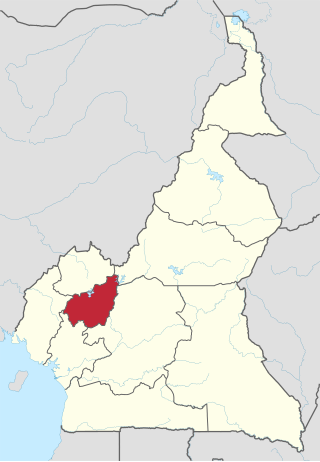
The West Region is 14,000 km2 of territory located in the central-western portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Northwest Region to the northwest, the Adamawa Region to the northeast, the Centre Region to the southeast, the Littoral Region to the southwest, and the Southwest Region to the west. The West Region is the smallest of Cameroon's ten regions in area, yet it has the highest population density.

Romania's administration is relatively centralized and administrative subdivisions are therefore fairly simplified.
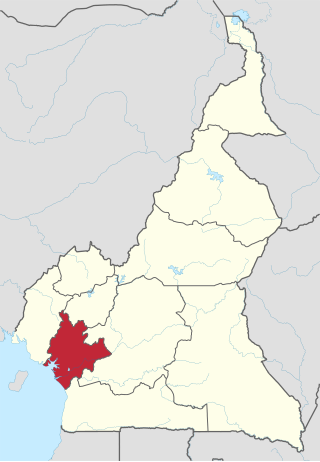
The Littoral Region is a region of Cameroon. Its capital is Douala. As of 2004, its population was 3,174,437. Its name is due to the region being largely littoral, and associated with the sea coast.
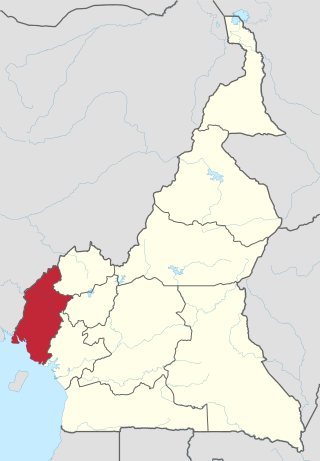
The Southwest Region or South-West Region is a region in Cameroon. Its capital is Buea. As of 2015, its population was 1,553,320. Along with the Northwest Region, it is one of the two Anglophone (English-speaking) regions of Cameroon. Various Ambazonian nationalist and separatist factions regard the Sud-Ouest region as being distinct as a polity from Cameroon.

The regions of Cameroon are divided into 58 divisions or departments. The divisions are further subdivided into subdivisions (arrondissements) and districts. The divisions are listed below, by Macro-Region and region.

Cameroon Radio Television (CRTV) is a major radio and television broadcasting company in Cameroon.
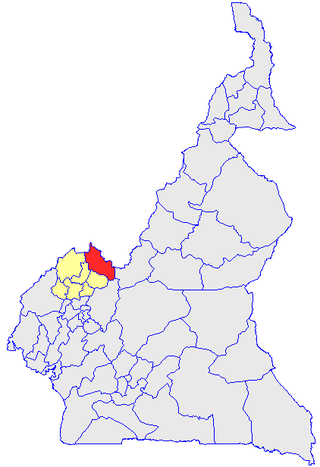
Donga-Mantung (Mantungia) is a division of the Northwest Region of Cameroon. The division covers an area of 4279 km2 and as of 2001 had a total population of 337,533. The capital city of the division is Nkambe.

The Republic of Cameroon is a decentralized unitary state.
















